Abstract
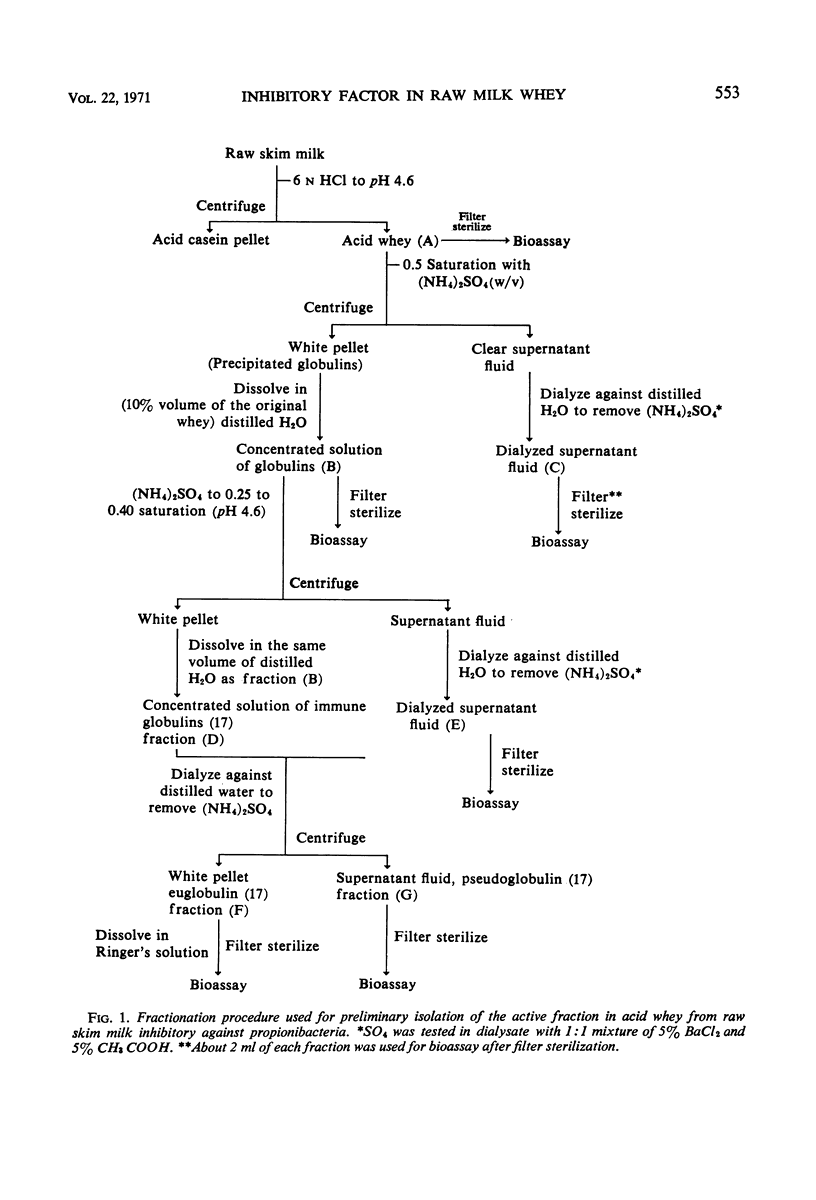
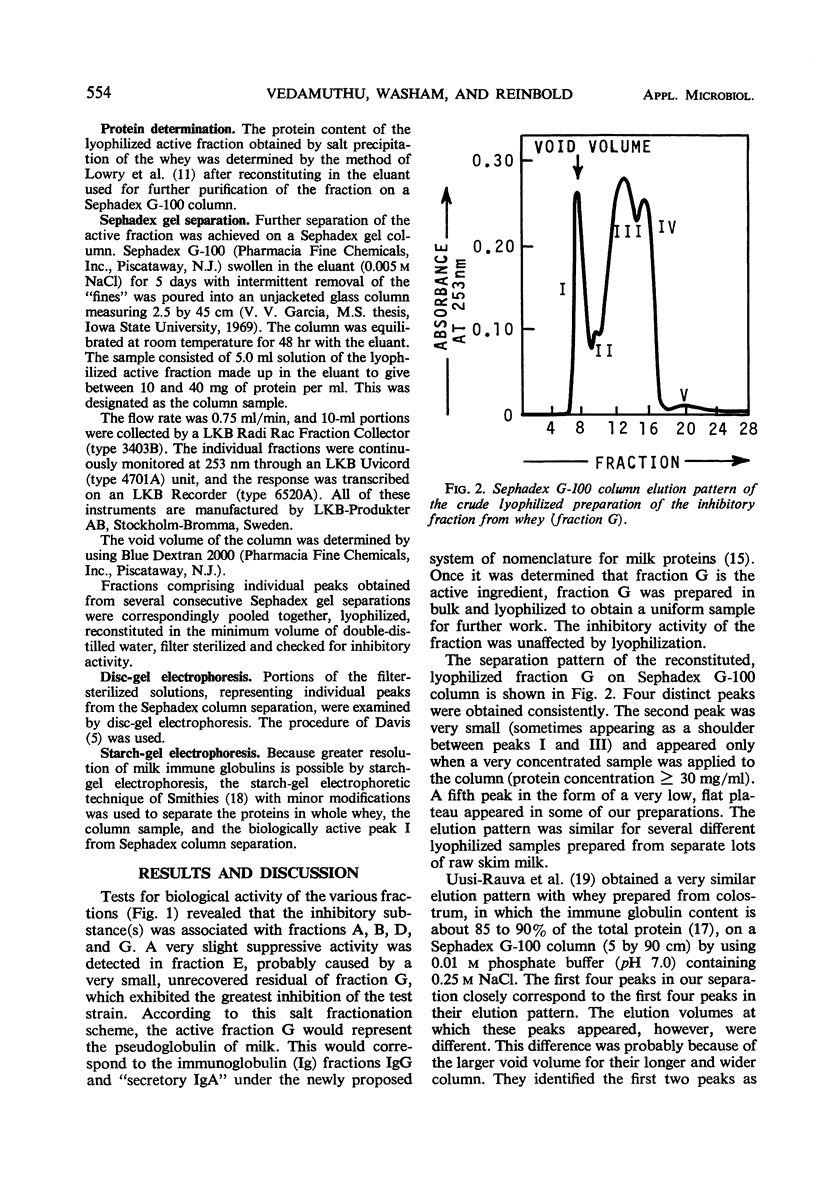
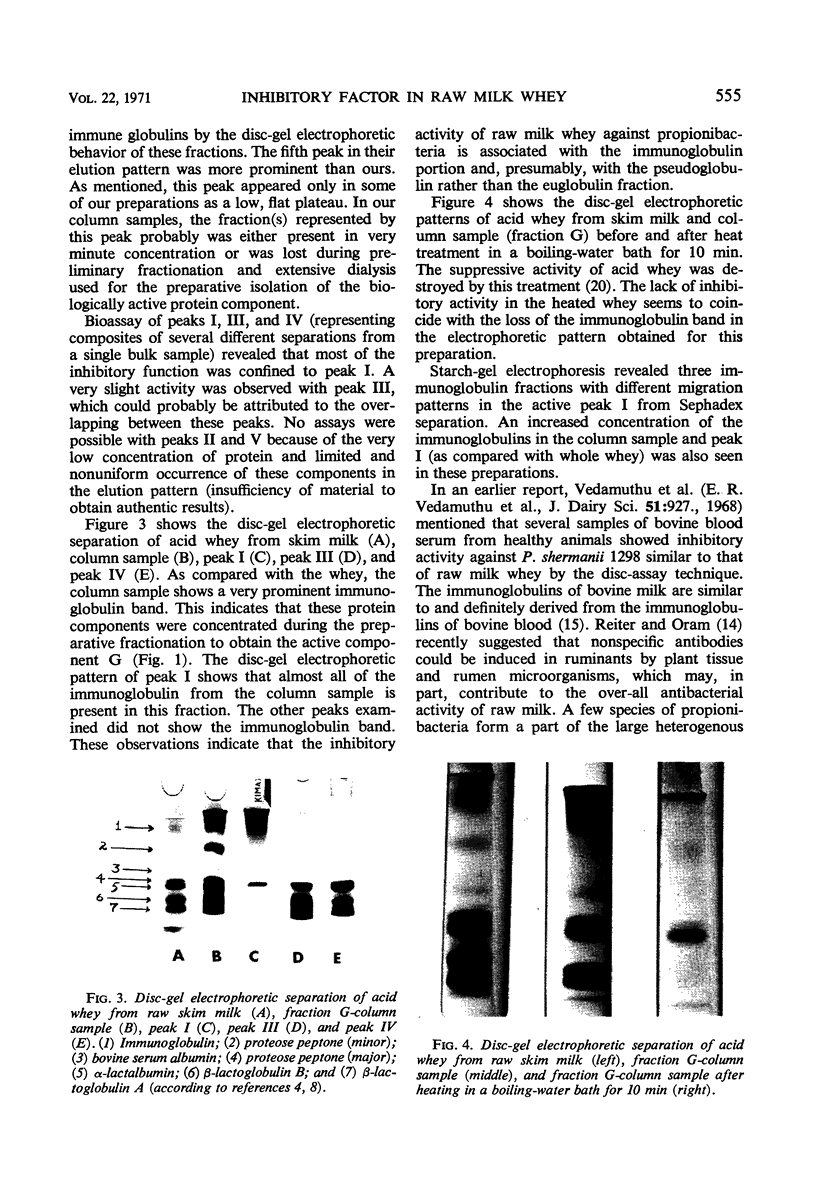
Preparative isolation of the active component(s) in skim milk whey inhibitory for propionibacteria was made by using (NH4)2SO4 salt fractionation. The crude preparation was further purified by Sephadex G-100 column separation. Disc-gel electrophoresis of the active peak from the Sephadex elution pattern (peak I) showed that this fraction contained almost all of the immune globulin in the column sample. The biologically inactive peaks did not contain any immune globulin. Starch-gel electrophoresis of the active peak revealed the presence of three separate immune globulin fractions. A correlation was also observed between hemolytic reaction of propionibacterial strains and relative resistance to whey inhibition. The investigation showed that one of the immune globulins of milk, pseudoglobulin, was mainly responsible for the suppressive activity of whey.