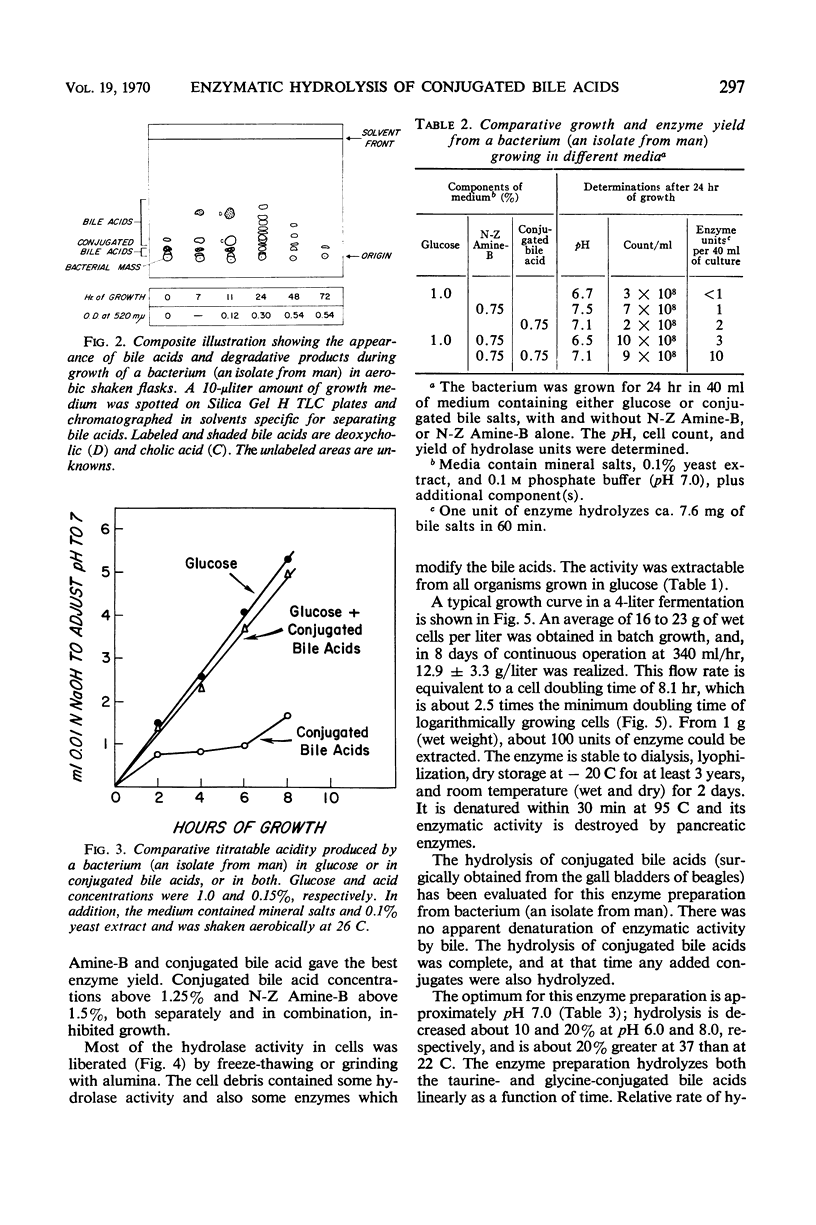
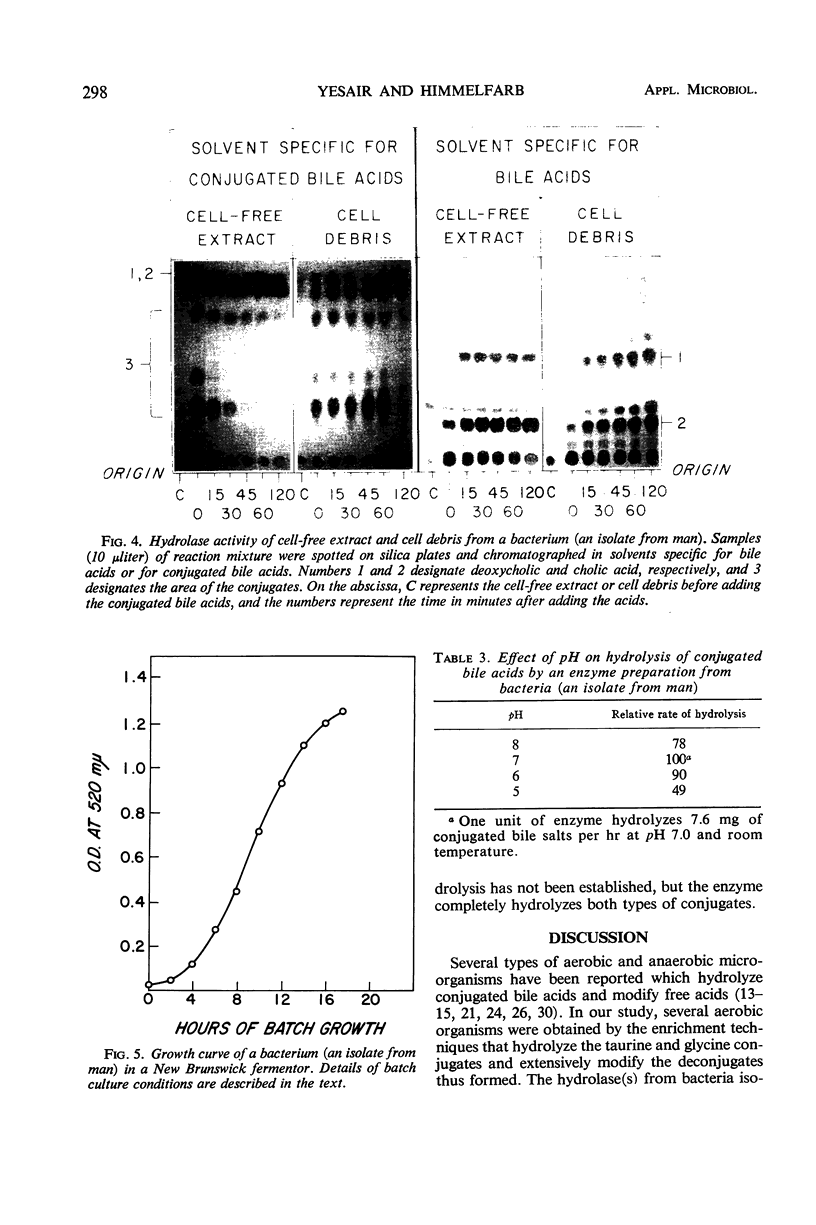
Abstract
By means of an aerobic enrichment culture technique, several bacteria that hydrolyze conjugated bile acids and modify the formed deconjugates were isolated from feces of man, rat, and chicken and from soil. Hydrolase activity was intracellular and extractable, and the yield of the enzymes was increased by adding the conjugated bile acids to the culture media. The hydrolase from bacterium of human origin was stable, having a pH optimum at about 7.0. All bile acid conjugates were hydrolyzed linearly as a function of time.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUMGARTEN A. MICRO METHOD OF HAPTOGLOBIN TYPING USING ACRYLAMIDE GELS. Nature. 1963 Aug 3;199:490–491. doi: 10.1038/199490b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B. Effect of tauro-cholic acid on the pH/activity curve of rat pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Jan;13(1):149–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. Studies on lipid metabolism in the small intestine with observations on the role of bile salts. J Clin Invest. 1960 May;39:730–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI104090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of steatorrhea in the blind loop syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1815–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI105289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Shiner M. The deconjugation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1237–1238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel M. The biological splitting of conjugated bile acids. Biochem J. 1936 Nov;30(11):2111–2116. doi: 10.1042/bj0302111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN F., WIRTS C. W., KRAMER S. The relationship of afferent limb stasis and bacterial flora to the production of postgastrectomy steatorrhea. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jan;40:47–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., BERGSTROM S., LINDSTEDT S., NORMAN A. Turnover and nature of fecal bile acids in germfree and infected rats fed cholic acid-24-14C; bile acids and steroids 41. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):467–471. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., NORMAN A., SJOVALL J. Influence of E. coli infection on turnover and metabolism of cholic acid in germ-free rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Nov;91:93–100. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., STANIER R. Y. The bacterial oxidation of tryptophan. III. Enzymatic activities of cell-free extracts from bacteria employing the aromatic pathway. J Bacteriol. 1951 Dec;62(6):691–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.6.691-709.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAKAWA S., SAMUELSSON B. TRANSFORMATION OF CHOLIC ACID IN VITRO BY CORYNEBACTERIUM SIMPLEX. BILE ACIDS AND STEROIDS. 132. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:94–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Physico-chemical state of lipids in intestinal content during their digestion and absorption. