Abstract
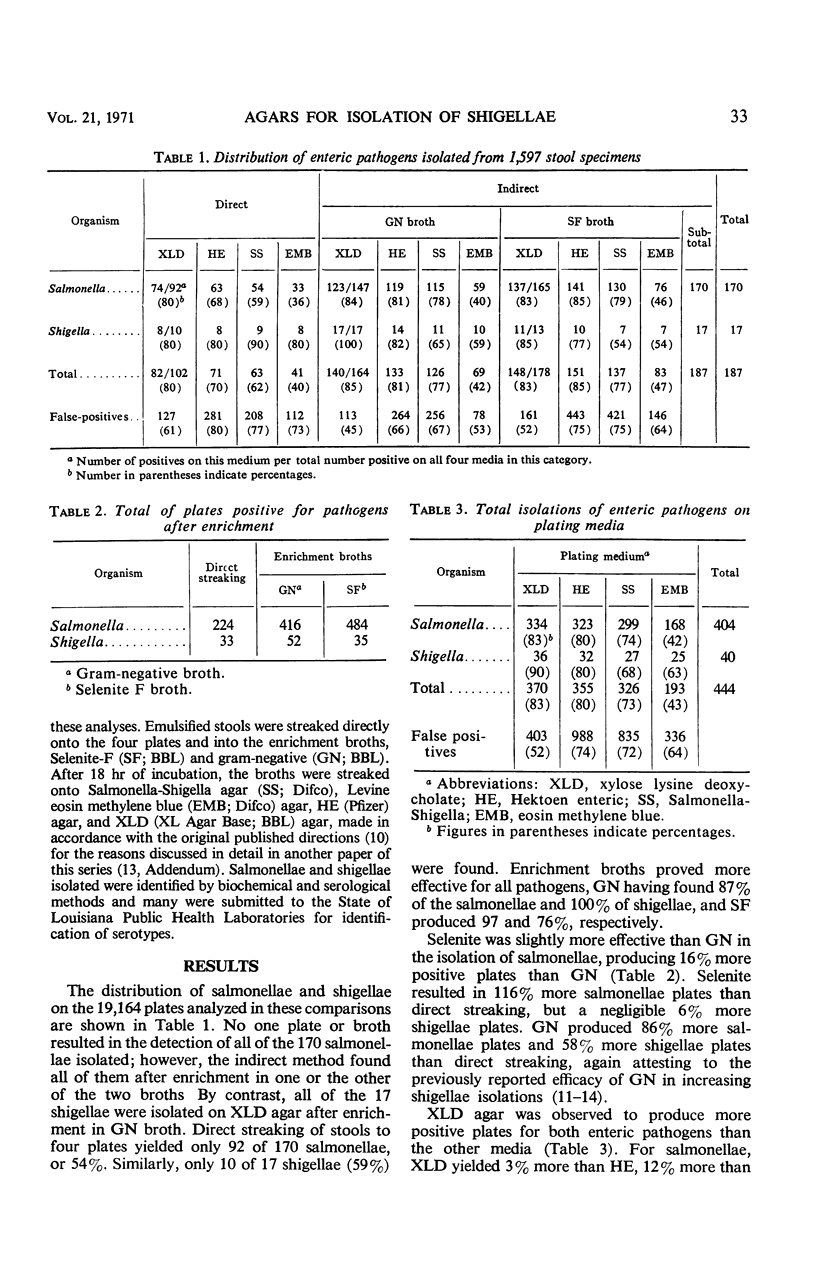
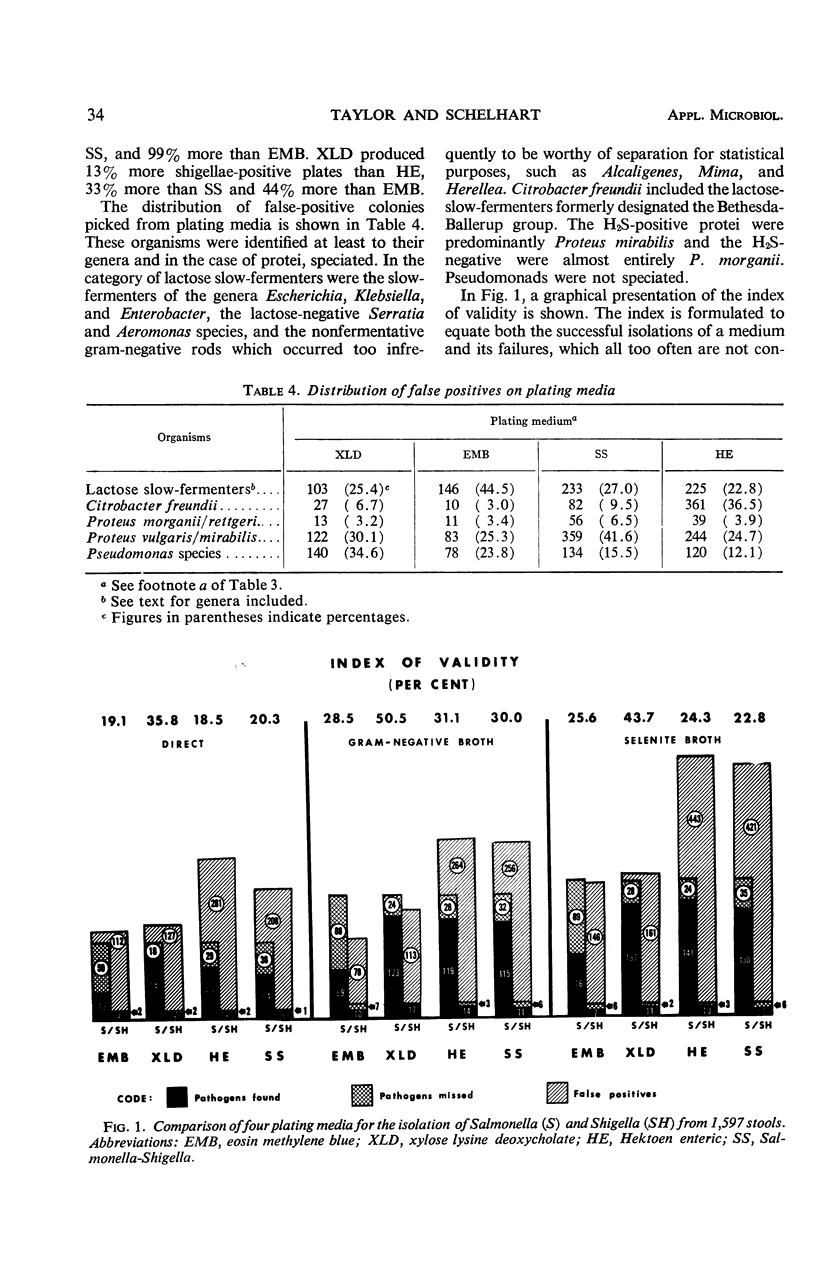
Two enrichment broths and four plating media were compared for efficiency of detection of enteric pathogens from 1,597 stool specimens. Of 170 salmonellae isolated from the composite of all methods, direct streaking yielded but 54%, whereas enrichment in gram-negative broth found 87% and Selenite-F broth 97%. By contrast, gram-negative broth produced 100% of the 17 shigellae, Selenite-F broth but 77%, and direct streaking only 59%. Thus, enrichment methods produced almost twice the number of both pathogens as direct streaking. Comparison of the plating media revealed xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD) and Hektoen enteric agar to be equal in their abilities to find both pathogens. Both were moderately better than Salmonella-Shigella agar and markedly superior to eosin methylene blue agar. XLD fround 83% of salmonellae produced by the composite of four media and 90% of the shigellae. Hektoen enteric agar found 80% of both. Salmonella-Shigella agar detected 74 and 68%, respectively, and eosin methylene blue agar only 42 and 63%. The numbers of false positives accruing to each medium, however, showed Hektoen enteric and Salmonella-Shigella agars to produce more than twice as many false-positive plates as XLD. Similarly, Selenite-F broth resulted in many more false-positives for all plating media than did gram-negative broth. Consequently, the index of validity, which equates successful isolation of pathogens with total pickings, favored XLD and gram-negative broth as the media of choice, with direct streaking the poorest method by all counts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hentges D. J. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the normal intestinal flora. I. Mechanisms of inhibition by Klebsiella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1369–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1369-1373.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the normal intestinal flora. II. Mechanisms of inhibition by coliform organisms. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):513–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.513-517.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Kominos S., Siegel M. Isolation of Salmonellae and Shigellae from an artificial mixture of fecal bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):656–659. doi: 10.1128/am.18.4.656-659.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S., Metzger W. I. A new plating medium for the isolation of enteric pathogens. I. hektoen enteric agar. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):577–578. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.577-578.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S., Metzger W. I. A new plating medium for the isolation of enteric pathogens. II. Comparison of hektoen enteric agar with SS and EMB agar. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):579–581. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.579-581.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Koehler J. A., Gangarosa E. J., Sharrar R. G. Comparison of media for direct isolation and transport of Shigellae from Fecal specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Mar;19(3):434–437. doi: 10.1128/am.19.3.434-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I., Harris B. Isolation of shigellae. II. Comparison of plating media and enrichment broths. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):476–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I. Isolation of shigellae. I. Xylose lysine agars; new media for isolation of enteric pathogens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):471–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I., Schelhart D. Isolation of shigellae. V. Comparison of enrichment broths with stools. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1383–1386. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1383-1386.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. I., Schelhart D. Isolation of shigellae. VI. Performance of media with stool speciments. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1387–1393. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1387-1393.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


