Abstract
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) has attracted considerable interest as a potential vector for gene delivery. Wild-type virus is notable for the lack of association with any human disease and the ability to stably integrate its genome in a site-specific manner in a locus on human chromosome 19 (AAVS1). Use of a functional model system for AAV DNA integration into AAVS1 has allowed us to conclude that the recombination event is directed by cellular DNA sequences. Recombinant junctions isolated from our integration assay were analyzed and showed characteristics similar to those found in latently infected cell lines. The minimal DNA signals within AAVS1 required for targeted integration were identified and shown to contain functional motifs of the viral origin of replication. A replication mediated model of AAV DNA integration is proposed.
Full text
PDF

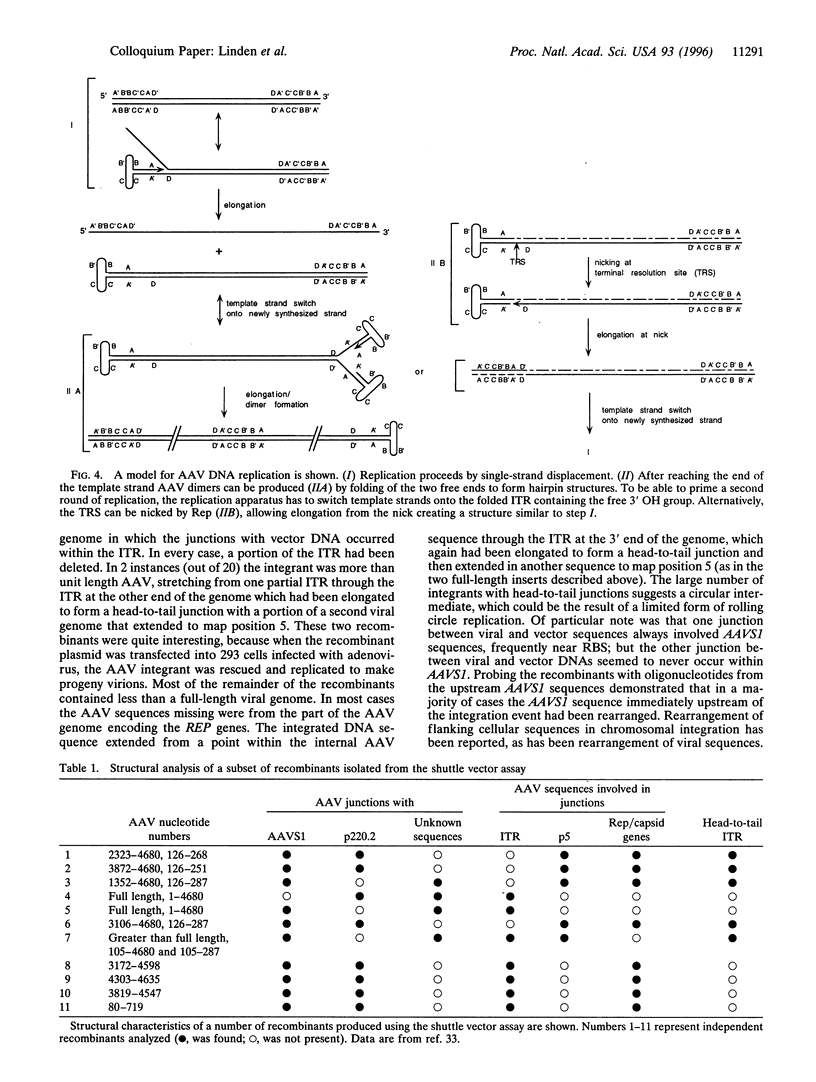
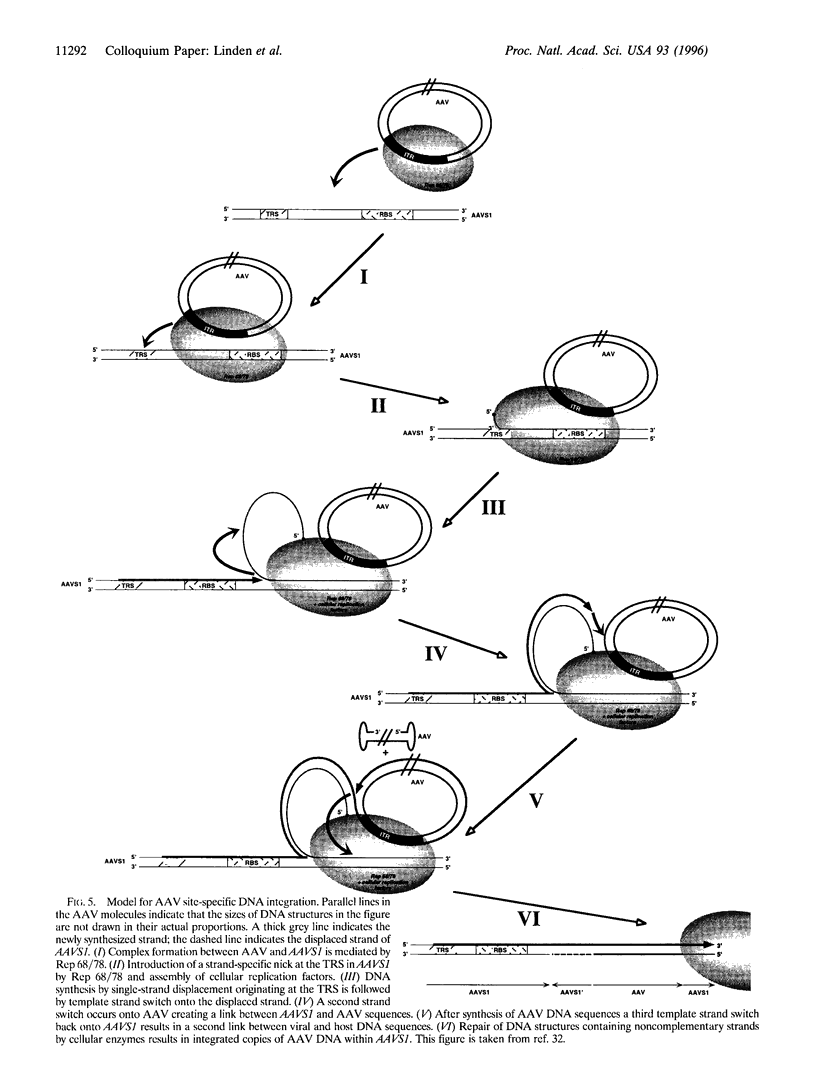


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATCHISON R. W., CASTO B. C., HAMMON W. M. ADENOVIRUS-ASSOCIATED DEFECTIVE VIRUS PARTICLES. Science. 1965 Aug 13;149(3685):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3685.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali R. R., Reichel M. B., Thrasher A. J., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C., Kanuga N., Hunt D. M., Bhattacharya S. S. Gene transfer into the mouse retina mediated by an adeno-associated viral vector. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 May;5(5):591–594. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.5.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Pinkerton T. C., Thomas G. F., Hoggan M. D. Detection of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-specific nucleotide sequences in DNA isolated from latently infected Detroit 6 cells. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):556–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Hoggan M. D., Kapikian A. Z., Austin J. B., Rowe W. P. Epidemiology of adenovirus-associated virus infection in a nursery population. Am J Epidemiol. 1968 Nov;88(3):368–378. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Janik J. E., Sebring E. D., Rose J. A. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 completely help adenovirus-associated virus replication. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):241–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.241-247.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K., Hoggan M. D., Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Integration of the adeno-associated virus genome into cellular DNA in latently infected human Detroit 6 cells. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):739–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.739-748.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Jackson C. L., Miller D. A., Leff T., Breslow J. L. The human apolipoprotein C-II gene sequence contains a novel chromosome 19-specific minisatellite in its third intron. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4787–4793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraud C., Winocour E., Berns K. I. Recombinant junctions formed by site-specific integration of adeno-associated virus into an episome. J Virol. 1995 Nov;69(11):6917–6924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.11.6917-6924.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraud C., Winocour E., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus is directed by a cellular DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10039–10043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Complementation of adeno-associated virus growth with temperature-sensitive mutants of human adenovirus types 12 and 5. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):239–242. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Blacklow N. R., Rowe W. P. Studies of small DNA viruses found in various adenovirus preparations: physical, biological, and immunological characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1467–1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Partial purification of adeno-associated virus Rep78, Rep52, and Rep40 and their biochemical characterization. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1119–1128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1119-1128.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90526-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplitt M. G., Leone P., Samulski R. J., Xiao X., Pfaff D. W., O'Malley K. L., During M. J. Long-term gene expression and phenotypic correction using adeno-associated virus vectors in the mammalian brain. