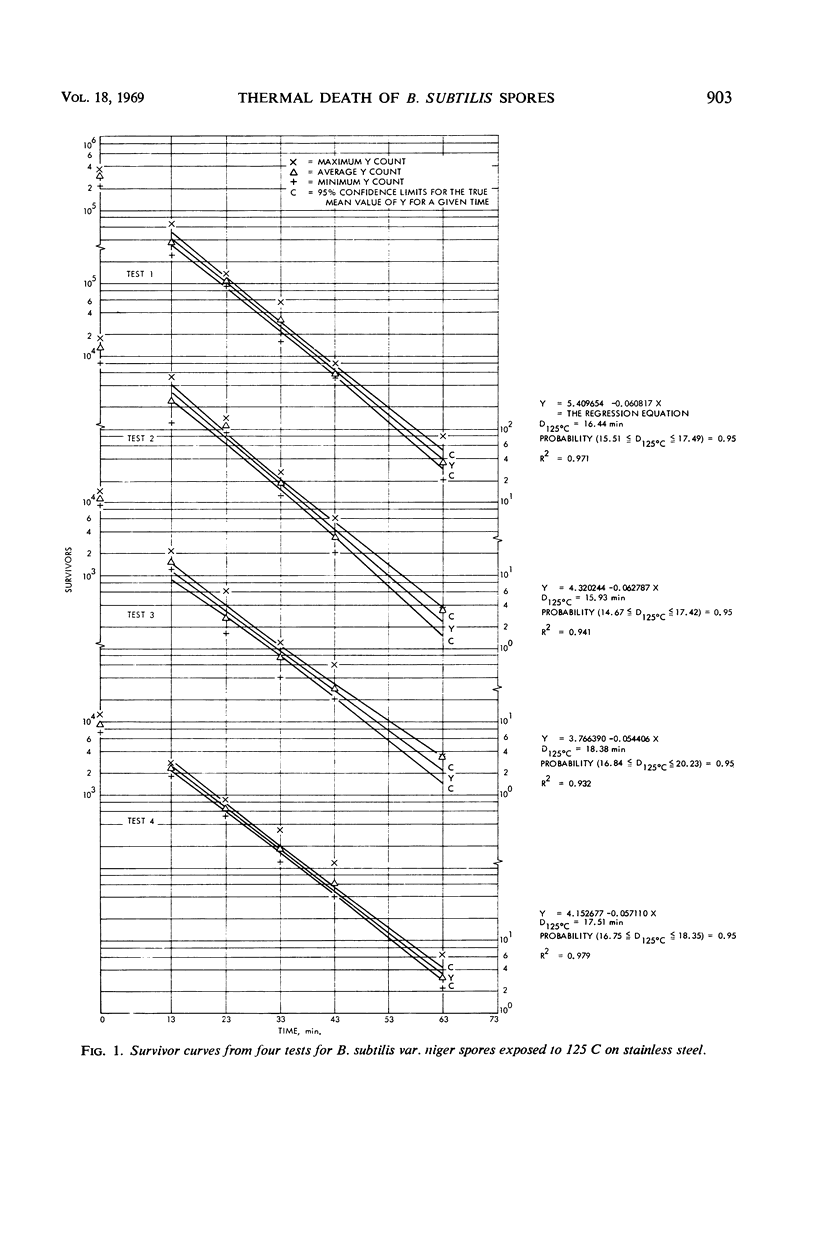
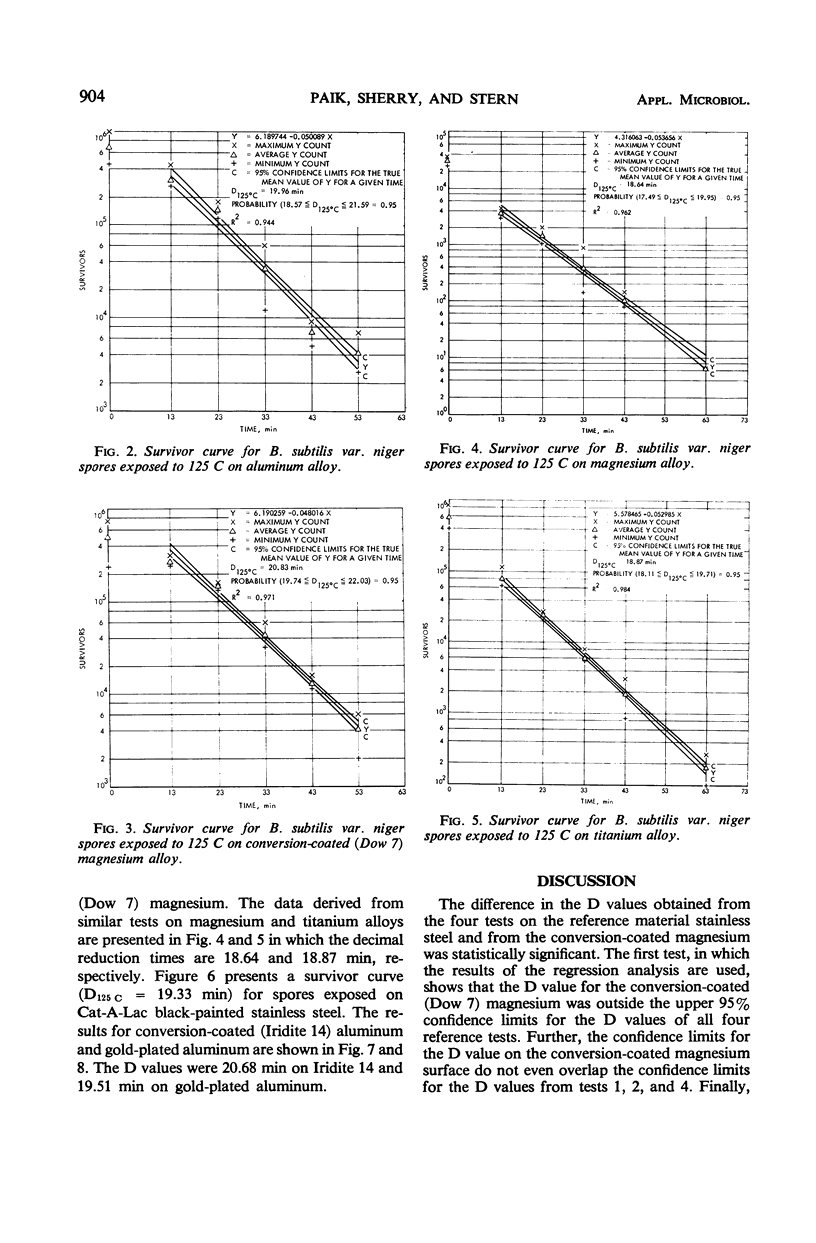
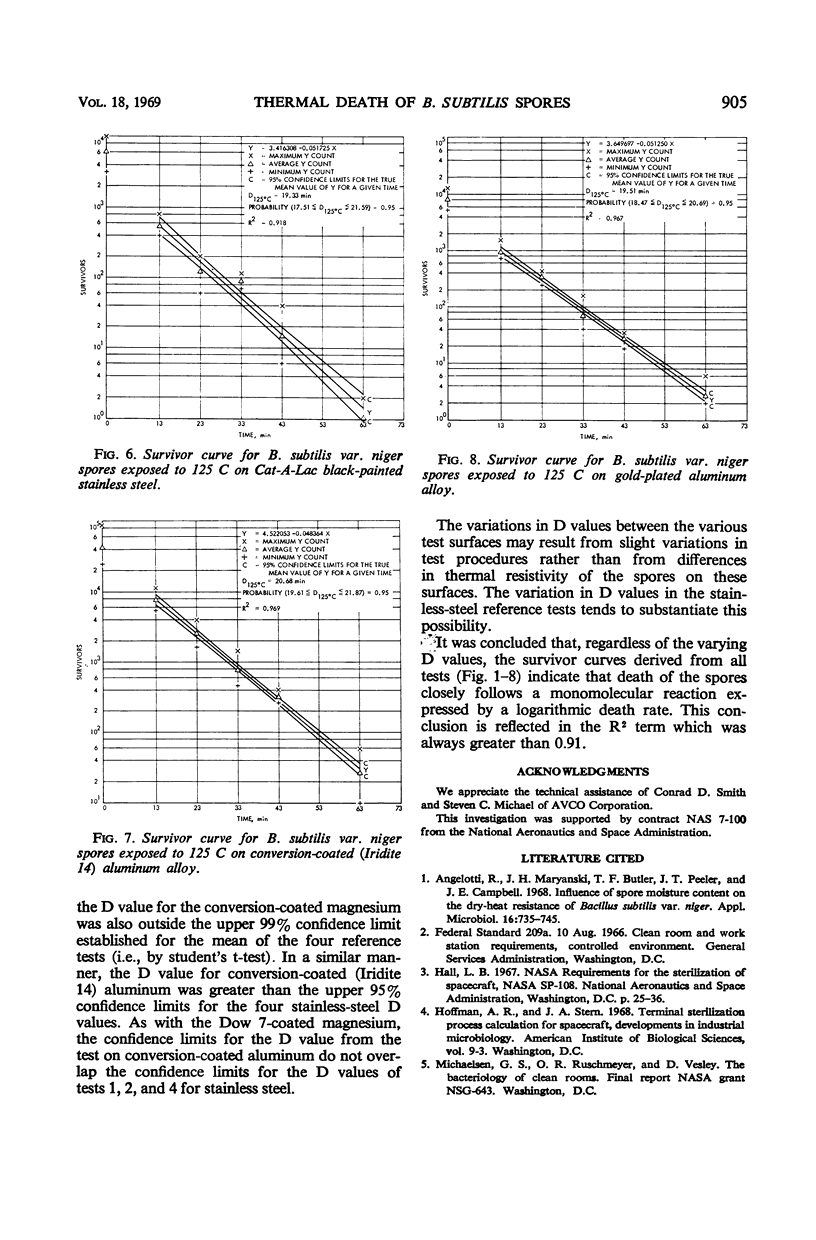
Abstract
Dry-heat sterilization of planetary lander capsules requires a knowledge of the thermal resistivity of microorganisms in the environment to which they will be subjected during sterilization of the space hardware. The dry-heat resistance of Bacillus subtilis var. niger spores on various lander capsule materials was determined at 125 C. Eight surface materials were evaluated, including a reference material, stainless steel. Survivor curves were computed, and decimal reduction times (D values) were obtained by a linear regression analysis. In four tests on stainless steel, the average value of D at 125 C was 17.07 min. The D values for the other seven materials tested ranged from 18.64 min on magnesium surfaces to 20.83 min on conversion-coated magnesium. Of the materials evaluated, the results indicate that there is only a significant difference in the thermal resistance of B. subtilis var. niger spores on conversion-coated magnesium and conversion-coated aluminum from that on the reference material, stainless steel. The differences in D values for all the test surfaces may be the result of variations in test procedures rather than the effect of the surfaces on the thermal resistivity of the spores.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelotti R., Maryanski J. H., Butler T. F., Peeler J. T., Campbell J. E. Influence of spore moisture content on the dry-heat resistance of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Appl Microbiol. 1968 May;16(5):735–745. doi: 10.1128/am.16.5.735-745.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


