Abstract
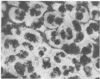
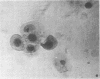
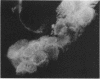
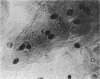
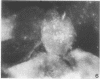
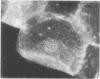
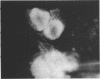
Adenovirus disease was diagnosed in 2 hr by staining exfoliated infected oropharyngeal cells with fluorescein-tagged rabbit antisera to adenovirus types 4 and 7. The method was as sensitive as the standard virus isolation procedures, but serological cross reactions were observed. Viral antigens were detected in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of infected cells. Infection was accompanied by the outpouring of large numbers of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and smaller numbers of mononuclear cells. The method provides a model for the study of the cellular response to viral upper respiratory disease.
Full text
PDF



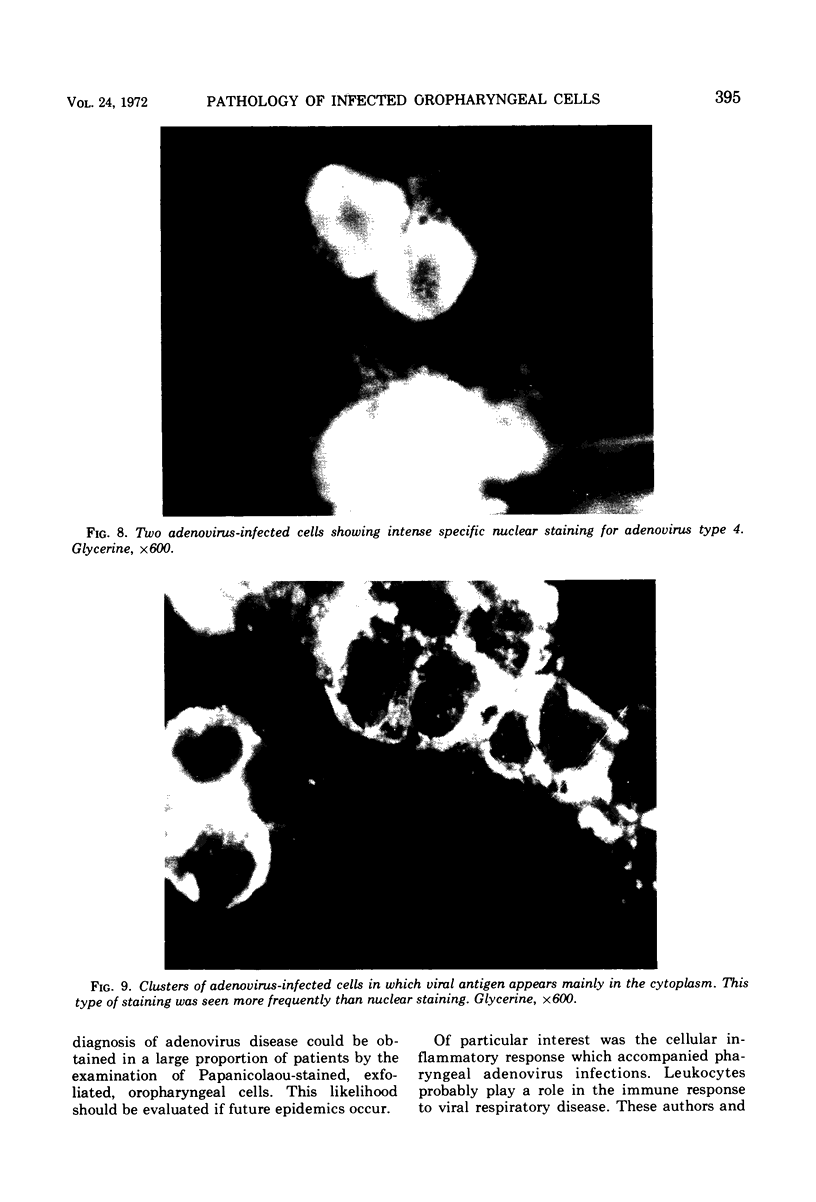


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIEGELEISEN J. Z., Jr, SCOTT L. V., LEWIS V., Jr Rapid diagnosis of herpes simplex virus infections with fluorescent antibody. Science. 1959 Mar 6;129(3349):640–641. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3349.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYER G. S., DENNY F. W., Jr, GINSBERG H. S. Sequential cellular changes produced by types 5 and 7 adenoviruses in HeLa cells and in human amniotic cells; cytological studies aided by fluorescein-labelled antibody. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:827–844. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier A. M., Wohlenberg C., Rosenthal J., Mage M., Notkins A. L. Inhibition or enhancement of immunological injury of virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M., Ludwig W., Heubner R. J., Cate T. R., Chu L. W. Immunization by selective infection with type 4 adenovirus grown in human diploid tissue cultures. I. Safety and lack of oncogenicity and tests for potency in volunteers. JAMA. 1966 Feb 7;195(6):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr Immunopathology of experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):757–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.757-763.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne V. E., Blumberg B. S., Millman I. Detection of Australia antigen in human tissue culture preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):1051–1057. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson W. P., Purcell R. H., Gundelfinger B. F., Love J. W., Ludwig W., Chanock R. M. Immunization by selective infection with type 4 adenovirus grown in human diploid tissue culture. II. specific protective effect against epidemic disease. JAMA. 1966 Feb 7;195(6):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z. Approaches to antiviral chemotherapy. Am J Med. 1971 Dec;51(6):699–703. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. P. Herpes-simplex virus as a cause of Bell's palsy. Lancet. 1972 Apr 29;1(7757):937–939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEREIRA H. G., ALLISON A. C., BALFOUR B. Multiplication of adenovirus type 5 studied by infectivity titrations and by the fluorescent antibody technique. Virology. 1959 Mar;7(3):300–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. M., Dudding B. A., Romano S. V., Russell P. K. Enteric immunization with live adenovirus type 21 vaccine. II. Systemic and local immune responses following immunization. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):300–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.300-304.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno I., Kitamoto O., Kawamura A., Jr Diverse immunocytologic findings of nasal smears in influenza. N Engl J Med. 1966 Feb 3;274(5):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196602032740502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., McCormick D. P., Smith E. P., Clark D. L., Beam W. E., Jr Acute respiratory disease: clinical and epidemiologic observations of military trainees. Mil Med. 1971 Dec;136(12):873–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]