Abstract
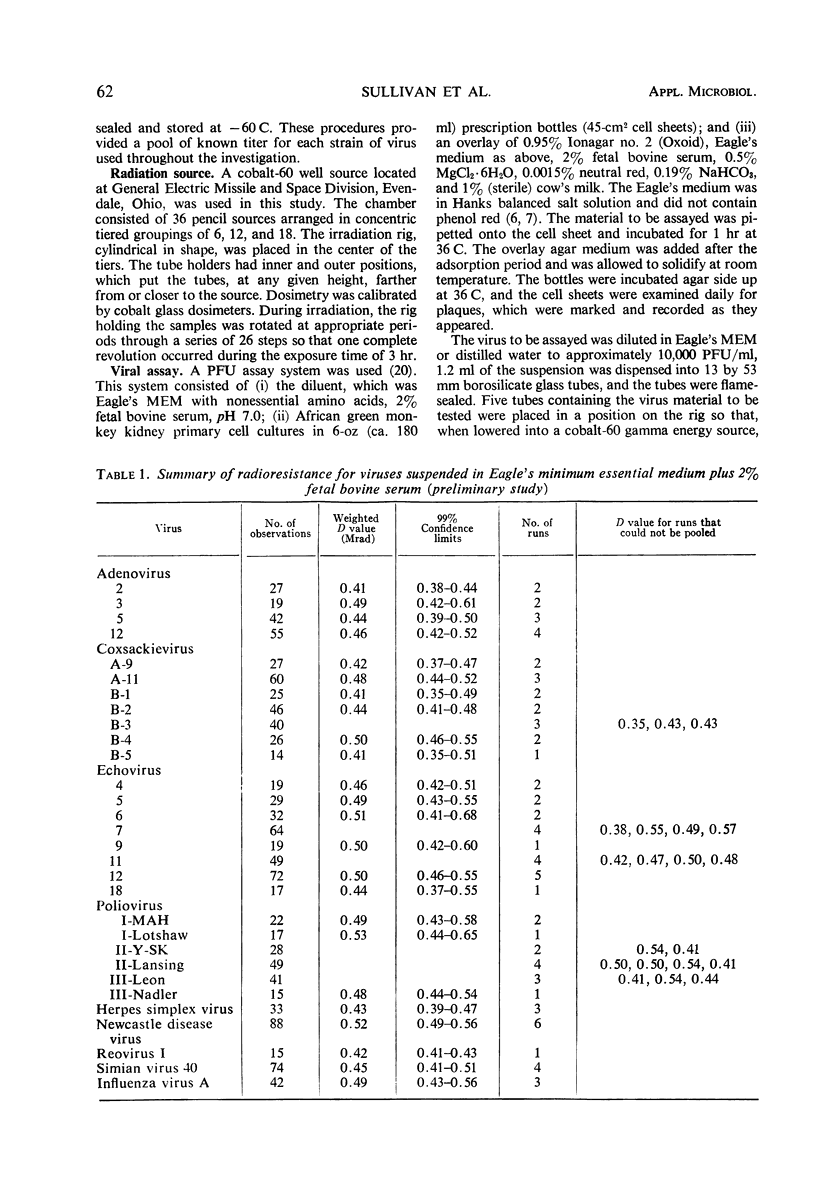
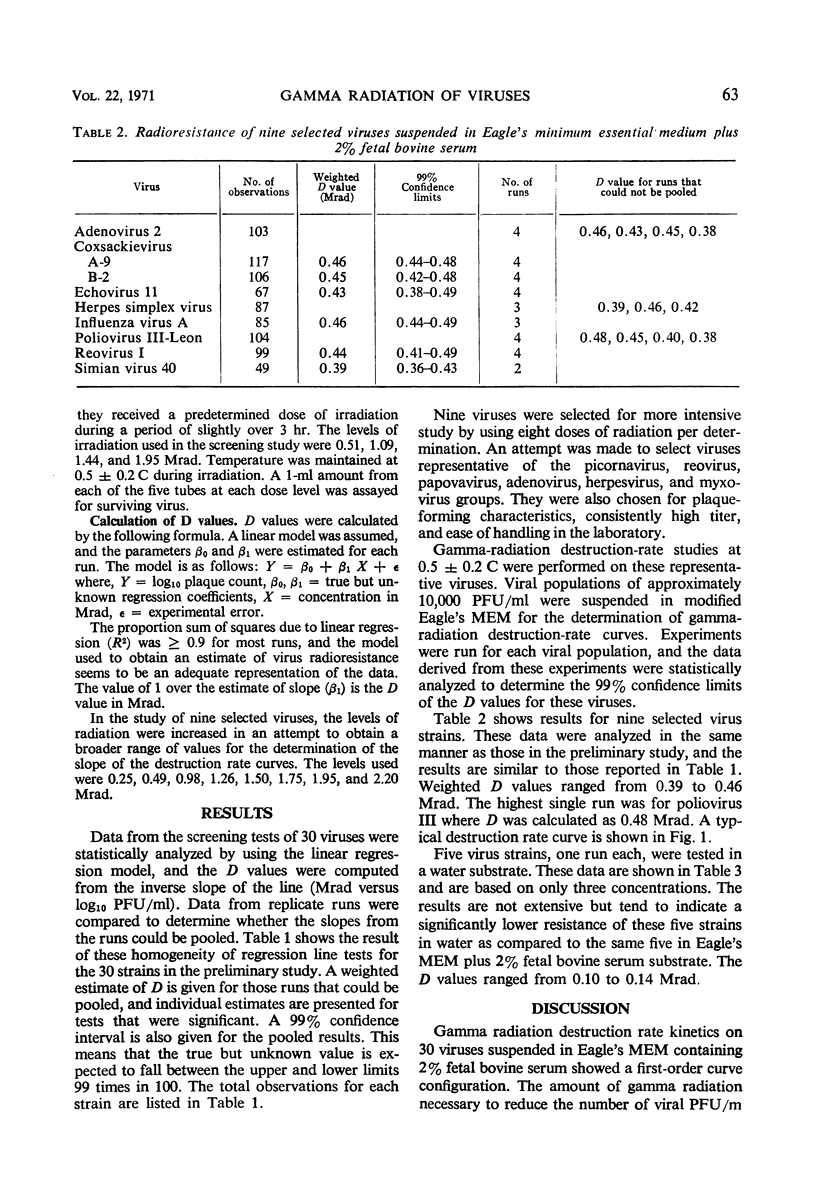
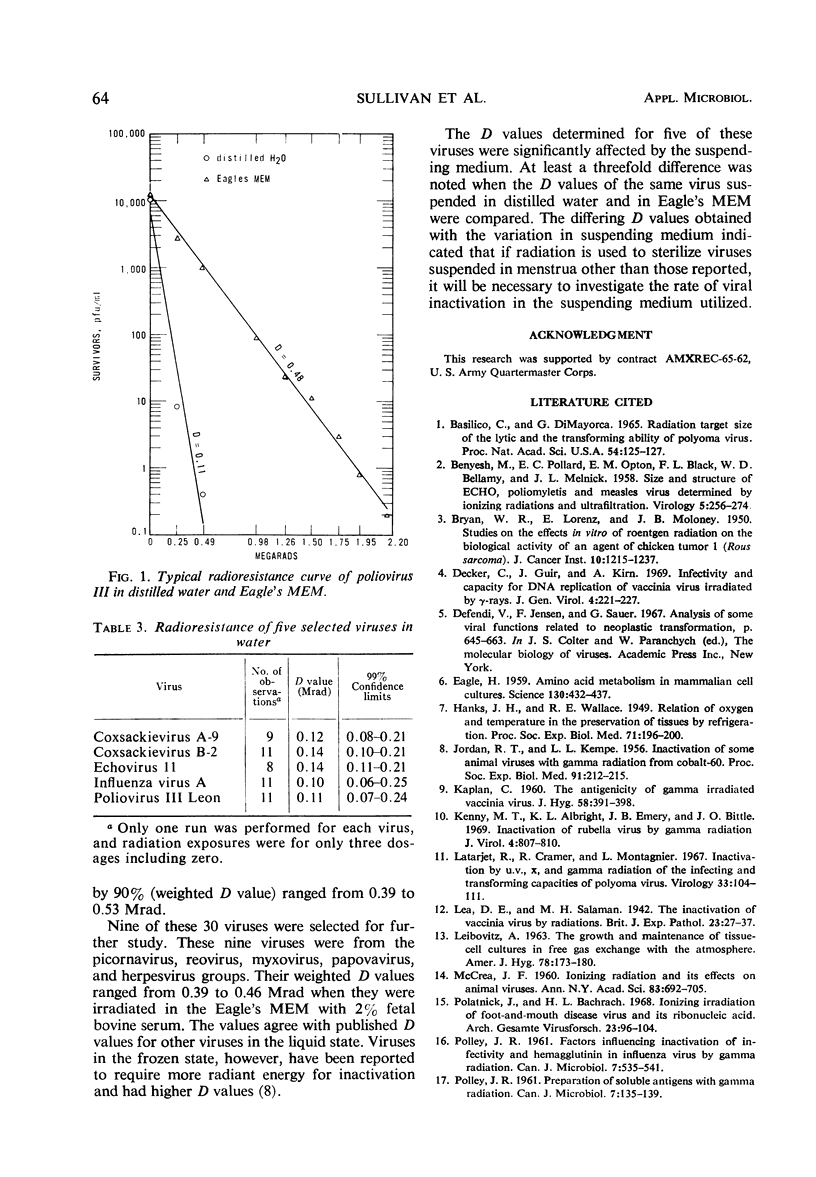
Decimal reduction values (D value) for 30 viruses were determined. The weighted D values of the viruses suspended in Eagle's minimum essential medium ranged from 0.39 to 0.53 Mrads. It was necessary to increase the radiation dose by a factor of >3 to inactivate virus suspended in Eagle's minimum essential medium as compared to the same virus suspended in distilled water. The destruction rate curves were of a first-order reaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENYESH M., POLLARD E. C., OPTON E. M., BLACK F. I., BELLAMY W. D., MELNICK J. L. Size and structure of ECHO, poliomyelitis, and measles viruses determined by ionizing radiation and ultrafiltration. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):256–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYAN W. R., LORENZ E., MOLONEY J. B., SELLS M. T., THOMAS M. A. Studies on the effects in vitro of Roentgen radiation on the biological activity of the agent of chicken tumor I(Rous sarcoma). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1950 Jun;10(6):1215–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Di Mayorca G. Radiation target size of the lytic and the transforming ability of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):125–127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C., Guir J., Kirn A. Infectivity and capacity for DNA replication of vaccinia virus irradiated by gamma-rays. J Gen Virol. 