Abstract
To produce an artificial fruiting body of Armillaria mellea on the oak sawdust medium, seven strains of A. mellea were used. The top surface of oak sawdust medium covered with ground raw carrot was inoculated with each of 7 strains and cultured for 30 days at 25℃ in the dark condition until the mycelia of A. mellea completely colonized the medium from top to bottom. Then, the mycelia which were fully covered on the top surface of the medium were scratched slightly with a spatula and filled with tap water for 3 hours. To induce the primordial formation, the 7 strains of A. mellea were transferred to the growth chamber under the illumination (350 lux) of 12 hours and relative humidity of 85 ± 5% in a day and then cultured at 16 ± 1℃. Only A. mellea IUM 949 could form primordia on the sawdust medium, but the other strains did not make primordia at the same condition. The primordia of A. mellea IUM 949 were formed 10 days after complete colonization of the medium and the fruiting bodies were produced 7 days after a primordial formation. The experimental results suggested that IUM 949 strain might be a good candidate for mass production of fruiting bodies of A. mellea.
Keywords: Armillaria mellea, Fruiting bodies, Ground raw carrot, Primordium
Armillaria mellea (Vahl. ex Fr), one of edible and medicinal mushrooms belonging to Tricholomataceae, Agaricales has been known to be inhabited as a parasite or saprophyte on many woody plant hosts such as the coniferous or broad-leaved trees from spring to Autumn, and also engaged in the symbiotic relationship with Gastrodia elata, one of medicinal herbs (Park and Lee, 1991). The fruiting body of A. mellea has been known to possess protein-polysaccharide substance, one of medicinally important chemical compounds (Kim et al., 1983). The protein-polysaccharide substance has exhibited good therapeutic and inhibitory effects against esophagus cancer, hypertension and paralysis (Li et al., 1993).
In Asian countries such as China and Japan, the researches related to A. mellea have been focused on an artificial production of fruiting bodies to secure precious medicinal mushroom resources (Li et al., 1993; Iwao and Namio, 1994, 1995; Namio, 1996). In Korea, as a part of investigating the possibility of artificial cultivation of new edible wild mushrooms, Cha (1981) tried sawdust culture for the cultivation of A. mellea. Kim et al. (1992) reported fruiting body of A. mellea was produced firstly on sawdust of Quercus spp. Although Kim et al. (1992) suggested the possibility of mass production of A. mellea in Korea, the artificial production of A. mellea has been not realized in Korea. Therefore, this study was initiated to realize mass production of A. mellea, and compared with that of Kim et al. (1992).
Materials and Methods
Cultures
Seven strains of A. mellea were obtained from the Culture Collection of Wild Mushroom Species (CCWM) in the Department of Biology, University of Incheon (Table 1). Seven strains of A. mellea were transferred to PDA, incubated at 25℃ in the dark condition until they exhibited a full growth, and kept at 5℃ before use.
Table 1.
Strains of Armillaria mellea used in this study
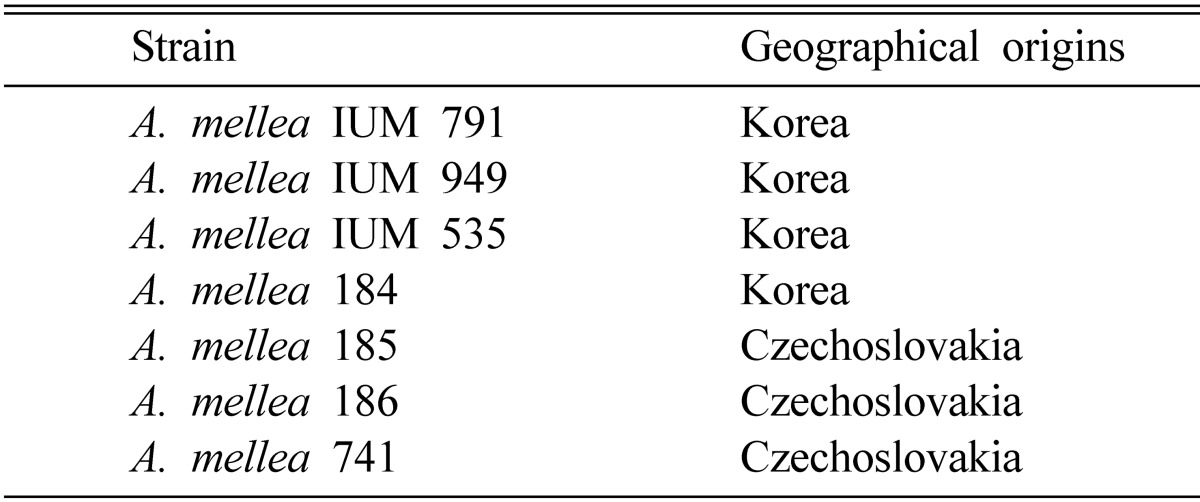
The formation of fruiting body of A. mellea
The preparation of liquid inoculum
To prepare each liquid inoculum of 7 strains, a 1.2 cm plug of each inoculum was removed with cork borer from 10 days old cultures of A. mellea. Then, 6 pieces of the plug were inoculated on the 100 ml of sterilized PDB (potato dextrose broth + 2% malt extract, pH 6.0) within a triangular flask (250 ml) and incubated for 30 days at 24 ± 1℃ in the shaking incubator (150 rpm/min).
