Abstract
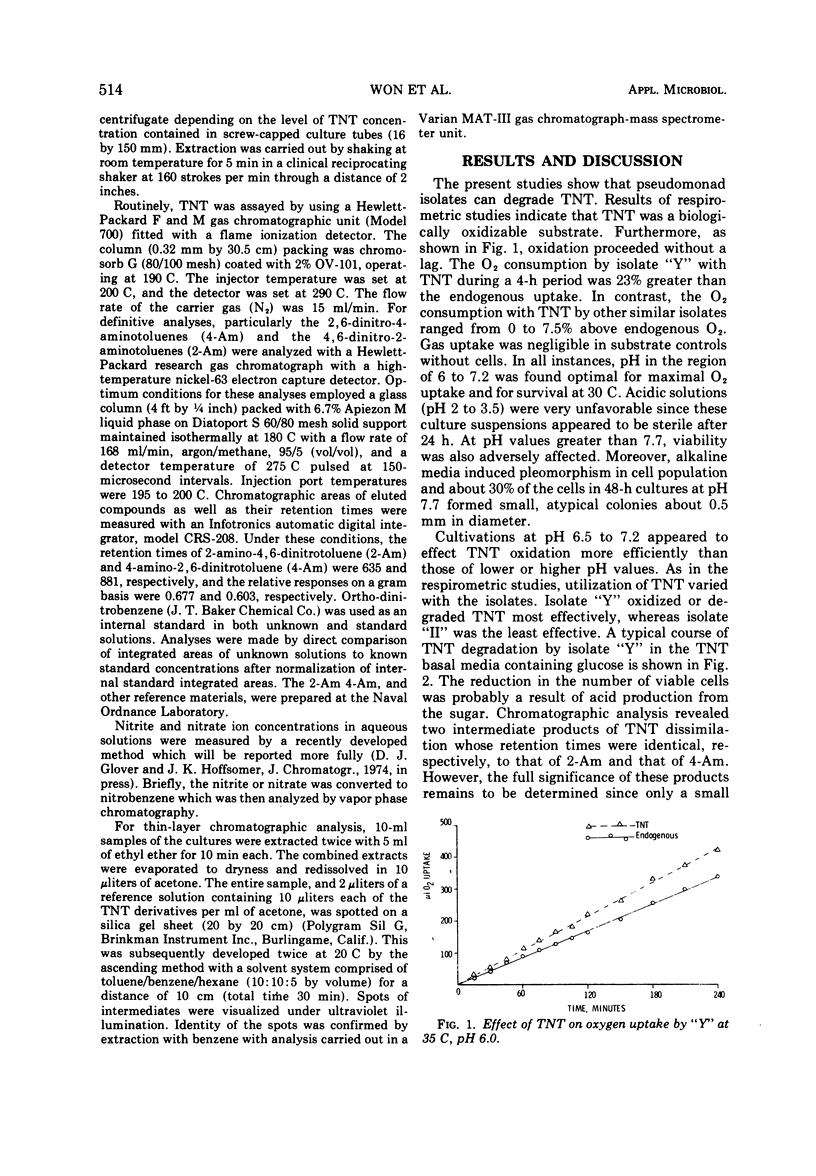
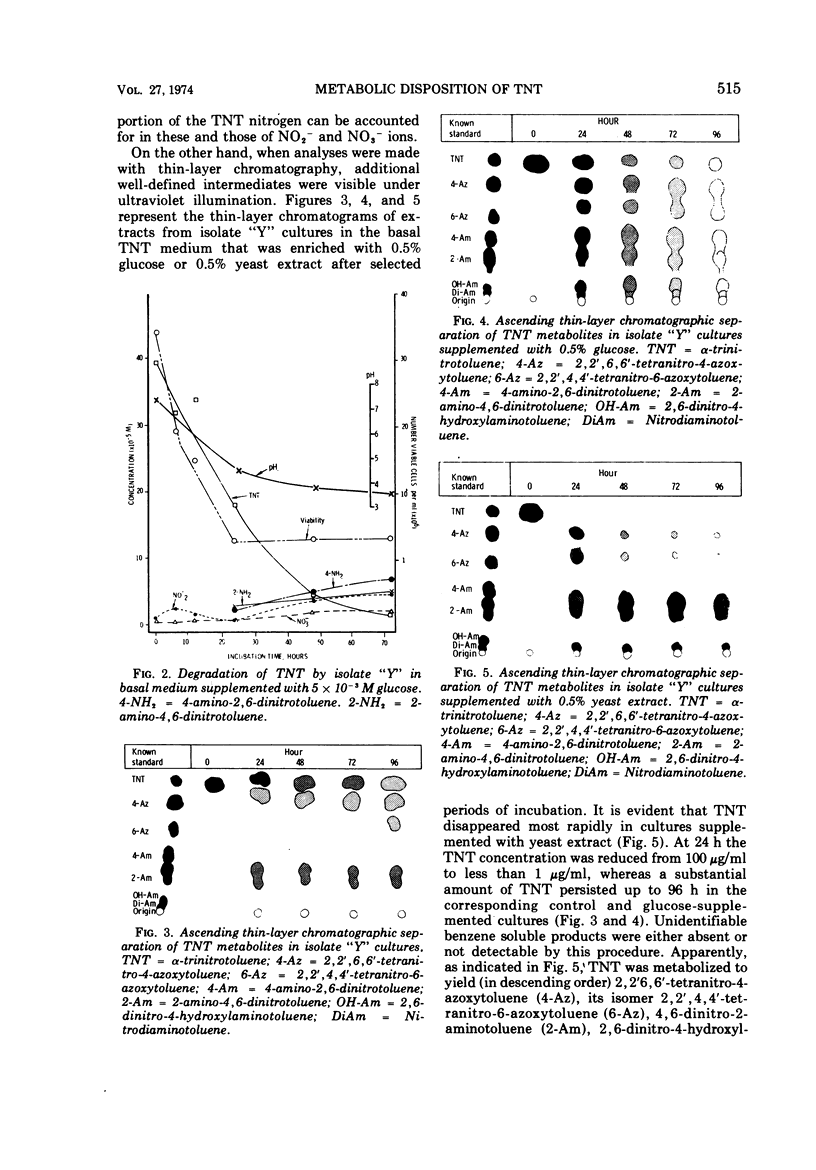
Three pseudomonas-like organisms have been shown to metabolically oxidize 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT). Capability for this oxidative dissimilation varied with each organism. Of the three, isolate „Y” was the most proficient, isolate „I” was less, and isolate „II” was the least. For accelerated TNT degradation, addition of glucose or a nitrogenous substance was essential. Complete dissimilation within 24 h by isolate „Y” cultures supplemented with 0.5% yeast extract is presumed since no TNT was detectable.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Channon H. J., Mills G. T., Williams R. T. The metabolism of 2:4:6-trinitrotoluene (alpha-T.N.T.). Biochem J. 1944;38(1):70–85. doi: 10.1042/bj0380070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





