Abstract
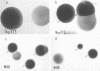
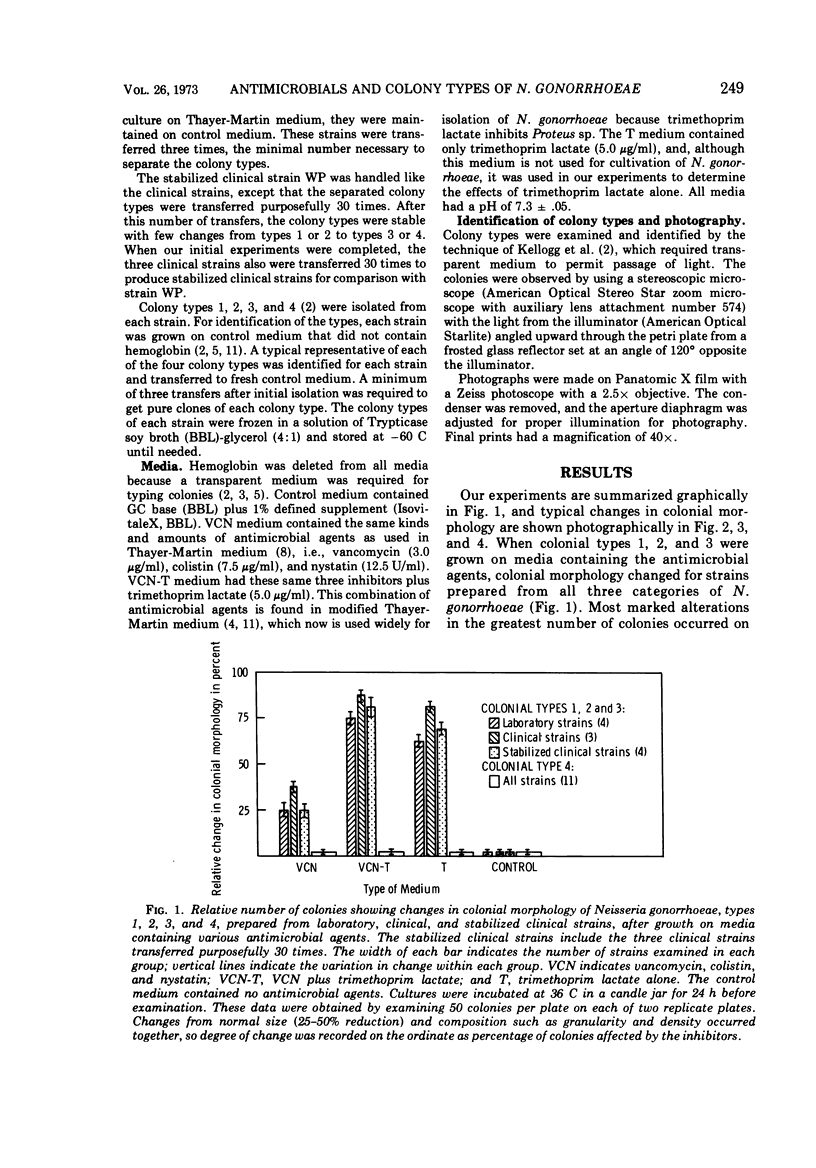
Stable colonial types 1, 2, 3, and 4 were prepared from eight strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Four of the strains, termed laboratory strains, had been transferred over 100 times; three strains, termed clinical strains, were transferred only three to five times after isolation from patients, and one stabilized clinical strain was transferred purposefully 30 times after isolation from a patient. Colonial types of the three categories were grown on four media containing the following agents at the level used in diagnostic media: (i) vancomycin, colistin, and nystatin; (ii) these antibiotics plus trimethoprim lactate; (iii) trimethoprim lactate alone; and (iv) a control with no antimicrobial agents. When grown on media containing the antimicrobial agents, colonial types 1, 2, and 3 of all strains showed specific and consistent changes that precluded accurate identification of the types. In general, the colonies were smaller, more dense to transmission of light, and more granular than colonies grown on control medium. More colonies showed these type changes in the clinical strains and on media containing trimethoprim lactate. Colonies of type 4 showed little or no change. The changes in colonial morphology of types 1, 2, and 3 were pronounced enough to make colony typing difficult if the antimicrobial agents, particularly trimethoprim lactate, were present in media.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchik M. T., Kraus S. J. Neisseria gonorrhoeae: colonial morphology of rectal isolates. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):986–989. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.986-989.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Jr, Lester A. Transgrow, a medium for transport and growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. HSMHA Health Rep. 1971 Jan;86(1):30–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pariser D. M., Pittard W. B., 3rd Primary isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae on hemoglobin-free Thayer-Martin medium. Public Health Rep. 1970 Jun;85(6):532–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. II. Freeze-fracture, freeze-etch studies on gonocci. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1258–1271. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Glynn A. A. Gonococci in urethral exudates possess a virulence factor lost on subculture. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):382–384. doi: 10.1038/227382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. J., Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Maintenance of virulent gonococci in laboratory culture. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 12;236(67):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio236186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]