Abstract
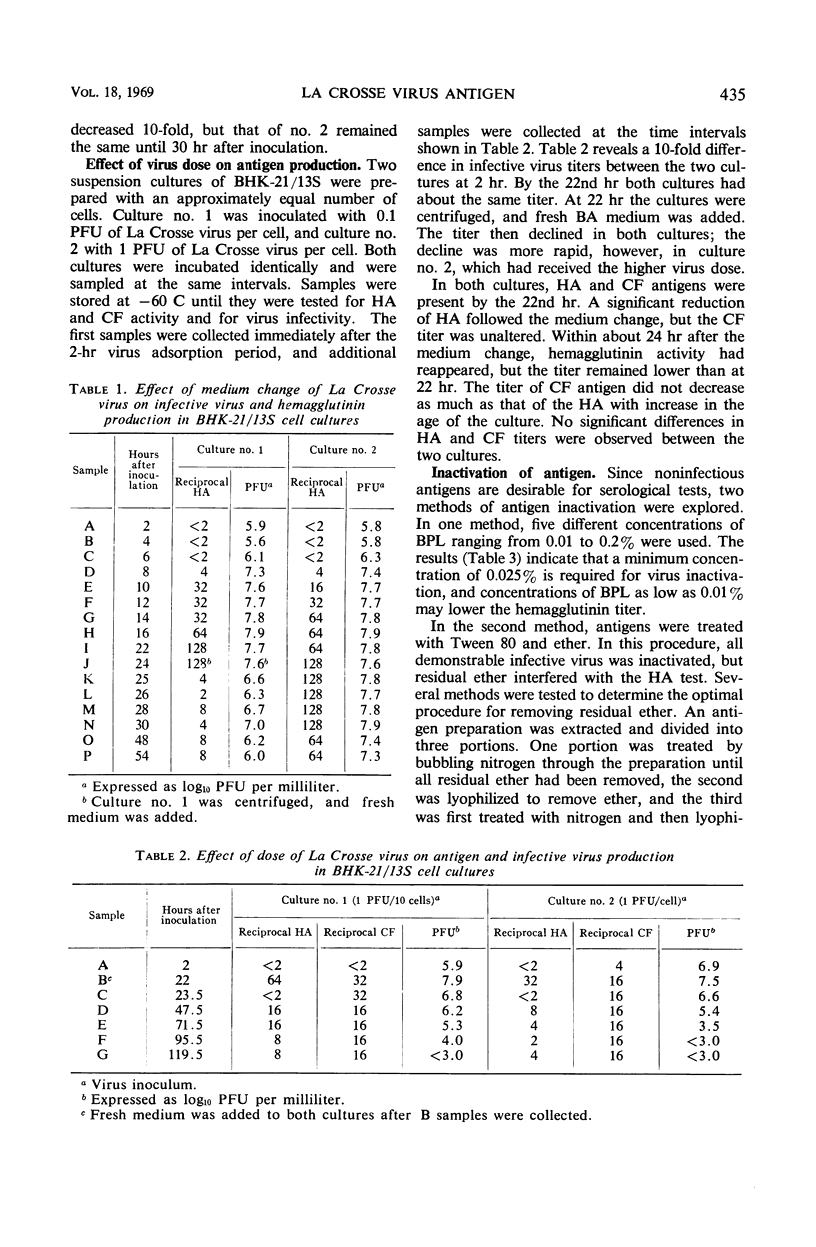
Hemagglutinating and complement-fixing antigens of La Crosse virus (California arbovirus group) were produced in serum-free suspension cultures of BHK-21/13S cells. The appearance and production of these antigens were correlated with the titer of infectious virus. No significant differences in antigen titers were produced by varying virus dose 10-fold. Hemagglutinin appeared 6 to 8 hr after inoculation and reached peak titer in 14 to 22 hr. Both β-propiolactone and Tween 80-ether treatment inactivated infectious virus in the antigens. Unlyophilized antigen was stable at -60, 5 and 24 C for at least 117 days but not for 1 year. Lyophilized antigen was stable for at least a year, however, at -20 and 5 C. Cell culture-produced antigen was more sensitive than brain-produced antigen in detecting hemagglutination inhibition antibody in human sera.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMON W. M., REEVES W. C. California encephalitis virus, a newly described agent. Calif Med. 1952 Nov;77(5):303–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. D., Casey H. L., Stewart J. A., Hall A. D. Rubella complement fixing antigen prepared by alkaline extraction of virus grown in suspension culture of BHK-211 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Murphy F. A., Fields B. N., Reese D. R. Hemagglutinin of rabies and some other bullet-shaped viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1037–1042. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Stewart J. A., Hall A. D. Rubella hemagglutinin prepared in serum free suspension culture of BHK-21 cells. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1967;45(2):182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammon W. M., Sather G. History and recent reappearance of viruses in the California encephalitis group. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):199–204. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Coleman P. H. California group arboviruses: immunodiffusion studies. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Whitfield S. G., Coleman P. H., Calisher C. H., Rabin E. R., Jenson A. B., Melnick J. L., Edwards M. R., Whitney E. California group arboviruses: electron microscopic studies. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Aug;9(1):44–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUICK D. T., SMITH A. G., LEWIS A. L., SATHER G. E., HAMMON W. M. CALIFORNIA ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS INFECTION: A CASE REPORT. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:456–459. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., CASTELLANO G. A., PELON W., HUEBNER R. J., WOLMAN F. INACTIVATION OF THE INFECTIVITY OF VIRAL HEMAGGLUTINATING ANTIGENS WITH THE USE OF BETAPRONE. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Dec;64:983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather G. E., Hammon W. M. Antigenic patterns within the California-encephalitis-virus group. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jul;16(4):548–557. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON W. H., EVANS A. S. CALIFORNIA ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS STUDIES IN WISCONSIN. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:230–244. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON W. H., KALFAYAN B., ANSLOW R. O. ISOLATION OF CALIFORNIA ENCEPHALITIS GROUP VIRUS FROM A FATAL HUMAN ILLNESS. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:245–253. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikasingh E. S., Spence L., Downs W. G. The use of adjuvant and sarcoma 180 cells in the production of mouse hyperimmune ascitic fluids to arboviruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):219–226. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


