Abstract
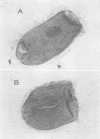
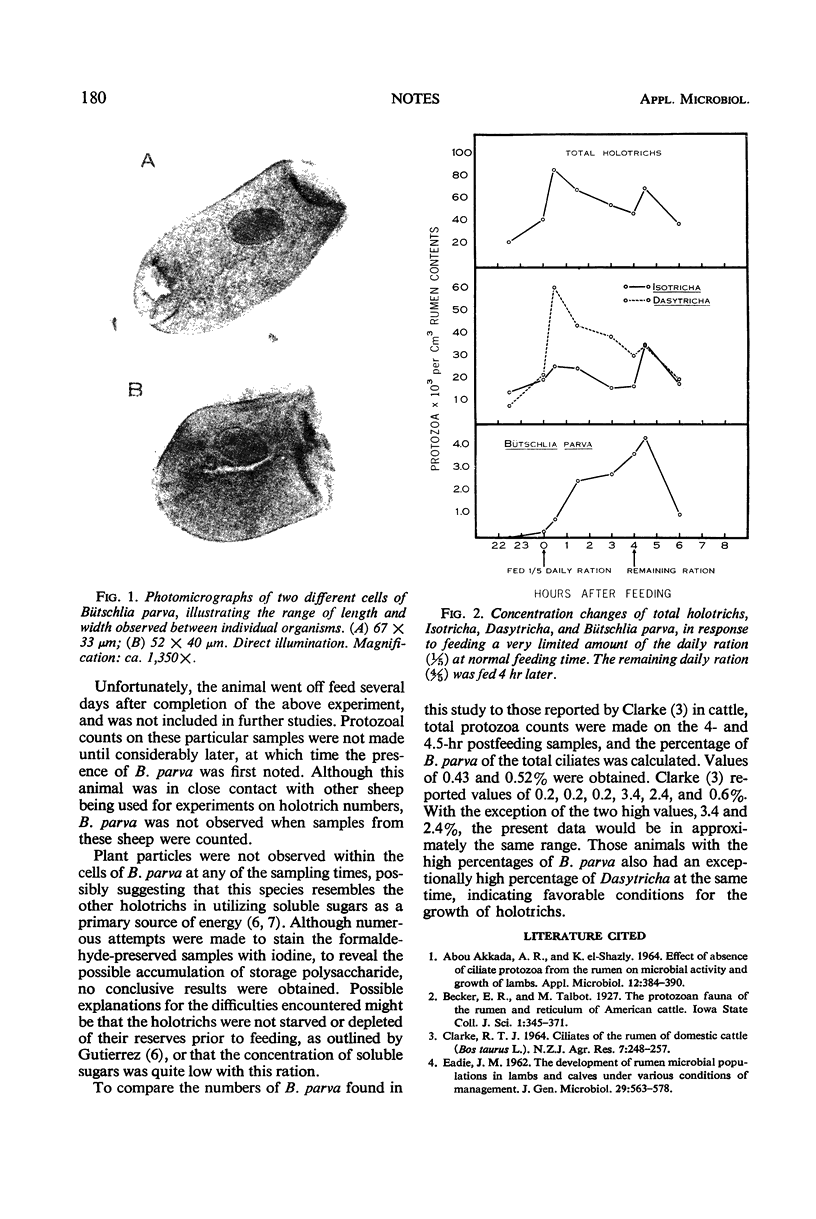
The holotrich ciliate protozoa, Bütschlia parva Schuberg, has been observed in the rumen of the ovine. Limited data suggest that the concentration of B. parva in the rumen follows a diurnal cycle similar to that of the other holotrichs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOUAKKADA A. R., EL-SHAZLY K. EFFECT OF ABSENCE OF CILIATE PROTOZOA FROM THE RUMEN ON MICROBIAL ACTIVITY AND GROWTH OF LAMBS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:384–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTIERREZ J. Experiments on the culture and physiology of holotriches from the bovine rumen. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):516–522. doi: 10.1042/bj0600516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD B. H. The biochemistry of rumen protozoa. 1. Carbohydrate fermentation by Dasytricha and Isotricha. Biochem J. 1959 Apr;71(4):671–675. doi: 10.1042/bj0710671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naga M. A., Abou Akkada A. R., el-Shazly K. Establishment of rumen ciliate protozoa in cow and water buffalo (Bosbubalus L.) calves under late and early weaning systems. J Dairy Sci. 1969 Jan;52(1):110–112. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(69)86510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Kanegasaki S. Densities of ruminal protozoa of sheep established under different dietary conditions. J Dairy Sci. 1969 Feb;52(2):250–255. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(69)86538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURSER D. B. A diurnal cycle for Holotrich protozoa of the rumen. Nature. 1961 May 27;190:831–832. doi: 10.1038/190831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURSER D. B., WEISER H. H. INFLUENCE OF TIME OF ADDITION OF ANTIBIOTIC ON THE IN VITRO LIFE OF RUMEN HOLOTRICH PROTOZOA. Nature. 1963 Oct 19;200:290–290. doi: 10.1038/200290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER A. C. Some factors influencing the rumen microbial population. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:129–146. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. C. Diurnal changes in the concentrations of micro-organisms in the rumens of sheep fed limited diets once daily. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):213–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. C. Diurnal changes in the concentrations of micro-organisms in the rumens of sheep fed to appetite in pens or at pasture. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. C. Periodic changes in the concentrations of micro-organisms in the rumen of a sheep fed a limited ration every three hours. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):237–241. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]