Abstract
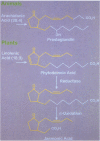
The activation of plant defensive genes in leaves of tomato plants in response to herbivore damage or mechanical wounding is mediated by a mobile 18-amino acid polypeptide signal called systemin. Systemin is derived from a larger, 200-amino acid precursor called prosystemin, similar to polypeptide hormones and soluble growth factors in animals. Systemin activates a lipid-based signaling cascade, also analogous to signaling systems found in animals. In plants, linolenic acid is released from membranes and is converted to the oxylipins phytodienoic acid and jasmonic acid through the octadecanoid pathway. Plant oxylipins are structural analogs of animal prostaglandins which are derived from arachidonic acid in response to various signals, including polypeptide factors. Constitutive overexpression of the prosystemin gene in transgenic tomato plants resulted in the overproduction of prosystemin and the abnormal release of systemin, conferring a constitutive overproduction of several systemic wound-response proteins (SWRPs). The data indicate that systemin is a master signal for defense against attacking herbivores. The same defensive proteins induced by wounding are synthesized in response to oligosaccharide elicitors that are generated in leaf cells in response to pathogen attacks. Inhibitors of the octadecanoid pathway, and a mutation that interrupts this pathway, block the induction of SWRPs by wounding, systemin, and oligosaccharide elicitors, indicating that the octadecanoid pathway is essential for the activation of defense genes by all of these signals. The tomato mutant line that is functionally deficient in the octadecanoid pathway is highly susceptible to attacks by Manduca sexta larvae. The similarities between the defense signaling pathway in tomato leaves and those of the defense signaling pathways of macrophages and mast cells of animals suggests that both the plant and animal pathways may have evolved from a common ancestral origin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop P. D., Makus D. J., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor activity in tomato leaves resides in oligosaccharides enzymically released from cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolter C. J. Methyl Jasmonate Induces Papain Inhibitor(s) in Tomato Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1993 Dec;103(4):1347–1353. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasseaud L. F., Hawkins D. R., Cameron B. D., Fry B. J., Saggers V. H. The metabolic fate of bentazon in the rat. Xenobiotica. 1972 May;2(3):269–276. doi: 10.3109/00498257209111057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constabel C. P., Bergey D. R., Ryan C. A. Systemin activates synthesis of wound-inducible tomato leaf polyphenol oxidase via the octadecanoid defense signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doares S. H., Narvaez-Vasquez J., Conconi A., Ryan C. A. Salicylic Acid Inhibits Synthesis of Proteinase Inhibitors in Tomato Leaves Induced by Systemin and Jasmonic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1995 Aug;108(4):1741–1746. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.4.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echtenacher B., Männel D. N., Hültner L. Critical protective role of mast cells in a model of acute septic peritonitis. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):75–77. doi: 10.1038/381075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7713–7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Octadecanoid Precursors of Jasmonic Acid Activate the Synthesis of Wound-Inducible Proteinase Inhibitors. Plant Cell. 1992 Feb;4(2):129–134. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Ryan C. A. Wound-Induced Proteinase Inhibitor in Plant Leaves: A Possible Defense Mechanism against Insects. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):776–777. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach H., Müller M. J., Kutchan T. M., Zenk M. H. Jasmonic acid is a signal transducer in elicitor-induced plant cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2389–2393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N., Taylor J. E., Roberts J. A. Isolation of a mRNA encoding a nucleoside diphosphate kinase from tomato that is up-regulated by wounding. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jul;25(4):739–742. doi: 10.1007/BF00029611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildmann T., Ebneth M., Peña-Cortés H., Sánchez-Serrano J. J., Willmitzer L., Prat S. General roles of abscisic and jasmonic acids in gene activation as a result of mechanical wounding. Plant Cell. 1992 Sep;4(9):1157–1170. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.9.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner J., Pearce G., Ryan C. A., Browse J. Isolation of signaling mutants of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Dec;241(5-6):595–601. doi: 10.1007/BF00279902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaviya R., Ikeda T., Ross E., Abraham S. N. Mast cell modulation of neutrophil influx and bacterial clearance at sites of infection through TNF-alpha. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):77–80. doi: 10.1038/381077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Pandiella A. Membrane-anchored growth factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:515–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
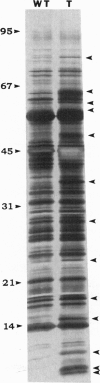
- McGurl B., Orozco-Cardenas M., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. Overexpression of the prosystemin gene in transgenic tomato plants generates a systemic signal that constitutively induces proteinase inhibitor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9799–9802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGurl B., Pearce G., Orozco-Cardenas M., Ryan C. A. Structure, expression, and antisense inhibition of the systemin precursor gene. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.1549783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco-Cardenas M., McGurl B., Ryan C. A. Expression of an antisense prosystemin gene in tomato plants reduces resistance toward Manduca sexta larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8273–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pautot V., Holzer F. M., Reisch B., Walling L. L. Leucine aminopeptidase: an inducible component of the defense response in Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9906–9910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce G., Johnson S., Ryan C. A. Structure-activity of deleted and substituted systemin, an 18-amino acid polypeptide inducer of plant defensive genes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce G., Strydom D., Johnson S., Ryan C. A. A polypeptide from tomato leaves induces wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor proteins. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):895–897. doi: 10.1126/science.253.5022.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Goldyne M., Granström E., Hamberg M., Hammarström S., Malmsten C. Prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:997–1029. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller A., Bergey D. R., Ryan C. A. Induction of wound response genes in tomato leaves by bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidases. Plant Cell. 1995 Nov;7(11):1893–1898. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller A., Ryan C. A. Systemin--a polypeptide defense signal in plants. Bioessays. 1996 Jan;18(1):27–33. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo S., Okamoto M., Seto H., Ishizuka K., Sano H., Ohashi Y. Tobacco MAP kinase: a possible mediator in wound signal transduction pathways. Science. 1995 Dec 22;270(5244):1988–1992. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5244.1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Smeekens S. P., Ohagi S., Chan S. J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23435–23438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Could nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) enhance the progression of bacterial infections to toxic shock syndrome? Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Oct;21(4):977–980. doi: 10.1093/clinids/21.4.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usami S., Banno H., Ito Y., Nishihama R., Machida Y. Cutting activates a 46-kilodalton protein kinase in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8660–8664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick B. A., Zimmerman D. C. Biosynthesis of jasmonic Acid by several plant species. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):458–461. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor synthesis in tomato leaves : induction by chitosan oligomers and chemically modified chitosan and chitin. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):787–790. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]