Abstract
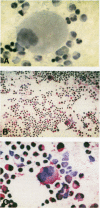
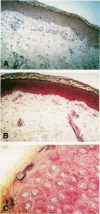
AIM/BACKGROUND: The Mx proteins are known to be specifically and dose dependently induced in mononuclear cells (MNC) by type I interferons (IFN). The aim of this study was to establish a staining method for the human intracellular Mx proteins, MxA and MxB, in leucocytes and bone marrow and skin cells. METHODS: Several monoclonal antibodies directed against the MxA and MxB proteins were generated. These antibodies were used to stain Mx proteins in both frozen and paraffin wax sections using the standard alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) method. RESULTS: Granulocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes extracted from freshly collected blood from 21 healthy subjects did not stain. After incubating MNC from these subjects with IFN alpha 2b for 48 hours, Mx proteins were detected in monocytes and lymphocytes. Within two days of starting treatment with subcutaneous IFN alpha 2b, granulocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes of 16 patients with cancer stained strongly for Mx proteins. The intensity of staining was correlated with the Mx content of whole blood measured using a specific ELISA. Prior to IFN treatment, cells from bone marrow and skin tissue specimens were negative for Mx proteins with the exception of endothelial cells. During treatment with IFN alpha 2b, nearly all cells from bone marrow and skin stained intensely. CONCLUSIONS: These new monoclonal antibodies facilitate the detection of Mx positive cells in peripheral blood and in frozen or paraffin wax specimens. The advantage of this staining method is that individual cells which have responded to viruses or biologically active IFN alpha, beta or omega can be identified.
Full text
PDF


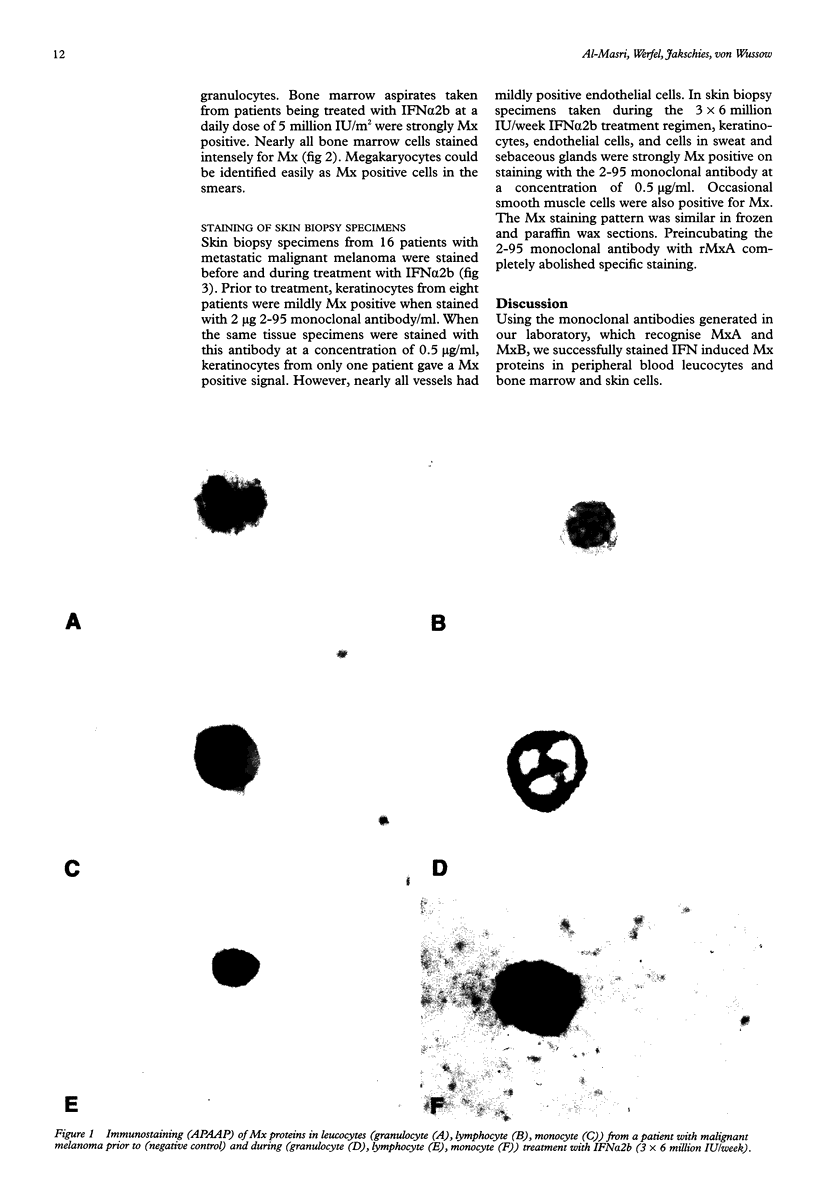
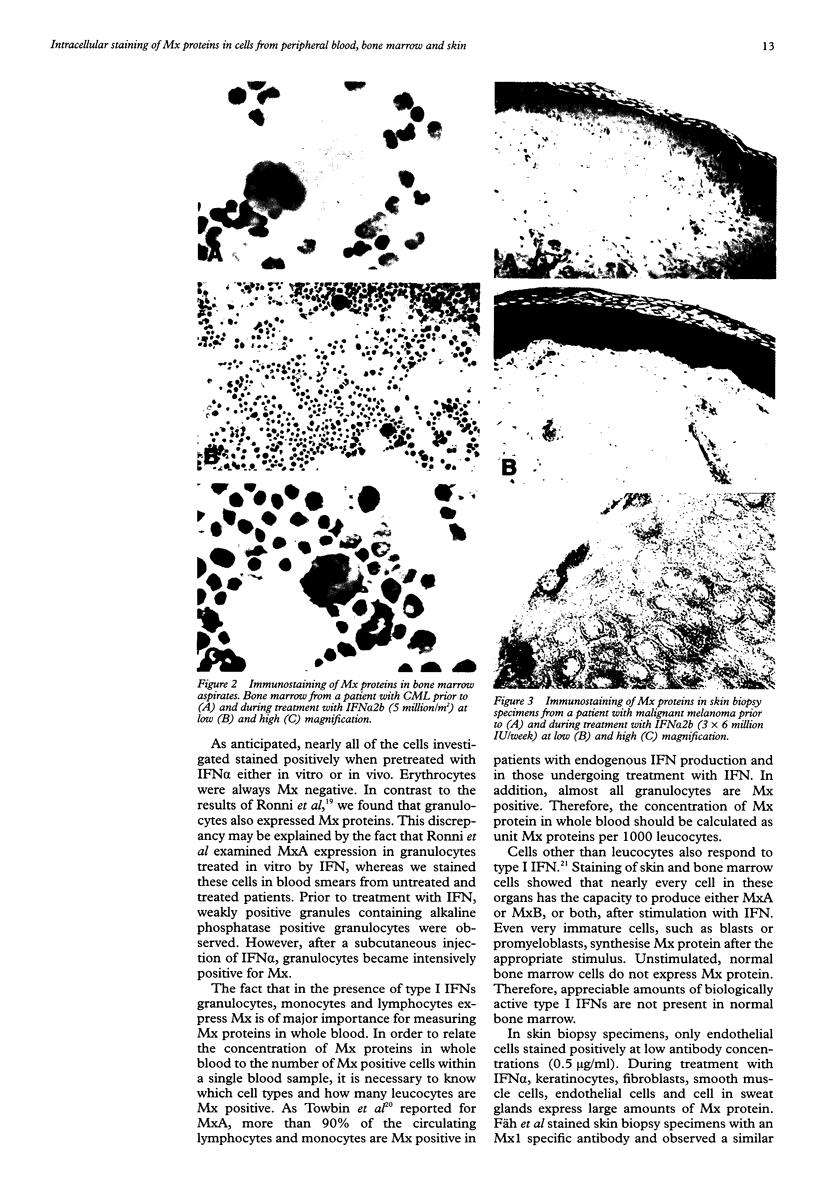

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Fäh J., Hurt N., Samuel C. E., Thomis D., Bazzigher L., Pavlovic J., Haller O., Staeheli P. cDNA structures and regulation of two interferon-induced human Mx proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5062–5072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. W., Gurwith M. J., Waddell D., Merigan T. C. Cutaneous interferon production in patients with Hodgkin's disease and other cancers infected with varicella or vaccinia. N Engl J Med. 1970 Nov 26;283(22):1182–1187. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197011262832202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Gothelf Y., Vaiman D., Chen L., Revel M., Chebath J. Interleukin-6 induces the (2'-5') oligoadenylate synthetase gene in M1 cells through an effect on the interferon-responsive enhancer. Cytokine. 