Abstract
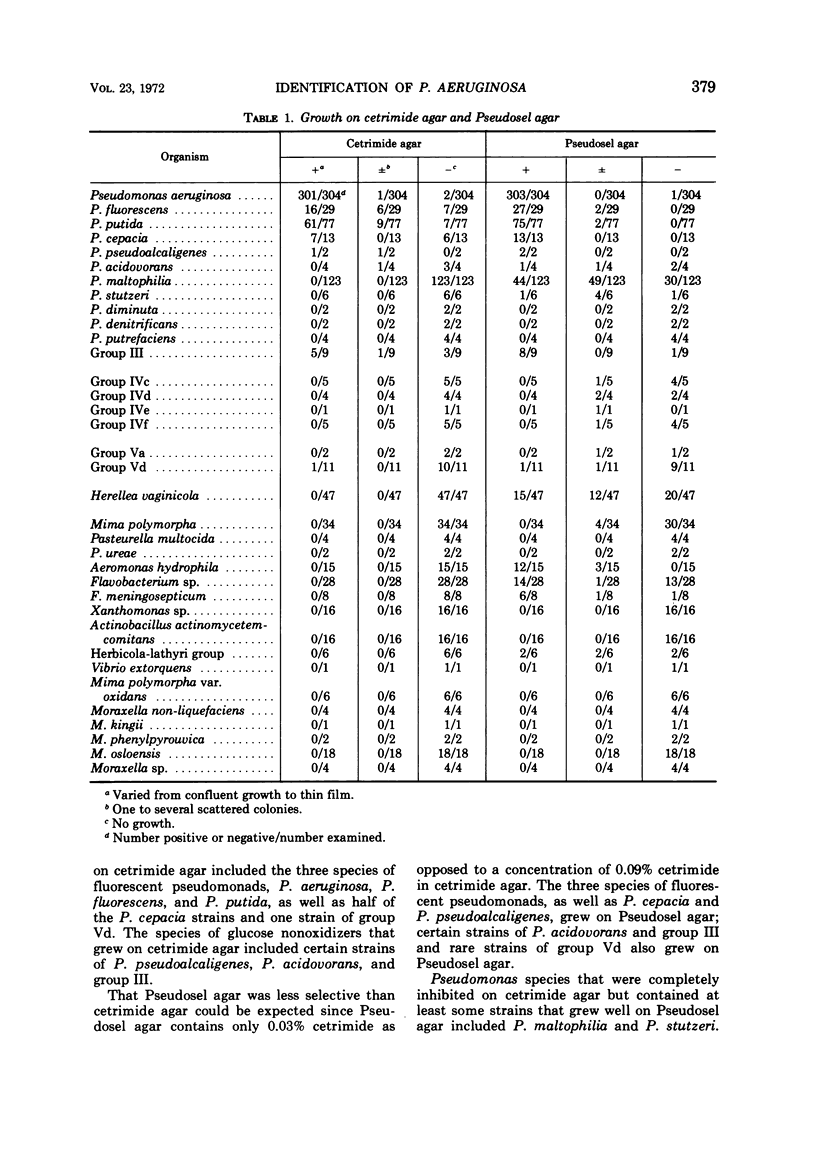
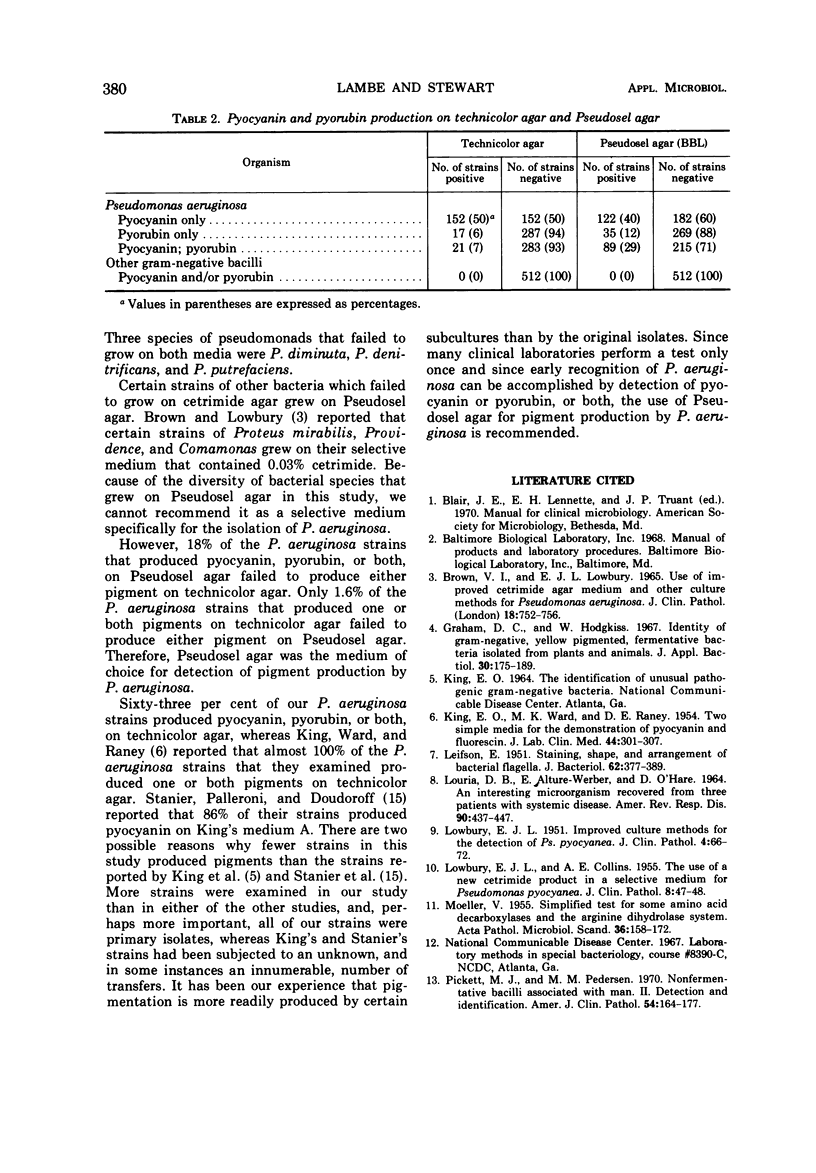
Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and thirty-five other species of gramnegative bacilli was observed on 0.03% cetrimide in heart infusion agar medium and Pseudosel agar (BBL). The 0.03% cetrimide agar was more selective for growth of P. aeruginosa than was Pseudosel agar; however, certain bacteria other than P. aeruginosa also grew on the former medium. Although Pseudosel agar was not a highly selective medium for P. aeruginosa, it was preferable to technicolor agar for detection of the pyocyanin and pyorubin pigments produced by P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown V. I., Lowbury E. J. Use of an improved cetrimide agar medium and other culture methods for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;18(6):752–756. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.6.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. C., Hodgkiss W. Identity of gram negative, yellow pigmented, fermentative bacteria isolated from plants and animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;30(1):175–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1967.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. Staining, shape and arrangement of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.377-389.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., ALTURE WERBER E., O'HARE D. AN INTERESTING MICROORGANISM RECOVERED FROM THREE PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC DISEASE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Sep;90:437–447. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., COLLINS A. G. The use of a new cetrimide product in a selective medium for Pseudomonas pyocyanea. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Feb;8(1):47–48. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J. Improved Culture Methods for the Detection of Ps. pyocyanea. J Clin Pathol. 1951 Feb;4(1):66–72. doi: 10.1136/jcp.4.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MØLLER V. Simplified tests for some amino acid decarboxylases and for the arginine dihydrolase system. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(2):158–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1955.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M. J., Pedersen M. M. Nonfermentative bacilli associated with man. II. Detection and identification. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Aug;54(2):164–177. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. Cultural and biochemical characteristics of the genus Chromobacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):70–98. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKS P. K., MCCLESKEY C. S. IDENTITY OF THE PINK-PIGMENTED METHANOL-OXIDIZING BACTERIA AS VIBRIO EXTORQUENS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1065–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1065-1070.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Simon G. Potentially pathogenic, nonfermentative, H2S-producing gram-negative rod (1 b). Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):176–176. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.176-176.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


