Abstract
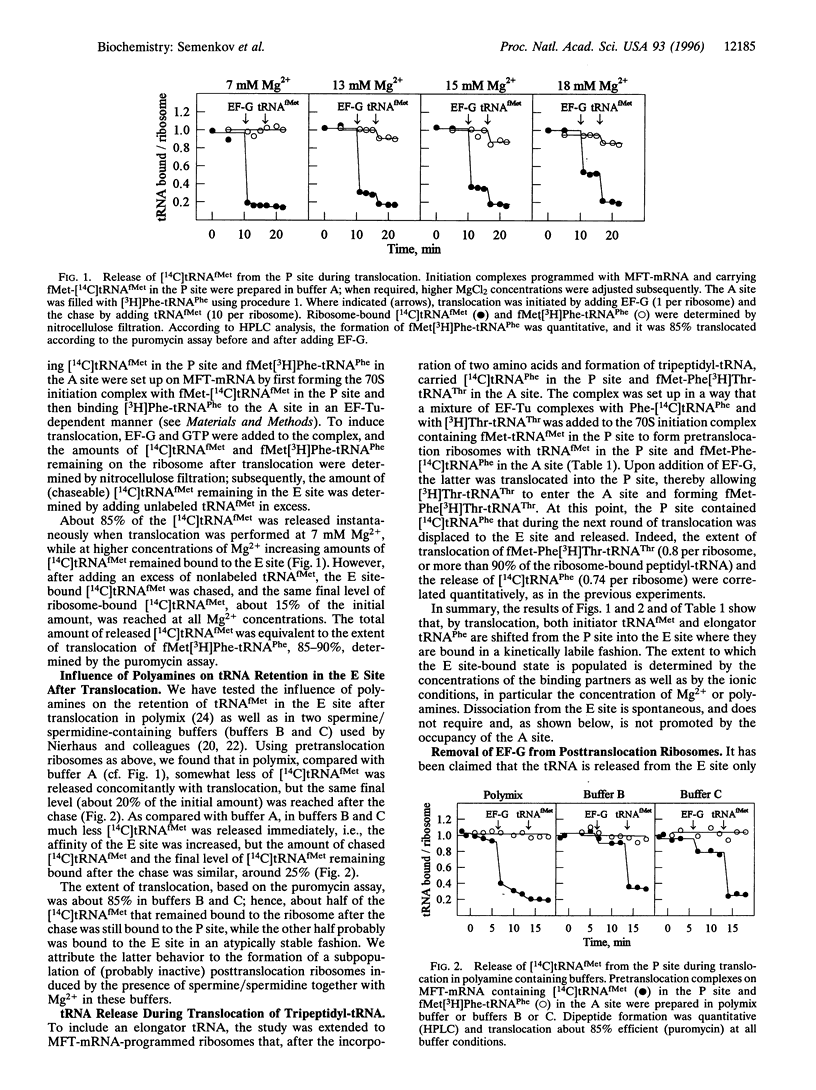
For the functional role of the ribosomal tRNA exit (E) site, two different models have been proposed. It has been suggested that transient E-site binding of the tRNA leaving the peptidyl (P) site promotes elongation factor G (EF-G)-dependent translocation by lowering the energetic barrier of tRNA release [Lill, R., Robertson, J. M. & Wintermeyer, W. (1989) EMBO J. 8, 3933-3938]. The alternative "allosteric three-site model" [Nierhaus, K.H. (1990) Biochemistry 29, 4997-5008] features stable, codon-dependent tRNA binding to the E site and postulates a coupling between E and aminoacyl (A) sites that regulates the tRNA binding affinity of the two sites in an anticooperative manner. Extending our testing of the two conflicting models, we have performed translocation experiments with fully active ribosomes programmed with heteropolymeric mRNA. The results confirm that the deacylated tRNA released from the P site is bound to the E site in a kinetically labile fashion, and that the affinity of binding, i.e., the occupancy of the E site, is increased by Mg2+ or polyamines. At conditions of high E-site occupancy in the posttranslocation complex, filling the A site with aminoacyl-tRNA had no influence on the E site, i.e., there was no detectable anticooperative coupling between the two sites, provided that second-round translocation was avoided by removing EF-G. On the basis of these results, which are entirely consistent with our previous results, we consider the allosteric three-site model of elongation untenable. Rather, as proposed earlier, the E site-bound state of the leaving tRNA is a transient intermediate and, as such, is a mechanistic feature of the classic two-state model of the elongating ribosome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal R. K., Penczek P., Grassucci R. A., Li Y., Leith A., Nierhaus K. H., Frank J. Direct visualization of A-, P-, and E-site transfer RNAs in the Escherichia coli ribosome. Science. 1996 Feb 16;271(5251):1000–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski C., Rodnina M. V., Wintermeyer W. Truncated elongation factor G lacking the G domain promotes translocation of the 3' end but not of the anticodon domain of peptidyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4202–4206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero R. A., Pon C. L., Canonaco M. A., Gualerzi C. O. Selection of the mRNA translation initiation region by Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6427–6431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geigenmüller U., Nierhaus K. H. Significance of the third tRNA binding site, the E site, on E. coli ribosomes for the accuracy of translation: an occupied E site prevents the binding of non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4527–4533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Geigenmüller U., Rheinberger H. J., Nierhaus L. H. The allosteric three-site model for the ribosomal elongation cycle. Analysis with a heteropolymeric mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7291–7301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grajevskaja R. A., Ivanov Y. V., Saminsky E. M. 70-S ribosomes of Escherichia coli have an additional site for deacylated tRNA binding. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Lucas-Lenard J. Stepwise synthesis of a tripeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C., Kurland C. G. Nucleoside triphosphate regeneration decreases the frequency of translation errors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3174–3178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov S. V., Makarov E. M., Semenkov YuP Quantitative study of interaction of deacylated tRNA with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Role of 50 S subunits in formation of the E site. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov S. V., Semenkov YuP Extension of Watson's model for the elongation cycle of protein biosynthesis. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):263–269. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Lepier A., Schwägele F., Sprinzl M., Vogt H., Wintermeyer W. Specific recognition of the 3'-terminal adenosine of tRNAPhe in the exit site of Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Robertson J. M., Wintermeyer W. Affinities of tRNA binding sites of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3245–3255. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Robertson J. M., Wintermeyer W. Binding of the 3' terminus of tRNA to 23S rRNA in the ribosomal exit site actively promotes translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3933–3938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Wintermeyer W. Destabilization of codon-anticodon interaction in the ribosomal exit site. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90516-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):142–148. doi: 10.1038/342142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H. The allosteric three-site model for the ribosomal elongation cycle: features and future. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):4997–5008. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfenov D. V., Saminskii E. M. Dezatsilirovannaia tRNK sviazyvaetsia s 50S subchastitsei ribosom Escherichia coli na spetsial'nom uchastke, ne sovpadaiushchem s uchastkom P'. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1985 Sep-Oct;19(5):1378–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen H., Wintermeyer W. tRNA topography during translocation: steady-state and kinetic fluorescence energy-transfer studies. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2749–2756. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Nierhaus K. H. Adjacent codon-anticodon interactions of both tRNAs present at the ribosomal A and P or P and E sites. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):97–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Nierhaus K. H. Allosteric interactions between the ribosomal transfer RNA-binding sites A and E. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9133–9139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Nierhaus K. H. Testing an alternative model for the ribosomal peptide elongation cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4213–4217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Sternbach H., Nierhaus K. H. Codon-anticodon interaction at the ribosomal E site. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9140–9143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Sternbach H., Nierhaus K. H. Three tRNA binding sites on Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. M., Paulsen H., Wintermeyer W. Pre-steady-state kinetics of ribosomal translocation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. M., Wintermeyer W. Mechanism of ribosomal translocation. tRNA binds transiently to an exit site before leaving the ribosome during translocation. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):525–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., El'skaya A. V., Semenkov YuP, Kirillov S. V. Number of tRNA binding sites on 80 S ribosomes and their subunits. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Fricke R., Wintermeyer W. Transient conformational states of aminoacyl-tRNA during ribosome binding catalyzed by elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12267–12275. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Semenkov Y. P., Wintermeyer W. Purification of fMet-tRNA(fMet) by fast protein liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1994 Jun;219(2):380–381. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Wintermeyer W. GTP consumption of elongation factor Tu during translation of heteropolymeric mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Wintermeyer W. Two tRNA-binding sites in addition to A and P sites on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90834-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. Ribosomal translocation: facts and models. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:75–114. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. Testing the classical two-tRNA-site model for the ribosomal elongation cycle. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 9;165(2):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triana F., Nierhaus K. H., Chakraburtty K. Transfer RNA binding to 80S ribosomes from yeast: evidence for three sites. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Aug;33(5):909–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