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHEESEMAN G. C., JAYNE-WILLIAMS D. J. AN INHIBITORY SUBSTANCE PRESENT IN MILK. Nature. 1964 Nov 14;204:688–689. doi: 10.1038/204688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudhery A. K., Mikolajcik E. M. Activity of Bacillus cerus proteinases in milk. J Dairy Sci. 1970 Mar;53(3):363–366. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(70)86210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman G. H., Jr, Swanson A. M. Changes in mixtures of whey protein and k-casein due to heat treatments. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Sep;48(9):1161–1167. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Glantz P. J. Escherichia coli agglutinins in cow serum, colostrum and the nursing calf. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Jul;34(3):213–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain N. C., Jasper D. E., Carroll E. J. Bactericidal activity for Aerobacter aerogenes of bovine serum and cell-free normal and mastitic milks. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Mar;28(123):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks H. S., Reinbold G. W., Hammond E. G., Clark W. S. Growth of propionibacteria at low temperatures. J Dairy Sci. 1967 Apr;50(4):589–591. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(67)87474-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reite B., Oram J. D. Bacterial inhibitors in milk and other biological fluids. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):328–330. doi: 10.1038/216328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Brunner J. R., Kalan E. B., Larson B. L., Melnychyn P., Swaisgood H. E., Waugh D. F. Nomenclature of the proteins of cow's milk: third revision. J Dairy Sci. 1970 Jan;53(1):1–17. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(70)86141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slyter L. L., Oltjen R. R., Kern D. L., Weaver J. M. Microbial species including ureolytic bacteria from the rumen of cattle fed purified diets. J Nutr. 1968 Feb;94(2):185–192. doi: 10.1093/jn/94.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]