Abstract
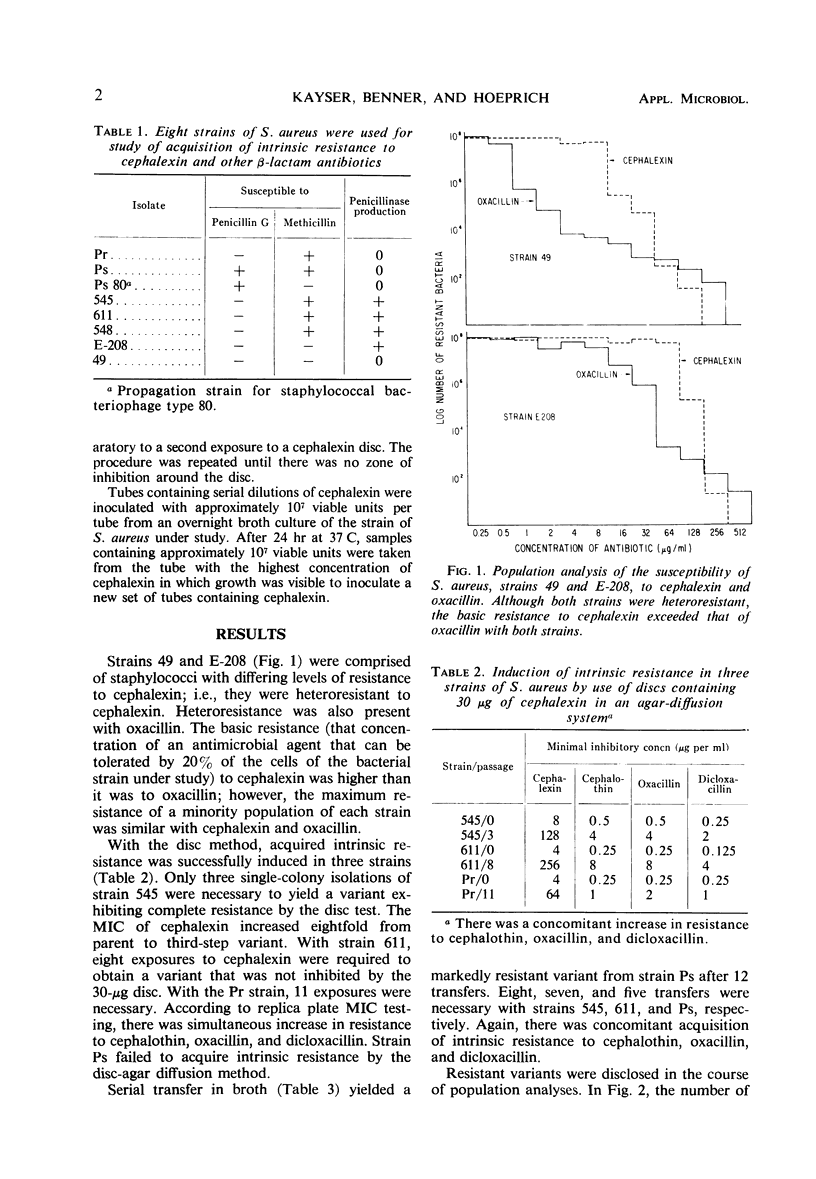
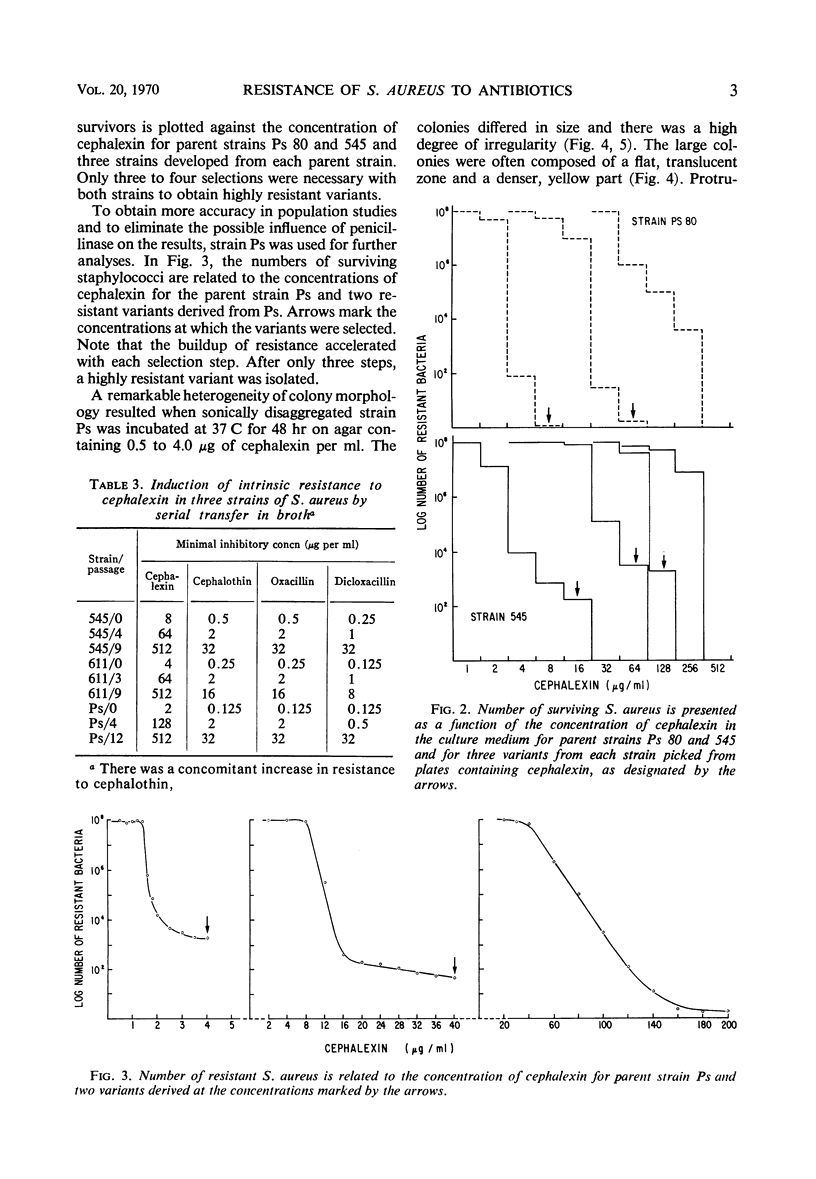
Staphylococcus aureus cells that are initially susceptible to cephalexin can be induced to acquire intrinsic resistance to cephalexin in comparatively few steps. Concomitantly, resistance to cephalothin, oxacillin, and dicloxacillin increases. By population analysis, there is heteroresistance to cephalexin in some strains of S. aureus. Heterogeneity in colonial morphology on prolonged incubation in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of cephalexin may constitute an expression of such heteroresistance.