The preparation of oak sawdust medium covered with the ground raw carrot
Preparation of stimulator suitable for mycelial growth of A. mellea
To prepare ground raw carrots as a stimulator for favorable mycelial growth of A. mellea (Iwao and Namio, 1995; Iwao, 1996), the raw carrot(Daucus carota) was used. Raw carrots were washed with tap water, broken to several pieces, put into a blendor (Waring, U.S.A.), ground throughly for 5 minutes, mixed finally with oak sawdust containing 30% rice bran to the ratio of 50% (v/v) and kept at 5℃ before use.
Preparation of oak sawdust medium
To prepare sawdust medium suitable for producing fruiting body of A. mellea, oak sawdust (Quercus variabilis) was mixed throughly with rice bran of 30% (v/v), adjusted to the moisture content of 70%, and put into the polyethylene plastic bottle (700 ml, 9 × 13 cm). After then, the surface of oak sawdust medium was covered with a small amount (an uniform thickness of about 1 cm) of ground raw carrots, inserted to make a hole with glass bar (diameter 1.5 cm × length 8 cm) in the center of the medium, and finally steam-sterilized for 90 minutes at 121℃.
The inoculation and culture of A. mellea
After each of 7 strains was incubated in the shaking incubator (150 rpm/min) for 30 days, 10 ml of each inoculum was removed from liquid culture medium, inoculated on the top surface of oak sawdust medium in the polyethylene plastic bottle (700 ml, 9 × 13 cm), and cultured for 30 days at 25℃ in the dark condition until the mycelia of A. mellea were completely colonized from the top to bottom of the medium.
The inducement of primordia and fruiting bodies of A. mellea
After the mycelia of A. mellea completely colonized the medium within the cultivation bottle, the top surface of the medium was scratched slightly with a spatula, and filled with tap water for 3 hours. After then, the tap water was removed from the bottle. To promote a good ventilation and avoid drying of the mycelial surface of the medium during primordial formation, the bottles were covered with ST cap (made of polypropylene) which were not equipped with a sponge filter and then transferred to the growth chamber (DL, DF-95G504M). The environmental condition of growth chamber was 16 ± 1℃ under the illumination (350 lux) of 12 hours and relative humidity of 85 ± 5% in a day. If primordia of A. mellea were appeared on the surface of oak sawdust medium, STcap was removed from the bottle.
Results and Discussions
Seven strains of A. mellea completely colonized the medium from top to bottom after 30 days of culture at 25℃. Then, the bottles were transferred to the growth chamber, and primordia were formed after 10 days of incubation (Fig. 2). Of 7 strains used, A. mellea IUM 949 was the only one strain to form primordia (Fig. 2). A. mellea IUM 949 strain can be used for a good candidate for mass production of fruiting body of A. mellea in the future.
Fig. 2.
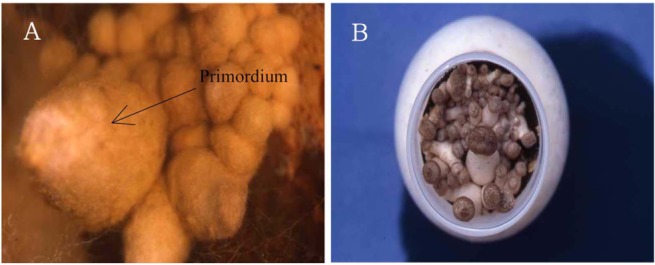
The primordium of Armillaria mellea IUM 949 formed on oak sawdust media covered with ground raw carrots. A. The initial primordia (18 ×) of Armillaria mellea IUM 949 on the surface of oak sawdust medium. B. Primordia of Armillaria mellea IUM 949 on the surface of oak sawdust medium after 3 days of primordium formation.
The mature fruiting bodies of A. mellea IUM 949 were observed within 7 days after primordial formation (Fig. 1). The numbers of fruiting bodies obtained from the bottle cultivation were ranged from 1 to 26 per bottle, and the mean numbers were 9 pieces per bottle (Table 2). The total weight of fresh fruiting bodies were ranged from 2.88 to 59.15 g per bottle, and the mean weight was 23.9 g per bottle (Table 2). From this experiment, the probability to produce primordia or fruiting bodies from wild A. mellea seems to be very low.
Fig. 1.

The fruiting bodies of Armillaria mellea IUM 949 on oak sawdust media covered with ground raw carrots.
Table 2.
