Abstract
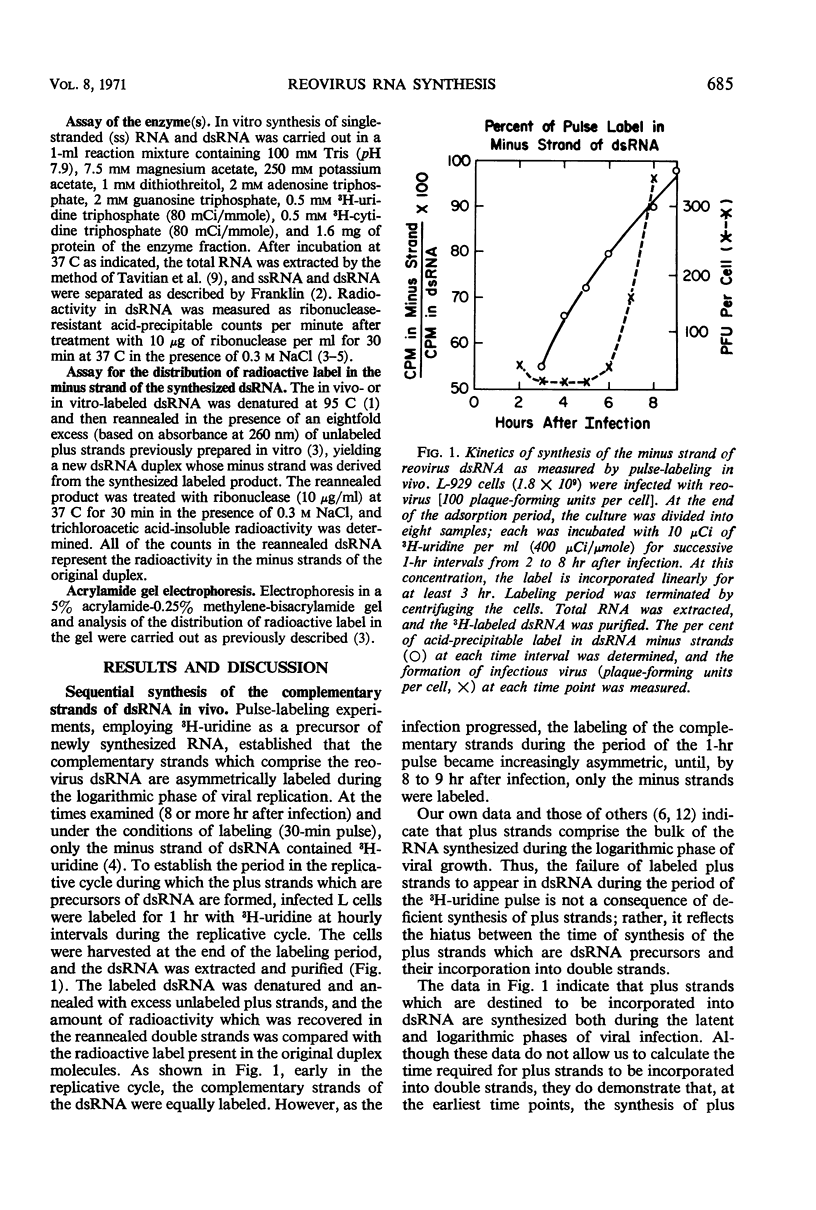
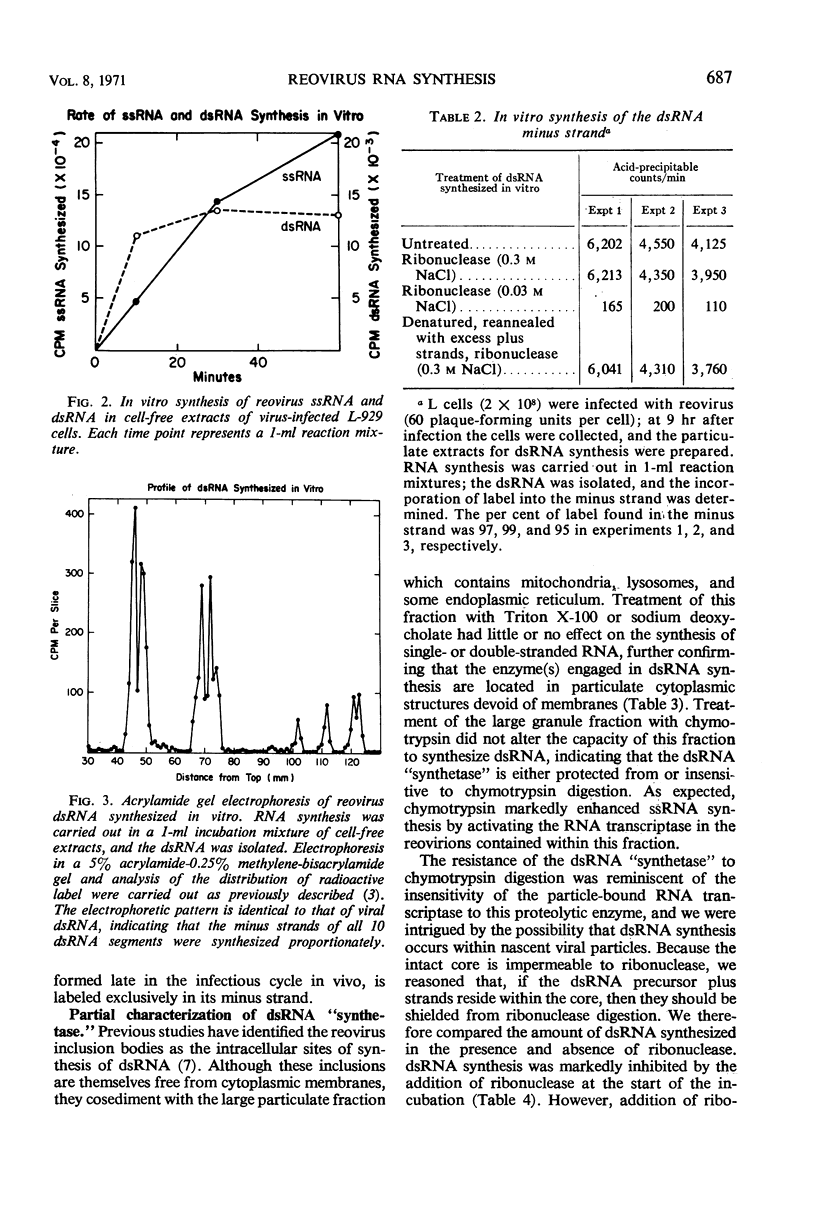
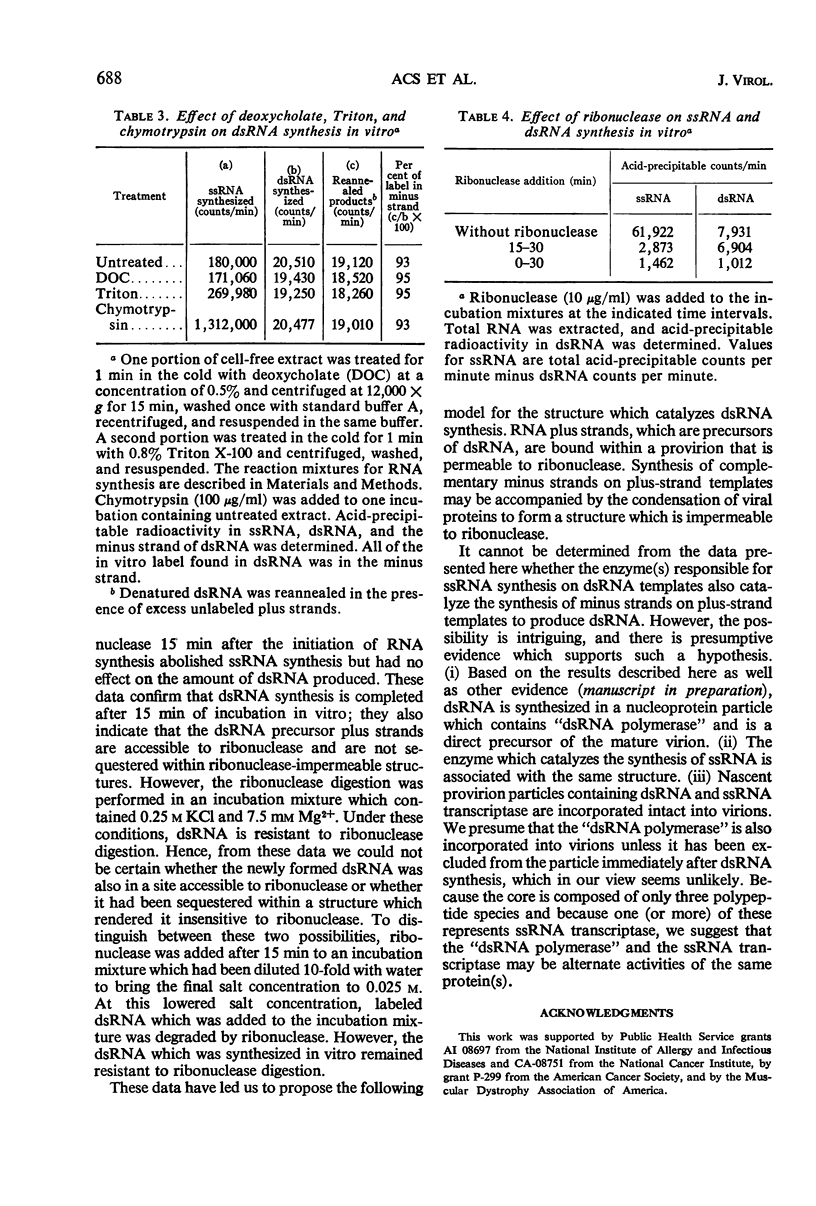
The complementary strands of reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid (ds RNA) are synthesized sequentially in vivo and in vitro. In both cases, preformed plus strands serve as templates for the synthesis of the complementary minus strands. The in vitro synthesis of dsRNA is catalyzed by a large particulate fraction from reovirus-infected cells. Treatment of this fraction with chymotrypsin or with detergents which solubilize cellular membranes does not alter its capacity to synthesize dsRNA. The enzyme or enzymes responsible for dsRNA synthesis remain sedimentable at 10,000 × g after these enzyme or detergent treatments, indicating their particulate nature. Pretreatment of this fraction with ribonuclease, however, abolishes its ability to catalyze dsRNA synthesis, emphasizing the single-stranded nature of the template and its location in a structure permeable to ribonuclease. In contrast, the newly formed dsRNA is resistant to ribonuclease digestion at low salt concentrations and hence is thought to reside within a ribonuclease-impermeable structure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Mendelsohn N., Schonberg M., Klett H., Silverstein S., Kapuler A. M., Acs G. Properties of RNA transcriptase in reovirus subviral particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):890–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN AND THE DIFFERENTIAL SYNTHESIS OF REOVIRUS AND L CELL RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonberg M., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Asynchronous synthesis of the complementary strands of the reovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):505–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Rada B. Reovirus-directed ribonucleic acid synthesis in infected L cells. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.24-35.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavitian A., Uretsky S. C., Acs G. Selective inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Gauntt C. J., Graham A. F. Reovirus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.869-877.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


