Abstract
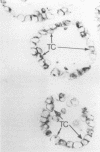
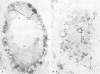
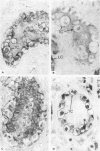
AIM: To study the immunohistochemical localisation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, IGF II, and IGF binding proteins 1-6 in intratubular germ cell neoplasia in the vicinity of solid germ cell tumours of the testis. METHODS: Testes were obtained from 13 patients (20-35 years old) who had undergone orchidectomy for treatment of a solid germ cell tumour. Tumour cells were verified histologically by their distinctive morphology and by visualisation of placental alkaline phosphatase immunoreactivity. RESULTS: The majority of carcinoma in situ (CIS) cells were immunopositive for IGF I, whereas no CIS cells stained for IGF II. Of all the IGF binding proteins investigated, CIS cells showed intense immunoreactivity for IGF binding protein 5 and lower expression of all other IGF binding proteins. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that the action of IGF binding protein 5 in CIS cells may modulate the activity of IGF I. This may be related to a proliferative advantage that could facilitate tumour development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antich M., Fabian E., Sarquella J., Bassas L. Effect of testicular damage induced by cryptorchidism on insulin-like growth factor I receptors in rat Sertoli cells. J Reprod Fertil. 1995 Jul;104(2):267–275. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.1040267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddle C., Li C. H., Schofield P. N., Tate V. E., Hopkins B., Engstrom W., Huskisson N. S., Graham C. F. Insulin-like growth factors and the multiplication of Tera-2, a human teratoma-derived cell line. J Cell Sci. 1988 Jul;90(Pt 3):475–484. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Peehl D. M., Baker B., Liu F., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor axis abnormalities in prostatic stromal cells from patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Nov;79(5):1410–1415. doi: 10.1210/jcem.79.5.7525636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff M., Schulze W. Combination of the peroxidase anti-peroxidase (PAP)- and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC)-techniques: an amplification alternative in immunocytochemical staining. Histochemistry. 1990;93(5):531–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00266413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann K. P., Loy V., Büttner P. Prevalence of bilateral testicular germ cell tumours and early detection based on contralateral testicular intra-epithelial neoplasia. Br J Urol. 1993 Mar;71(3):340–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1993.tb15955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström W., Hopkins B., Schofield P. Expression of growth regulatory genes in primary human testicular neoplasms. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forti G., Vannelli G. B., Barni T., Balboni G. C., Orlando C., Serio M. Sertoli-germ cells interactions in the human testis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Oct;43(5):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman A., Bruun E., Frimodt-Møller C., Skakkebaek N. E. Prevalence of carcinoma in situ and other histopathological abnormalities in testes of men with a history of cryptorchidism. J Urol. 1989 Oct;142(4):998–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38967-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman A., Hopman A. H., Ramaekers F. C., Skakkebaek N. E. Carcinoma in situ of the testis. Detection of malignant germ cells in seminal fluid by means of in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):497–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman A., von der Maase H., Skakkebaek N. E. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of carcinoma in situ of the testis. Eur Urol. 1993;23(1):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granerus M., Bierke P., Zumkeller W., Smith J., Engström W., Schofield P. N. Insulin-like growth factor II prevents apoptosis in a human teratoma derived cell line. Clin Mol Pathol. 1995 Jun;48(3):M153–M157. doi: 10.1136/mp.48.3.m153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granerus M., Schofield P., Bierke P., Engström W. Growth factors and apoptosis in development. The role of insulin like growth factor I and TGFbeta1 in regulating cell growth and cell death in a human teratocarcinoma derived cell line. Int J Dev Biol. 1995 Oct;39(5):759–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granerus M., Schofield P., Bierke P., Engström W. Growth factors and apoptosis in development. The role of insulin like growth factor I and TGFbeta1 in regulating cell growth and cell death in a human teratocarcinoma derived cell line. Int J Dev Biol. 1995 Oct;39(5):759–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M. C., Jeltsch W., Brecher J., Walt H. Alkaline phosphatase isozymes in human testicular germ cell tumors, their precancerous stage, and three related cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4696–4700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein A. F. Cellular components of early testicular cancer. Eur Urol. 1993;23 (Suppl 2):9–18. doi: 10.1159/000474693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein A. F., Schütte B., Becker H., Hartmann M. Morphology of normal and malignant germ cells. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hustin J., Collette J., Franchimont P. Immunohistochemical demonstration of placental alkaline phosphatase in various states of testicular development and in germ cell tumours. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfken K., Lauke H. Mitotic frequency in different early stages of testicular seminoma. Andrologia. 1996 Nov-Dec;28(6):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.1996.tb02811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen G. K., Henriksen O. B., von der Maase H. Carcinoma in situ of testicular tissue adjacent to malignant germ-cell tumors: a study of 105 cases. Cancer. 1981 Jun 1;47(11):2660–2662. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810601)47:11<2660::aid-cncr2820471123>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. I., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995 Feb;16(1):3–34. doi: 10.1210/edrv-16-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. I., Gockerman A., Busby W. H., Jr, Camacho-Hubner C., Clemmons D. R. Extracellular matrix contains insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5: potentiation of the effects of IGF-I. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):679–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanety H., Kattan M., Goldberg I., Kopolovic J., Ravia J., Menczer J., Karasik A. Increased insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) gene expression and protein production lead to high IGFBP-2 content in malignant ovarian cyst fluid. Br J Cancer. 1996 May;73(9):1069–1073. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasik A., Menczer J., Pariente C., Kanety H. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-2 are increased in cyst fluids of epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Feb;78(2):271–276. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.2.7508947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauke H., Seidl K., Hartmann M., Holstein A. F. Carcinoma-in-situ cells in cultured human seminiferous tubules. Int J Androl. 1991 Feb;14(1):33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1991.tb01060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Jones R. C., Blackshaw A. W. The cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) and estimation of its duration. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 Mar;88(2):481–490. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0880481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. Regulation of Leydig cell function by insulin-like growth factor-I and binding proteins. J Androl. 1995 May-Jun;16(3):193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T., Wang D., Nagpal M. L., Chang W. Human chorionic gonadotropin decreases insulin-like growth factor-I gene transcription in rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology. 1994 May;134(5):2142–2149. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.5.8156915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T., Wang D., Nagpal M. L., Shimasaki S., Ling N. Expression and regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1, -2, -3, and -4 messenger ribonucleic acids in purified rat Leydig cells and their biological effects. Endocrinology. 1993 May;132(5):1898–1904. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.5.7682935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loy V., Dieckmann K. P. Carcinoma in situ of the testis: intratubular germ cell neoplasia or testicular intraepithelial neoplasia? Hum Pathol. 1990 Apr;21(4):457–458. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90210-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajpert-De Meyts E., Skakkebaek N. E. The possible role of sex hormones in the development of testicular cancer. Eur Urol. 1993;23(1):54–61. doi: 10.1159/000474570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzén E. M. Chemical messengers between Sertoli cells and neighbouring cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1B):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigg C., Hedinger C. Atypical germ cells of the testis. Comparative ultrastructural and immunohistochemical investigations. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1984;402(4):439–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00734640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skakkebaek N. E., Berthelsen J. G., Giwercman A., Müller J. Carcinoma-in-situ of the testis: possible origin from gonocytes and precursor of all types of germ cell tumours except spermatocytoma. Int J Androl. 1987 Feb;10(1):19–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1987.tb00161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skakkebaek N. E. Possible carcinoma-in-situ of the testis. Lancet. 1972 Sep 9;2(7776):516–517. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91909-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli M., Avallet O., Vigier M., Saez J. M. Opposite vectorial secretion of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding proteins by pig Sertoli cells cultured in the bicameral chamber system. Endocrinology. 1992 Aug;131(2):985–987. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.2.1379171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant M. K., Thrasher J. B., Twomey P. A., Birnbaum R. S., Plymate S. R. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 and -3 expression in benign human prostate epithelium, prostate intraepithelial neoplasia, and adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Jan;81(1):411–420. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.1.8550786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos A., Oosterhuis J. W., de Jong B., Buist J., Schraffordt Koops H. Cytogenetics of carcinoma in situ of the testis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1990 May;46(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(90)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Bondy C. Anatomy of the insulin-like growth factor system in the human testis. Fertil Steril. 1993 Nov;60(5):897–904. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)56294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumkeller W., Schwander J., Mitchell C. D., Morrell D. J., Schofield P. N., Preece M. A. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, -II and IGF binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) in the plasma of children with Wilms' tumour. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(14):1973–1977. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(93)90455-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Záborszky L., Léránth C. Simultaneous ultrastructural demonstration of retrogradely transported horseradish peroxidase and choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity. Histochemistry. 1985;82(6):529–537. doi: 10.1007/BF00489974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaff W. E., Oosterhuis J. W., de Jong B., Dam A., van Putten W. L., Castedo S. M., Sleijfer D. T., Schraffordt Koops H. Ploidy of testicular carcinoma in situ. Lab Invest. 1992 Feb;66(2):166–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]