1991 Mar;3(2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödi G., Just M., Hernandez R., Hirt H. R. Circulating interferon in man after administration of exogenous human leukocyte interferon. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 May;54(5):1045–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Goedert J. J., Poon M. C., Preble O. T. Acid-labile alpha interferon. A possible preclinical marker for the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 8;309(10):583–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309083091003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fäh J., Pavlovic J., Burg G. Expression of MxA protein in inflammatory dermatoses. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995 Jan;43(1):47–52. doi: 10.1177/43.1.7822763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gala J. L., McLachlan J. M., Bell D. R., Michaux J. L., Ma D. D. Specificity and sensitivity of immunocytochemistry for detecting P-glycoprotein in haematological malignancies. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Jul;47(7):619–624. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.7.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Jordan G. W., Cupps T., Moutsopoulos H. M., Fauci A. S., Notkins A. L. Multiple interferons in the circulation of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):396–400. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Hendriks W., Althage A., Hemmi S., Bluethmann H., Kamijo R., Vilcek J., Zinkernagel R. M., Aguet M. Immune response in mice that lack the interferon-gamma receptor. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1742–1745. doi: 10.1126/science.8456301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschies D., Hochkeppel H., Horisberger M., Deicher H., von Wussow P. Emergence and decay of the human Mx homolog in cancer patients during and after interferon-alpha therapy. J Biol Response Mod. 1990 Jun;9(3):305–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschies D., Zachoval R., Müller R., Manns M., Nolte K. U., Hochkeppel H. K., Horisberger M. A., Deicher H., Von Wussow P. Strong transient expression of the type I interferon-induced MxA protein in hepatitis A but not in acute hepatitis B and C. Hepatology. 