Abstract
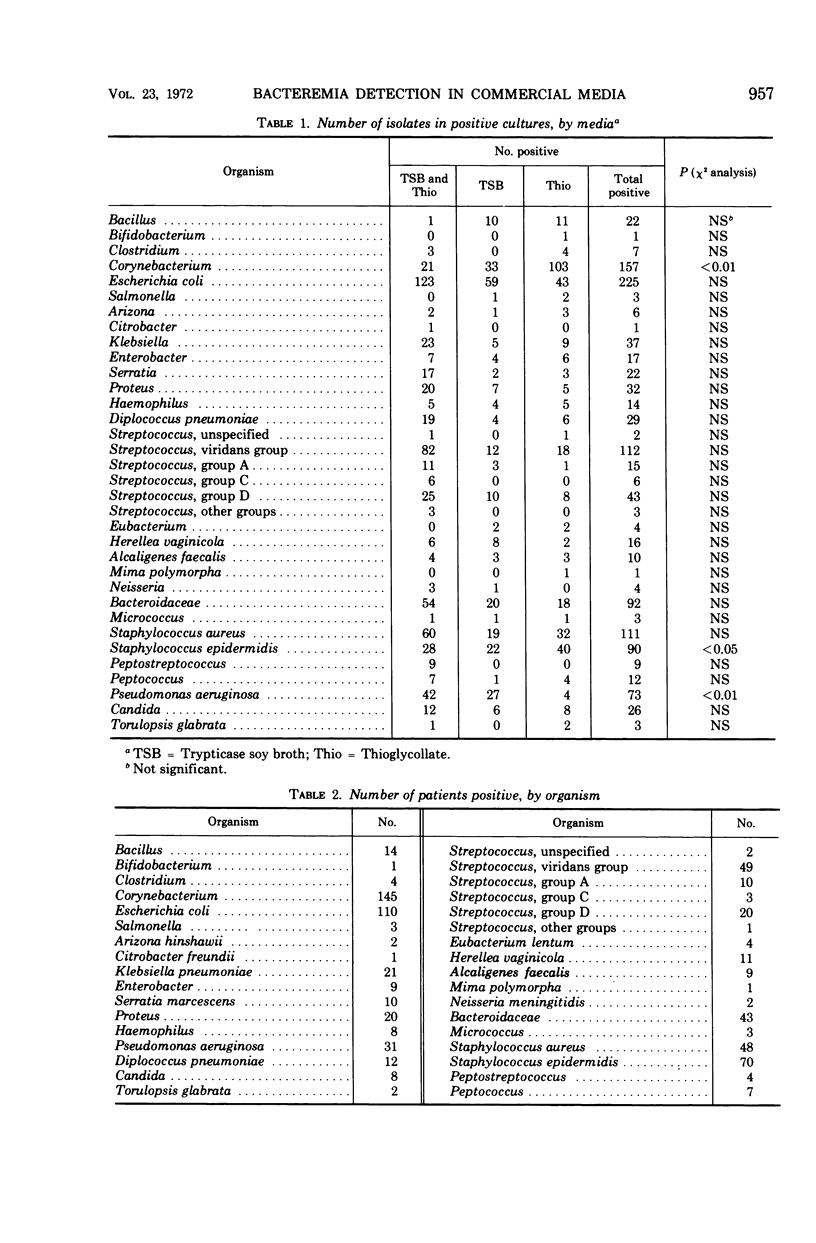
Analysis of the results of 13,162 blood cultures during a 9-month interval has shown that Pseudomonas aeruginosa statistically was recovered more frequently from Trypticase soy broth (TSB) than from Thioglycollate-135C and that contaminants, including Staphylococcus epidermidis and aerobic and anaerobic Corynebacterium species, were isolated with statistically greater frequency from Thioglycollate-135C than from TSB. No other statistically significant differences were found.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cayeux P., Acar J. F., Chabbert Y. A. Bacterial persistence in streptococcal endocarditis due to thiol-requiring mutants. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):247–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of two commercially available media for detection of bacteremia. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):604–607. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.604-607.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


