Abstract
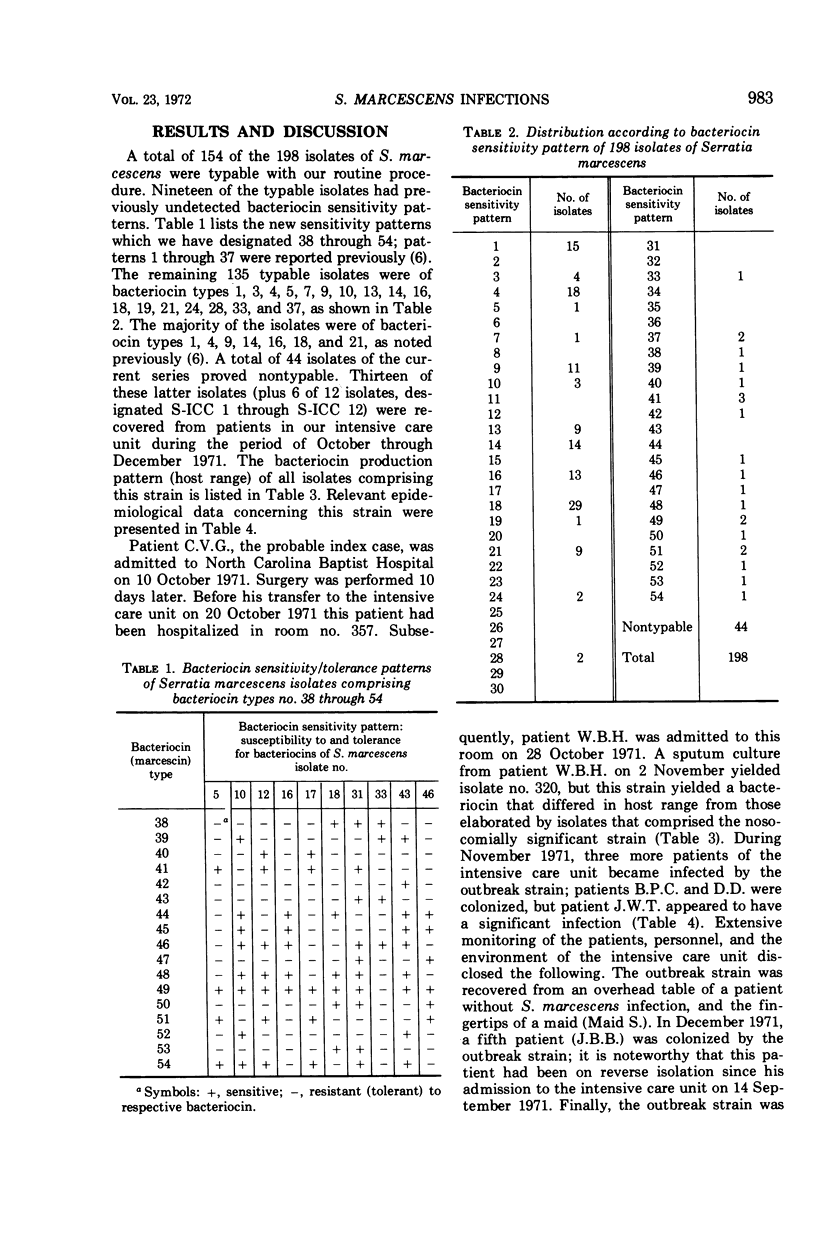
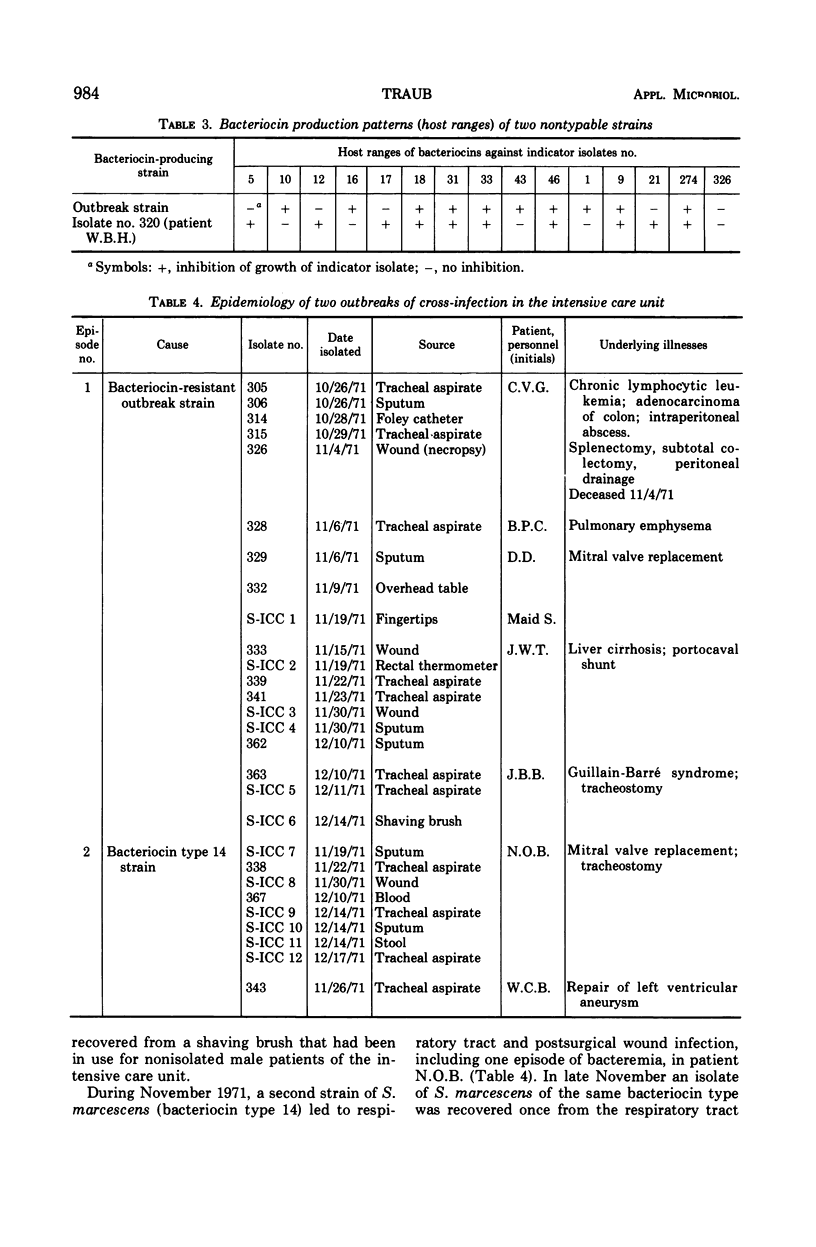
During an 8.5-month period, 198 additional isolates of Serratia marcescens were typed by bacteriocin sensitivity; 154 isolates were typable and were categorized according to our current system of 54 provisional bacteriocin sensitivity patterns. Two outbreaks of nosocomial infection due to S. marcescens occurred in our intensive care unit, involving two and five patients, respectively. The latter outbreak was caused by a strain of S. marcescens which was not sensitive to any of the 10 bacteriocins normally used. Therefore we developed a supplementary procedure based on bacteriocin production rather than bacteriocin sensitivity. Bacteriocin production was induced with mitomycin C, and the crude lysates were applied to 15 provisional bacteriocin indicator strains. The reverse typing procedure was necessary to determine the spread and ultimate subsidence of this particular outbreak of cross-infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman T. C., Clark J. J., Klemm L. Hand contamination of personnel as a mechanism of cross-infection in nosocomial infections with antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella-Aerobacter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Raymond E. A. Epidemiological surveillance of Serratia marcescens infections by bacteriocin typing. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1058–1063. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1058-1063.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Raymond E. A., Linehan J. Identification of Enterobacteriaceae in the clinical microbiology laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):303–308. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.303-308.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Raymond E. A., Startsman T. S. Bacteriocin (Marcescin) typing of clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):837–840. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.837-840.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