1994 Apr;19(4):857–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Applications of immobilized protein A in immunochemical techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):277–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis S. C., Saavedra M. C., Ceccoli C., Falcoff E., Feuillade M. R., Enria D. A., Maiztegui J. I., Falcoff R. Endogenous interferon in Argentine hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):428–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melén K., Keskinen P., Ronni T., Sareneva T., Lounatmaa K., Julkunen I. Human MxB protein, an interferon-alpha-inducible GTPase, contains a nuclear targeting signal and is localized in the heterochromatin region beneath the nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1996 Sep 20;271(38):23478–23486. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.38.23478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETRALLI J. K., MERIGAN T. C., WILBUR J. R. CIRCULATING INTERFERON AFTER MEASLES VACCINATION. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 22;273:198–201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507222730405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronni T., Melén K., Malygin A., Julkunen I. Control of IFN-inducible MxA gene expression in human cells. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1715–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Streuli M., Gresser I., Gugenheim J., Blanchard B., Guymarho J., Vignaux F., Gigou M. Interferon messenger RNA is produced constitutively in the organs of normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Schmitz A., Jakschies D., Von Wussow P., Horisberger M. A. A whole blood immunoassay for the interferon-inducible human Mx protein. J Interferon Res. 1992 Apr;12(2):67–74. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ytterberg S. R., Schnitzer T. J. Serum interferon levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):401–406. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Block B., Hartmann F., Deicher H. Intralesional interferon-alpha therapy in advanced malignant melanoma. Cancer. 1988 Mar 15;61(6):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880315)61:6<1071::aid-cncr2820610603>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Jakschies D., Hartung K., Deicher H. Presence of interferon and anti-interferon in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 1988;8(5):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00269199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Jakschies D., Hochkeppel H. K., Fibich C., Penner L., Deicher H. The human intracellular Mx-homologous protein is specifically induced by type I interferons. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2015–2019. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]