Full text
PDF
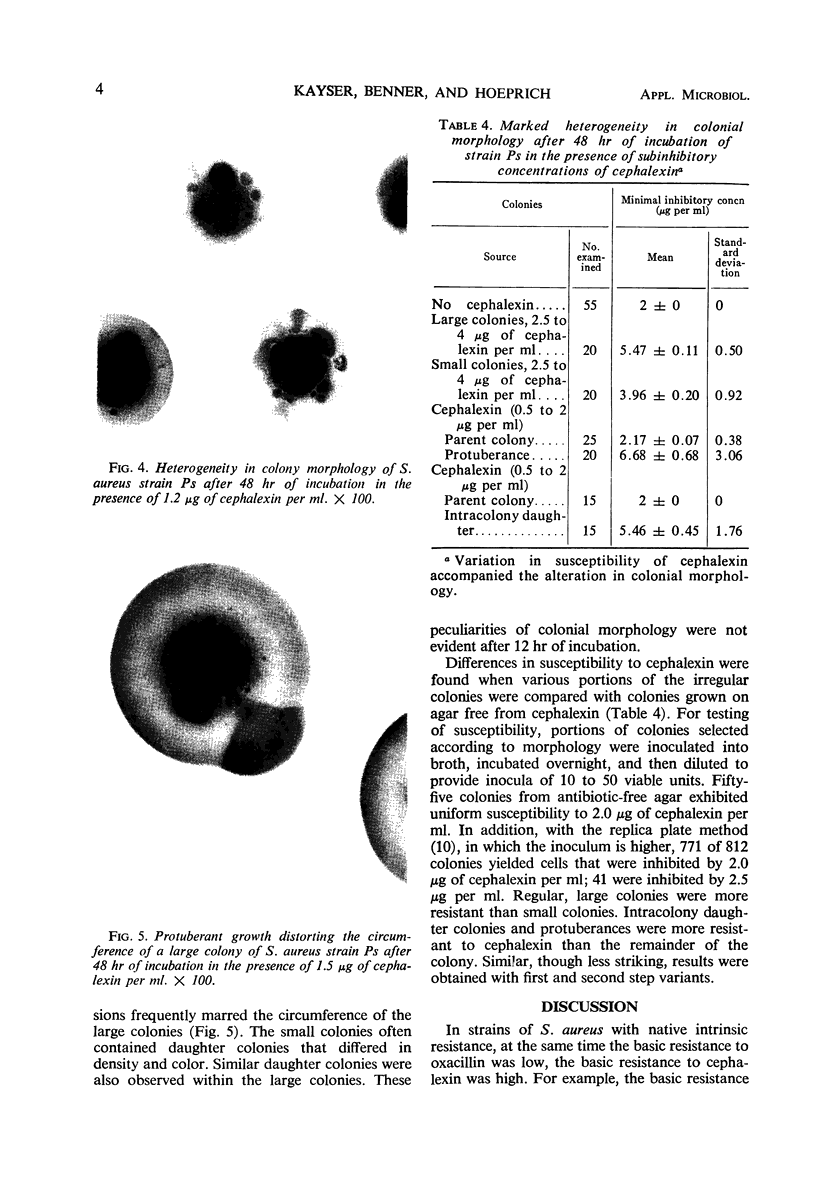

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYSON V., DEMEREC M. Patterns of resistance to antimicrobial agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Sep;53(2):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb42160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner E. J., Kayser F. H. Growing clinical significance of methcillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1968 Oct 5;2(7571):741–744. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M. Production of Staphylococcus Strains Resistant to Various Concentrations of Penicillin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Jan;31(1):16–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Benner E. J., Kayser F. H. Susceptibility of "methicillin"-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to 12 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX R., SMITH J. T. Stability of methiciilin and cloxacillin to staphylococcal penicillinase. Br Med J. 1963 Jul 27;2(5351):205–207. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5351.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser F. H. Uber die Oxacillinresistenz pathogener Staphylokokken. IV. Vorkommen und Bedeutung von Staphylokokkenstämmen mit "inhärenter Penicillinresistenz". Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1966;153(1):48–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser F. H., Wiemer U. Uber die Oxacillinresistenz pathogener Staphylokokken. I. Die Natur der Resistenz gegen Oxyacillin bei Staphylococcus pyogenes aureus. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1965;150(4):308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E. Cephalexin, a new orally absorbed cephalosporin antibiotic. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):765–769. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.765-769.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]