Abstract
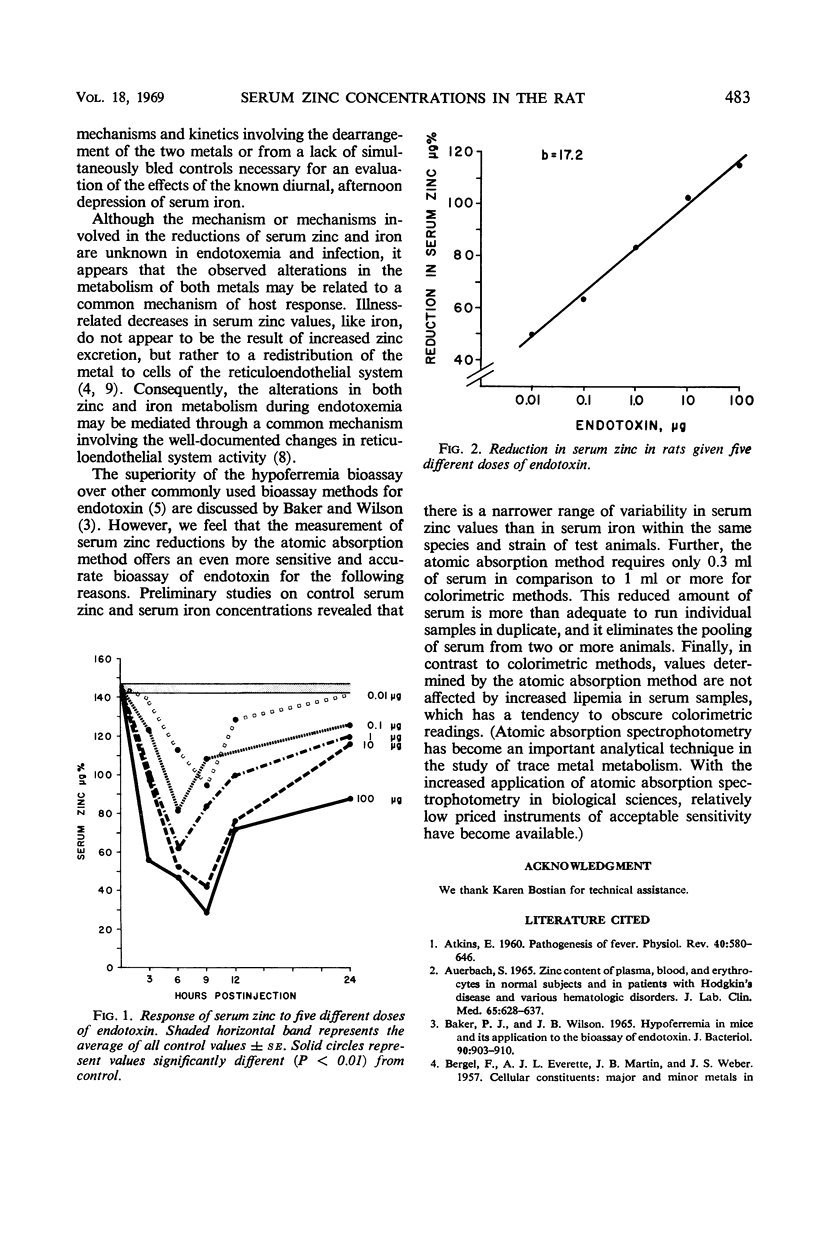
Serum zinc concentrations decreased significantly in a dose-dependent response after endotoxin administration in the rat. The reproducibility and sensitivity of the biological response offer a potential bioassay of endotoxin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E. Pathogenesis of fever. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:580–646. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUERBACH S. ZINC CONTENT OF PLASMA, BLOOD, AND ERYTHROCYTES IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH HODGKIN'S DISEASE AND VARIOUS HEMATOLOGIC DISORDERS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Apr;65:628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F., SCHULTZ G. A. Hypoferremia in rats following injection of bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Apr;106:870–871. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F., UPCHURCH H. F. Effects of bacteria endotoxin on plasma iron. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 May;110:191–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIKBLADH I. Studies on zinc in blood II. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3 (Suppl 2):1–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


