Abstract
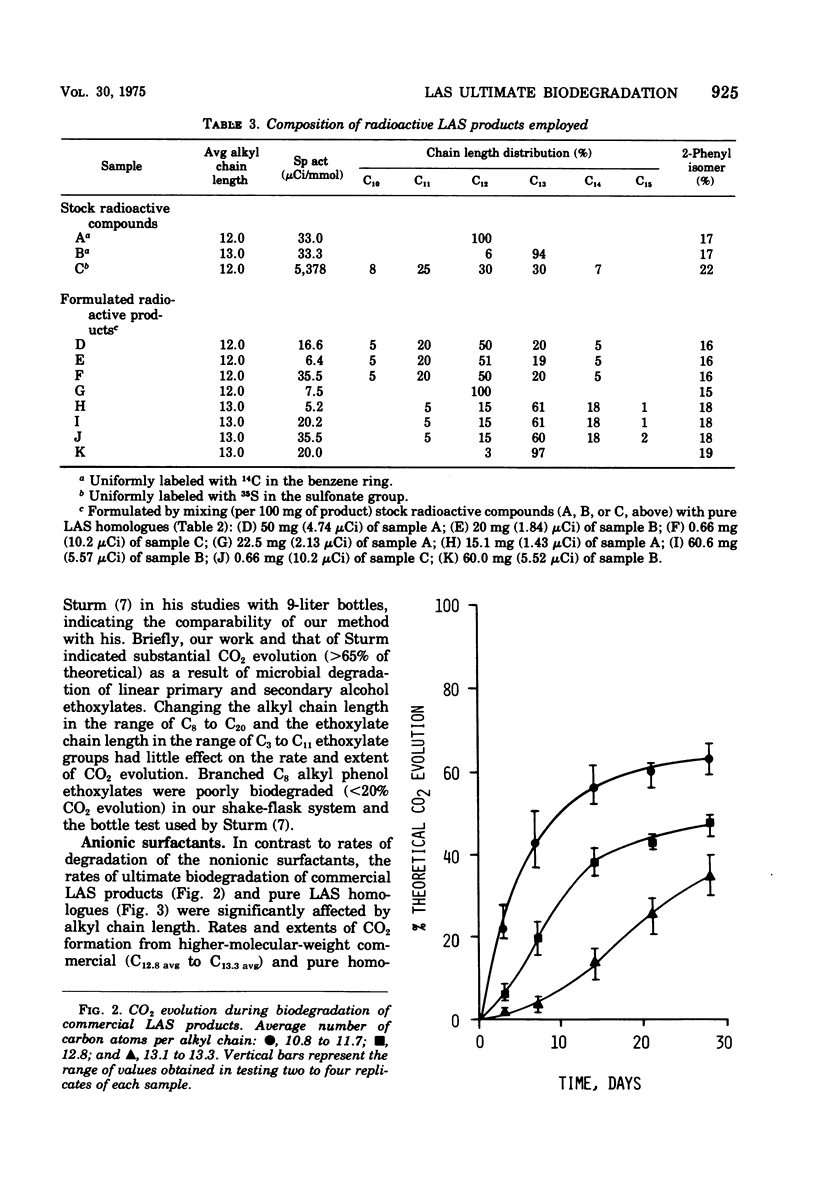
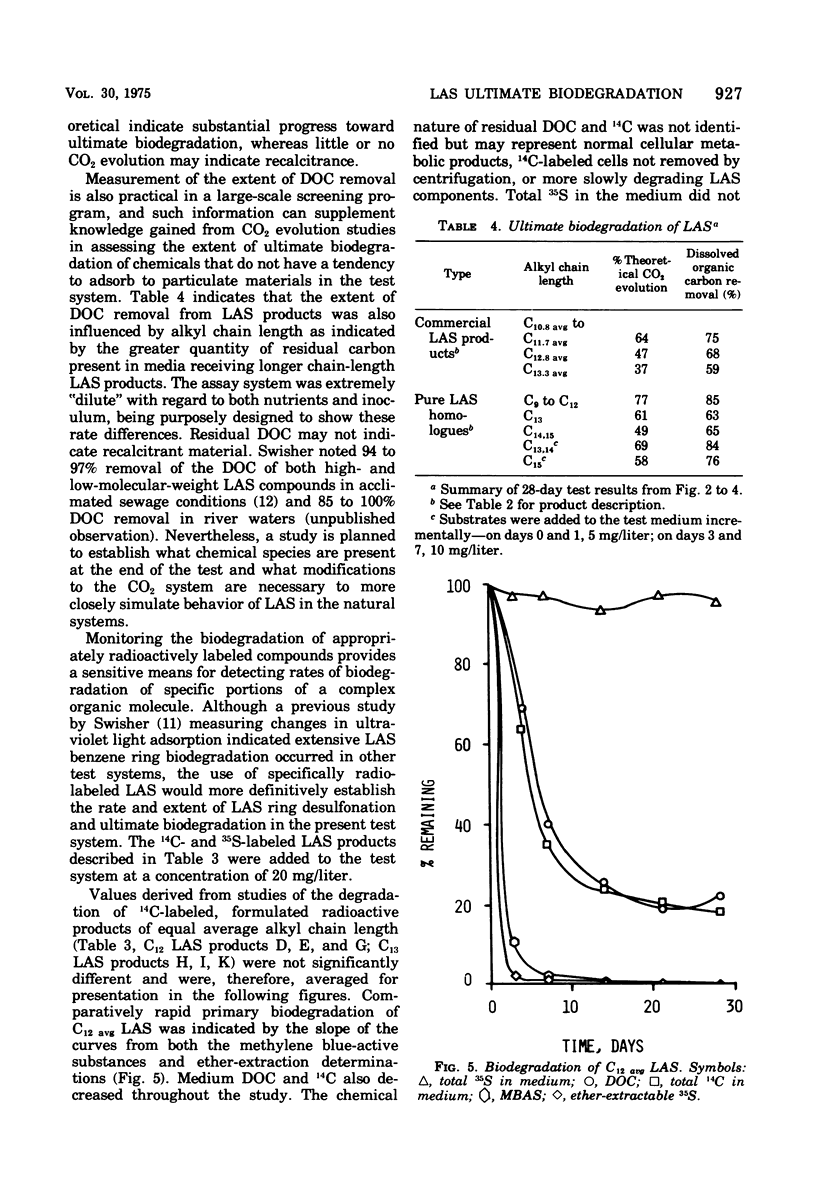
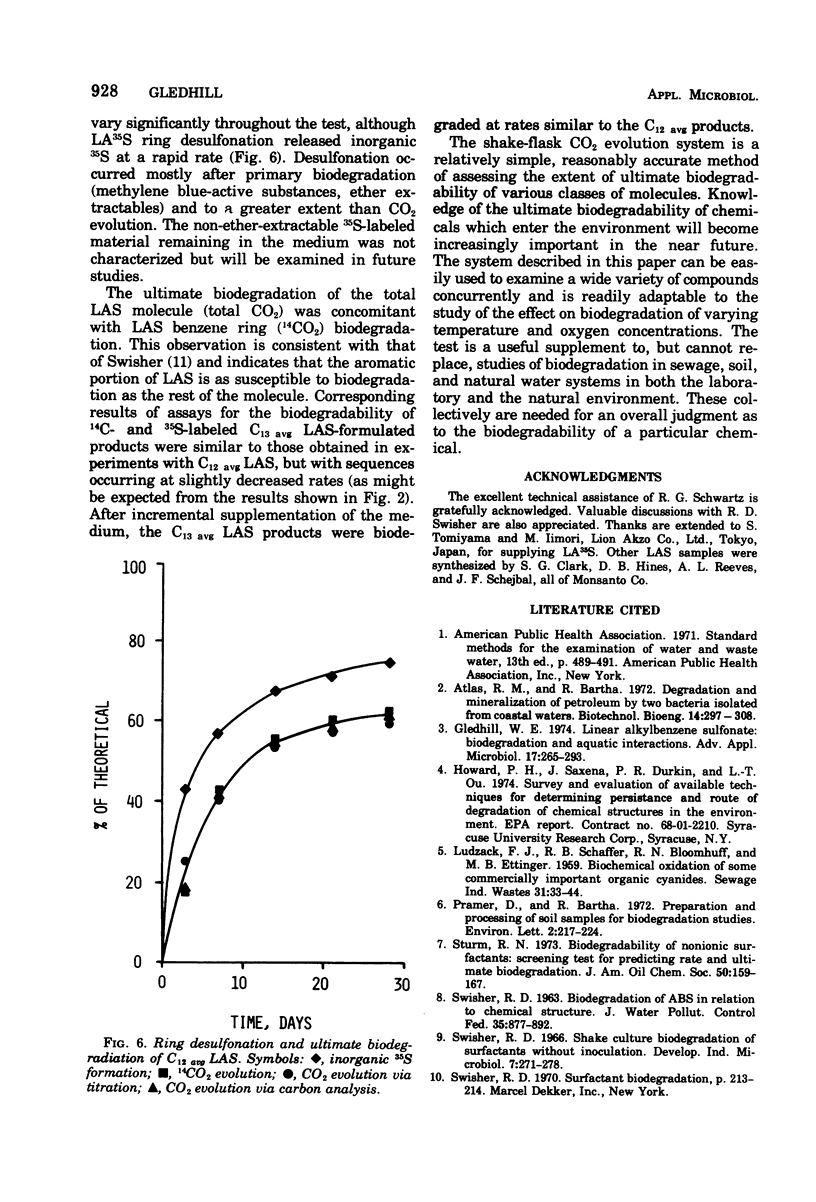
A relatively simple shake-flask system for determining CO2 evolution was developed to assess the ultimate biodegradability by soil and sewage micro-organisms of chemicals which enter the environment. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) were used as model compounds to evaluate the method and were found to undergo substantial biodegradation in this dilute system. At the 30 mg/liter test concentration, higher-molecular-weight LAS compounds were biodegraded at a slower rate and to a lesser extent than lower-molecular-weight LAS, an effect which was eliminated or greatly reduced upon incremental addition of the LAS to the test medium during the first week of incubation. LA35S was used to demonstrate rapid LAS desulfonation, and 14CO2 evolution studies with (14C) benzene ring-labeled LAS indicated concomitant biodegradation of the entire LAS molecule as well as the LAS aromatic component. The test can be employed to examine numerous compounds at the same time and is readily adapted to studies of the effect of variation in temperature and oxygen concentration on biodegradation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas R. M., Bartha R. Degradation and mineralization of petroleum by two bacteria isolated from coastal waters. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1972 May;14(3):297–308. doi: 10.1002/bit.260140303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill W. E. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonate: biodegradation and aquatic interactions. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):265–293. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70561-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. E., Duthie J. R. The biodegradability and treatability of NTA. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1968 Feb;40(2):306–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