The fruiting body of Armillaria mellea IUM 949 produced on oak sawdust media
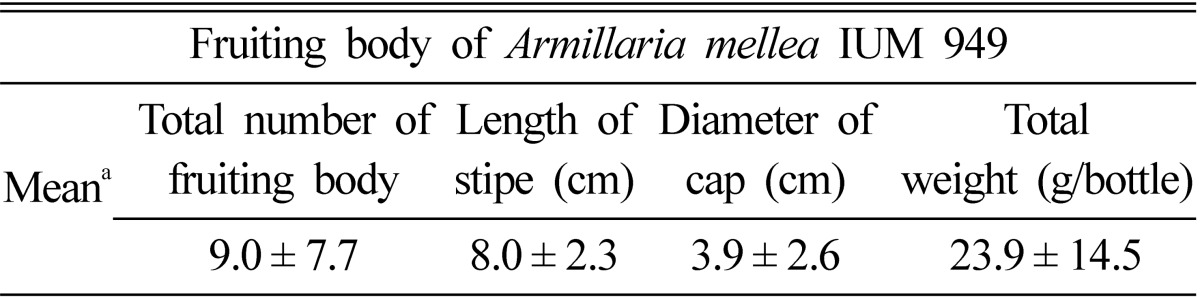
aThe values are the average of 24 replications and standard deviation.
Kim et al. (1992) reported that A. mellea completely colonized the medium after 70 days of culture at 24 ± 1℃ and then primordia were formed 7 days after a complete colonization of medium at 15℃. When our experimental results were compared with that of Kim et al. (1992), we obtained much more shorten incubation period than that of Kim et al. (1992) by the treatment of ground raw carrot and small sawdust medium. The reason seems to be resulted from some active substances of ground raw carrots rather than medium size.
In other studies, it was suggested that some ingredient of carrot must be beneficial to the rapid growth of A. mellea on sawdust media (Iwao and Namio, 1994, 1995). Also, Iwao (1996) reported that the covering of ground raw carrots is needed because some ingredients of carrot might stimulate the dark mycelial coat of A. mellea on top surface of oak sawdust medium and then result in the formation of its primordia. Thus, it will be necessary in the future to clarify the relationship between a primodial formation of A. mellea and an application of ground raw carrots.
In our study, it takes 47 days from an inoculation of A. mellea to production of its fruiting bodies on the sawdust medium. However, Kim et al. (1992) reported that culture period for producing fruiting bodies of A. mellea was ranged from 90 to 100 days. Our results showed that 43 days of culture period in producing fruiting body of A. mellea was more reduced as compared with those of Kim et al. (1992). The additional 43 days which were taken to produce fruiting bodies in the study of Kim et al. (1992) might be due to the large sized mushroom culturing bags or bottles containing a large amount of oak sawdust medium. Whenever a large amount of medium is used to incubate the mushroom culture, the culture period for completely colonizing the media is increased as compared to that of a small amount of medium. In our study, fruiting bodies of A. mellea were produced within a small polyethylene plastic bottles (the size of 9 × 13 cm), whereas Kim et al. (1992) used a large polyethylene bags (the size of 13 × 30 cm) to produce its fruiting bodies.
In this study, the drastically rapid mycelial growth of A. mellea was achieved by adding ground raw carrots to oak sawdust medium. Consequently, the addition of ground raw carrots to oak sawdust medium shortened production period of fruiting body by almost half as compared with previous study by Kim et al. (1992). Also, it is known that the addition of ground raw carrots to the medium promoted a primodial formation on oak sawdust media. Therefore, the result obtained from our study can be applied to mass production of other mushrooms as well as A. mellea.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by research grant (No. 204039-3) from Agriculture R & D Promotion Center (ARPC) in the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry.
References
- 1.Cha DY. Investigation on artificial cultures for new edible wild mushrooms (II) Korean J Mycol. 1981;9:123–128. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Iwao T, Namio T. Effect of adding carrot, Daucus carota variety sativa, to media in the rhizomorph production of Armillaria species. Mokuzai gakkaishi. 1994;40:213–219. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Iwao T, Namio T. Effects of primordium formation method and moisture content of medium on fruiting body production of Armillaria species. Mokuzai gakkaishi. 1995;41:211–217. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Iwao T. Effects of substrates and seeding methods on fruiting body production in the bottle cultivation of Armillaria species. Mokuzai gakkaishi. 1996;42:186–193. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim JS, Choi EC, Kim HR, Lee CK, Lee CO, Chung KS, Shim MJ, Kim BK. Studies on constituents of the higher fungi of Korea (XXXVII)-Antitumor components of Armillariella mellea. Korean J Mycol. 1983;11:151–157. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim HJ, Ko MK, Yi CK, Sung JM. Cultivation of Armillaria mellea mushrooms on a sawdust medium in polypropylene bags. Korean J Mycol. 1992;20:273–276. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li JZ, Hu X, Peng Y. Macrofungusflora of Hunan. China: Hunan Normal University Press; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park WH, Lee HD. Wild Fungi of Korea in Color. Seoul, Korea: Kyo-Hak Publishing Co.; 1991. [Google Scholar]