1969 Mar;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN R. T., KEMPE L. L. Inactivation of some animal viruses with gamma radiation from cobalt-60. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):212–215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN C. The antigenicity of gamma-irradiated vaccinia virus. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Dec;58:391–398. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Albright K. L., Emery J. B., Bittle J. L. Inactivation of rubella virus by gamma radiation. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):807–810. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.807-810.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIBOVITZ A. THE GROWTH AND MAINTENANCE OF TISSUE-CELL CULTURES IN FREE GAS EXCHANGE WITH THE ATMOSPHERE. Am J Hyg. 1963 Sep;78:173–180. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latarjet R., Cramer R., Montagnier L. Inactivation, by UV-, x-, and gamma-radiations, of the infecting and transforming capacities of polyoma virus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLEY J. R. Factors influencing inactivation of infectivity and hemagglutinin of influenza virus by gamma radiation. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Aug;7:535–541. doi: 10.1139/m61-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLEY J. R. Preparation of non-infective soluble antigens with gamma radiation. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Apr;7:135–139. doi: 10.1139/m61-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Bachrach H. L. Ionizing irradiation of foot-and-mouth disease virus and its ribonucleic acid. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(1):96–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01242118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Tribble H. R. Inactivation of Venezuelan Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus by gamma-Radiation. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1456–1459. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1456-1459.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Read R. B., Jr Method for recovery of viruses from milk and milk products. J Dairy Sci. 1968 Nov;51(11):1748–1751. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(68)87270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUB F. B., FRIEDEMANN U., BRASCH A., HUBER W. High intensity electrons as a tool for preparation of vaccines. I. Preparation of rabies vaccine. J Immunol. 1951 Nov;67(5):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON D., POLLARD E. Radiation studies on the infective property of Newcastle disease virus. Radiat Res. 1958 Feb;8(2):131–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESE C., POLLARD E. The effect of ionizing radiation on various properties of Newcastle disease virus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jun;50(2):354–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