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PHYSICOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON BILE SALTS. Gastroenterology. 1965 Apr;48:484–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. Micellar solubilization of fatty acids and monoglycerides by bile salt solutions. Nature. 1961 Jun 17;190:1106–1107. doi: 10.1038/1901106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSTEDT S., NORMAN A. The turnover of bile acids in the rat; bile acids and steroids 39. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Dec 31;38(2):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., GRUBB R. Hydrolysis of conjugated bile acids by Clostridia and enterococci; bile acids and steroids 25. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(6):537–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1955.tb04651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A. On the conjugation of bile acids in the rat; bile acids and steroids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954 Oct 20;32(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., SHORB M. S. In vitro formation of deoxycholic and lithocholic acid by human intestinal microorganisms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jul;110:552–555. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., SJOVALL J. On the transformation and enterohepatic circulation of cholic acid in the rat: bile acids and steroids 68. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):872–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., WIDSTROEM O. A. HYDROLYSIS OF CONJUGATED BILE ACIDS BY EXTRACELLULAR ENZYMES PRESENT IN RAT INTESTINAL CONTENTS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:442–444. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Gordon S., Reback J., Mendeloff A. I. The cleavage of bile acid conjugates by cell-free extracts from Clostridium perfringens. Life Sci. 1965 Oct;4(19):1887–1892. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTMAN O. W. Importance of diet, species, and intestinal flora in bile acid metabolism. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:896–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTMAN O. W., SHAH S., ANTONIS A., JORGENSEN B. Alteration of bile salts by bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Apr;109:959–965. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSCOE H. G., FAHRENBACH M. J. REMOVAL OF FECAL PIGMENTS AND ITS APPLICATION TO THE DETERMINATION OF FECAL BILE ACIDS IN THE RAT. Anal Biochem. 1963 Dec;6:520–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., BUTZ G. W., Jr, HARTMAN C. F. The blind-loop syndrome after gastric operations. Surgery. 1961 Nov;50:849–858. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Booth C. C. Jejunal bacteriology and bile-salt metabolism in patients with intestinal malabsorption. Lancet. 1966 Jul 2;2(7453):12–15. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Okubadejo O. A., Neale G., Booth C. C. Influence of abnormal bacterial flora on small intestinal function. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Dec;59(12):1244–1246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



