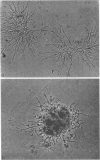
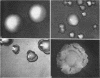
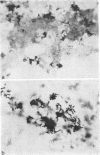
Abstract
The repeated isolation of Actinomyces naeslundii from clinical materials associated with disease led to a comparison of isolates from the normal mouth with isolates from pathological clinical materials not from the mouth area. No important differences were observed between the isolates from these two sources. A human case of empyema of the gall bladder, apparently due to A. naeslundii, is described.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock D. W., Georg L. K. Determination and analysis of Actinomyces israelii serotypes by fluorescent-antibody procedures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):581–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.581-588.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, MURPHY W. C., 3rd, PAUL F., STEPHAN R. M. Oral strains of Actinomyces. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):82–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.82-95.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert F. W., Jr, Brown J. M., Georg L. K. Identification of Actinomyces israelii and Actinomyces naeslundii by fluorescent-antibody and agar-gel diffusion techniques. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1287–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1287-1295.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Landfried S., Gerencser M. A. Morphological, biochemical, and serological studies on 64 strains of Actinomyces israelii. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):873–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.873-884.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L., LOVESTEDT S. A. An Actinomyces-like organism obtained from the human mouth. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1951 May 9;26(10):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]