Abstract
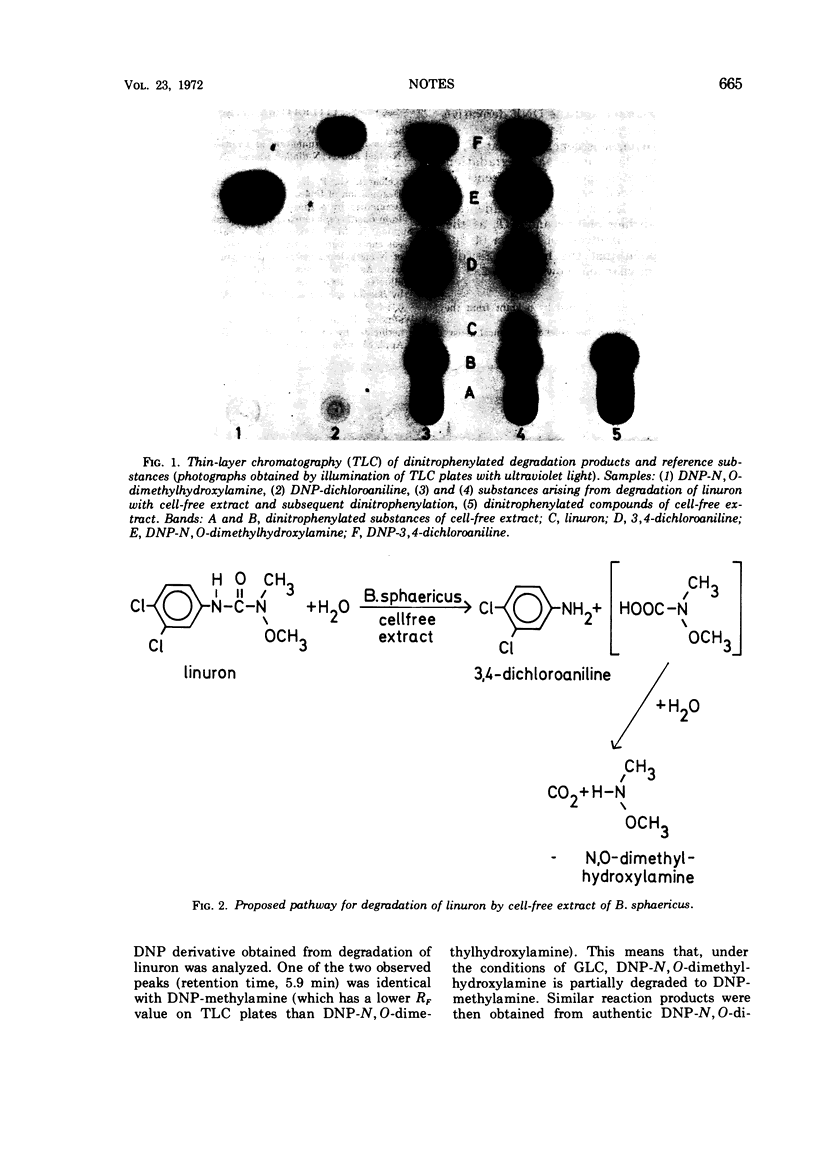
N, O-dimethylhydroxylamine was identified as a degradation product of linuron formed in the presence of extracts of Bacillus sphaericus ATCC 12123 by characterization of its dinitrophenyl derivative.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen P. R., Dauterman W. C. Colorimetric method for determination of amidase activity toward N-alkyl and N,N-dialkyl amides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt G., Wallnöfer P. R., Plapp R. Degradation of linuron and some other herbicides and fungicides by a linuron-inducible enzyme obtained from Bacillus sphaericus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):284–288. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.284-288.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallnöfer P. R., Bader J. Degradation of urea herbicides by cell-free extracts of Bacillus sphaericus. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):714–717. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.714-717.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]