Abstract
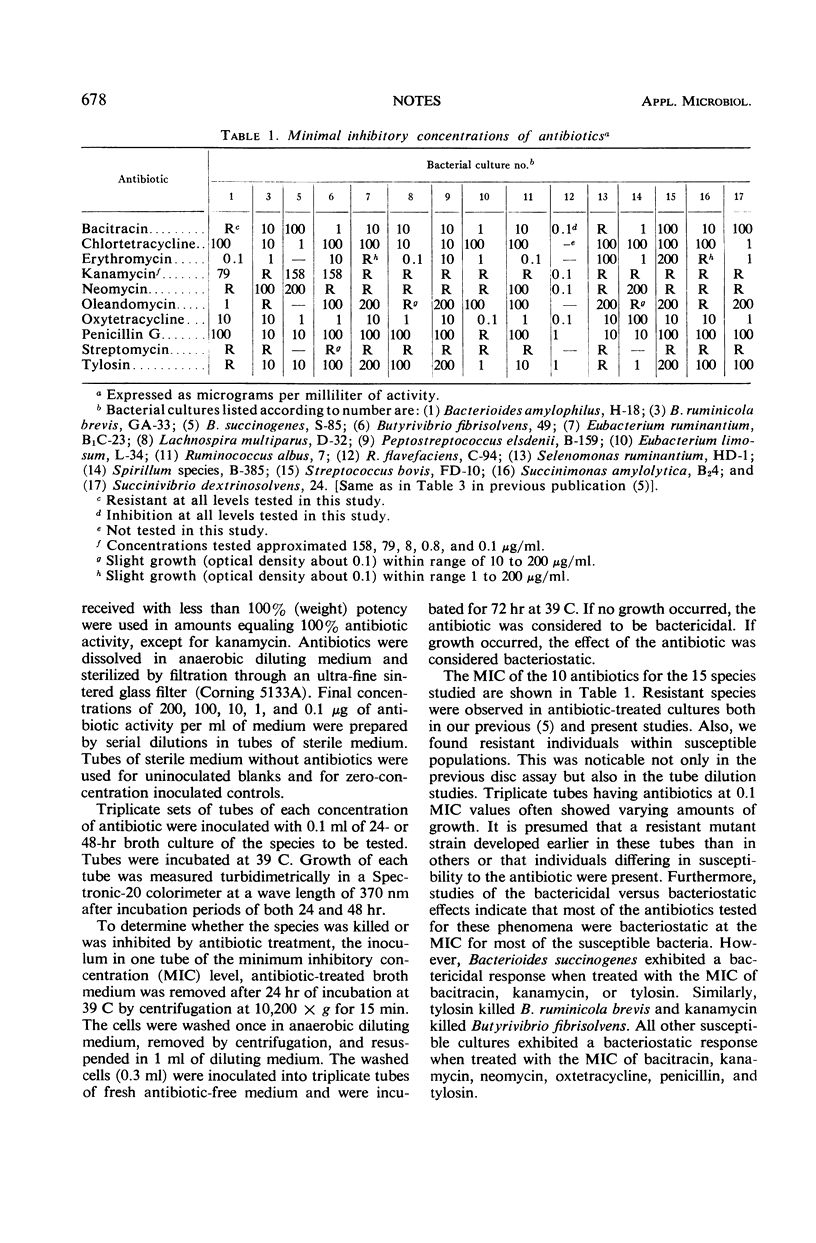
Fifteen species of ruminal bacteria were tested against 10 antibiotics in concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 200 μg/ml in an anaerobic tube dilution system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Infections due to anaerobes. Med Times. 1968 Feb;96(2):174–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Intestinal bacteria. The role they play in normal physiology, pathologic physiology, and infection. Calif Med. 1969 Jun;110(6):455–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulghum R. S., Baldwin B. B., Williams P. P. Antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic ruminal bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):301–307. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.301-307.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Anaerobic bacteria of the gastrointestinal flora and their occurrence in clinical infections. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):641–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Akkad I., Hobson P. N. Effect of antibiotics on some rumen and intestinal bacteria. Nature. 1966 Mar 5;209(5027):1046–1047. doi: 10.1038/2091046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


