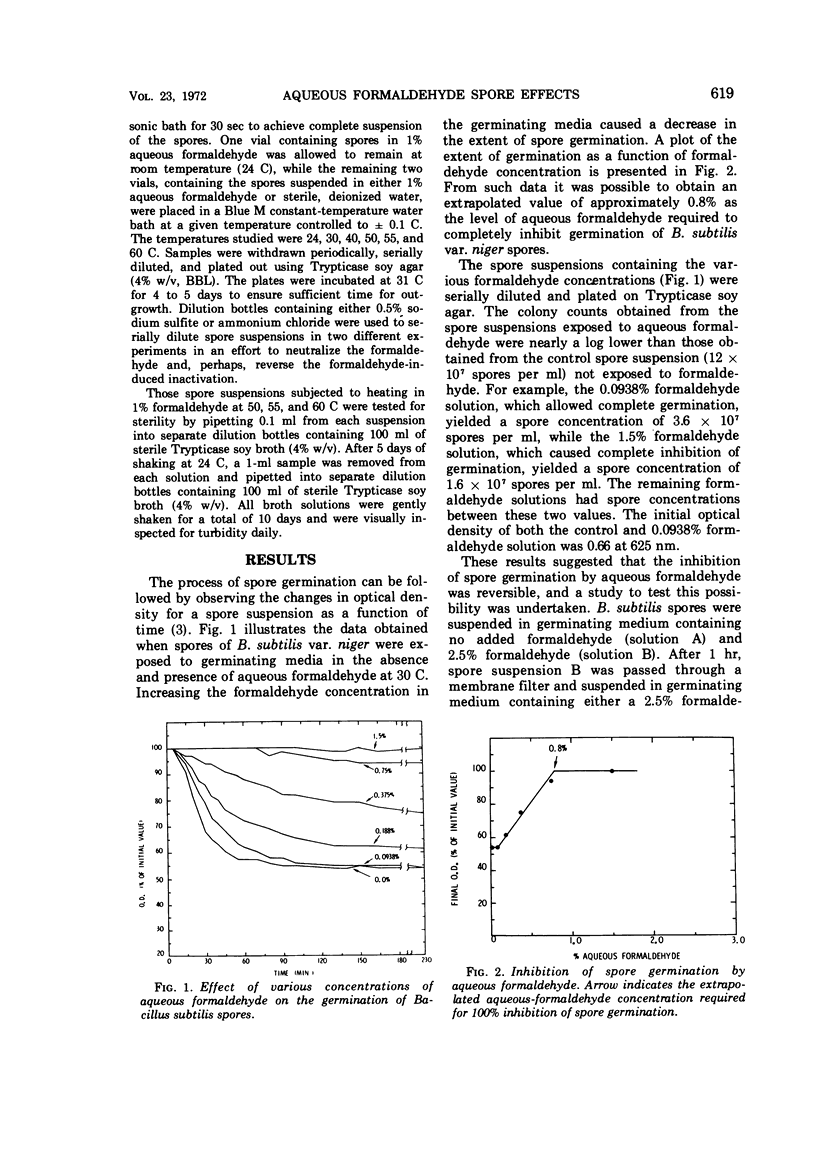
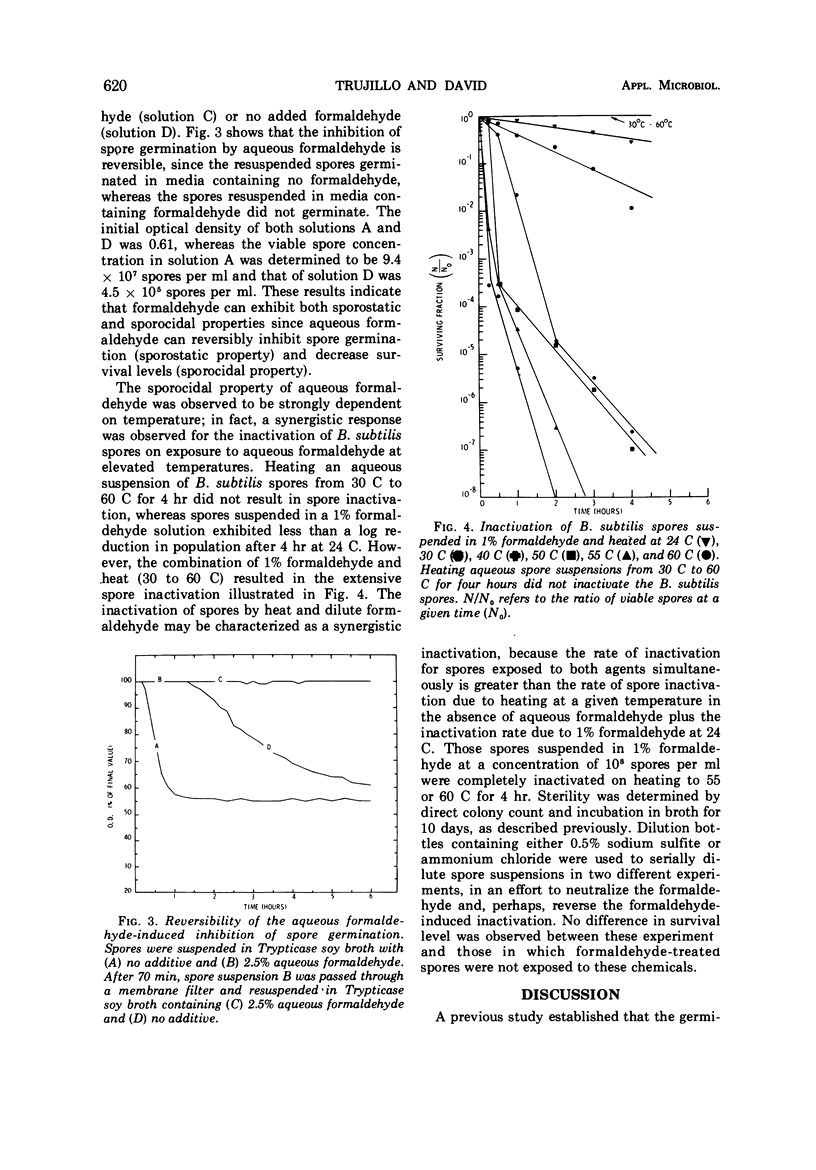
Abstract
Aqueous formaldehyde is shown to exert both sporostatic and sporocidal effects on Bacillus subtilis spores. The sporostatic effect is a result of the reversible inhibition of spore germination occasioned by aqueous formaldehyde; the sporocidal effect is due to temperature-dependent inactivation of these spores in aqueous formaldehyde. The physicochemical state of formaldehyde in solution provides a framework with which to interpret both the sporostatic and sporocidal properties of aqueous formaldehyde.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Tilley F. W. The Influence of Changes in Concentration and Temperature upon the Bactericidal Activity of Formaldehyde in Aqueous Solutions. J Bacteriol. 1945 Oct;50(4):469–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo R., Laible N. Reversible inhibition of spore germination by alcohols. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):620–623. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.620-623.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


