Abstract
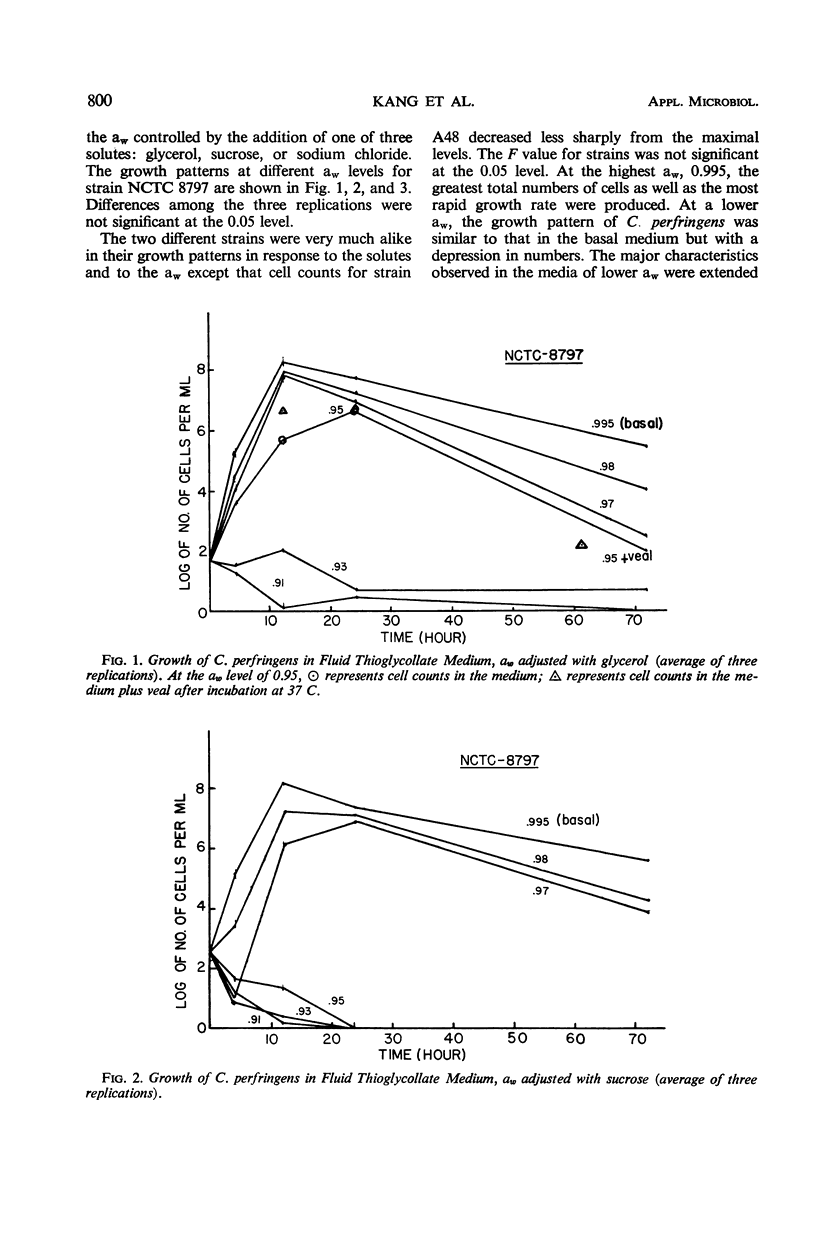
Requirements in terms of water activity (aw) for the growth, sporulation, and germination of Clostridium perfringens were determined. Strain A48 was used in all phases, and in addition either NCTC 8239 or NCTC 8797 was used for growth, sporulation, and germination studies. The desired aw of the test media was obtained by the addition of one of three solutes: glycerol, sucrose, or sodium chloride. The freezing point depression method was used to determine the aw. The basal medium for growth and germination was Fluid Thioglycollate Medium. It had an aw of 0.995 and produced maximum growth and fastest growth rate among the six levels of aw tested. The lowest aw supporting growth and germination of C. perfringens was between 0.97 and 0.95 in the test media made with sucrose or sodium chloride and 0.93 or below in the test media adjusted with glycerol. Spore production by C. perfringens in Ellner's or modified medium required a higher aw than growth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGELOTTI R., HALL H. E., FOTER M. J., LEWIS K. H. Quantitation of Clostridium perfringens in foods. Appl Microbiol. 1962 May;10:193–199. doi: 10.1128/am.10.3.193-199.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Parker A. C., Freame B. Combined effect of water activity, pH and temperature on the growth of Clostridium botulinum from spore and vegetative cell inocula. J Appl Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;30(3):420–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1967.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. THE COMPOSITION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN RELATION TO THE WATER ACTIVITY OF THE GROWTH MEDIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:205–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLNER P. D. A medium promoting rapid quantitative sporulation in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):495–496. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.495-496.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Cheney R., Woodburn M. Sporulation of Clostridium perfringens in a modified medium and selected foods. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):871–876. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.871-876.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifson E. Bacterial Spores. J Bacteriol. 1931 May;21(5):331–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.21.5.331-356.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss K. F., Strong D. H. Effect of suspending medium on heat resistance of spores of Clostridium perfringens. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):530–531. doi: 10.1038/215530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZOHA S. M., SADOFF H. L. Production of spores by a putrefactive anaerobe. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):203–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.203-206.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