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):148–154. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Berns K. I. Organization of adeno-associated virus DNA in latently infected Detroit 6 cells. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):460–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Linden R. M., Berns K. I. Characterization of a preferred site on human chromosome 19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5071–5078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Menninger J. C., Ward D. C., Berns K. I. Mapping and direct visualization of a region-specific viral DNA integration site on chromosome 19q13-qter. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Siniscalco M., Samulski R. J., Zhu X. D., Hunter L., Laughlin C. A., McLaughlin S., Muzyczka N., Rocchi M., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Graf L. H., Jr, Berns K. I. Adeno-associated virus gene expression inhibits cellular transformation by heterologous genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden R. M., Winocour E., Berns K. I. The recombination signals for adeno-associated virus site-specific integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7966–7972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff G., Wong K. K., Jr, Chatterjee S. Efficient gene transfer into nondividing cells by adeno-associated virus-based vectors. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5656–5666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5656-5666.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Miller A. D., Alexander I. E. Adeno-associated virus vectors preferentially transduce cells in S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8915–8919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Zhu X., Xiao X., Brook J. D., Housman D. E., Epstein N., Hunter L. A. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3941–3950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchert P., Langsford M., Käslin E., Kohli J. A specific DNA sequence is required for high frequency of recombination in the ade6 gene of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2157–2163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urcelay E., Ward P., Wiener S. M., Safer B., Kotin R. M. Asymmetric replication in vitro from a human sequence element is dependent on adeno-associated virus Rep protein. J Virol. 1995 Apr;69(4):2038–2046. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2038-2046.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P., Berns K. I. In vitro replication of adeno-associated virus DNA: enhancement by extracts from adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1996 Jul;70(7):4495–4501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.7.4495-4501.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P., Urcelay E., Kotin R., Safer B., Berns K. I. Adeno-associated virus DNA replication in vitro: activation by a maltose binding protein/Rep 68 fusion protein. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):6029–6037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.6029-6037.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindler F. W., Heilbronn R. A subset of herpes simplex virus replication genes provides helper functions for productive adeno-associated virus replication. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2476–2483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2476-2483.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman M. D., Kyöstiö S. R., Kotin R. M., Owens R. A. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) Rep proteins mediate complex formation between AAV DNA and its integration site in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5808–5812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson B., Hrynko T. A., Peak M. J., Winocour E. Replication of adeno-associated virus in cells irradiated with UV light at 254 nm. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1023–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1023-1030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson B., Koch T., Winocour E. Replication of adeno-associated virus in synchronized cells without the addition of a helper virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):972–981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.972-981.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalkinoglu A. O., Heilbronn R., Bürkle A., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. DNA amplification of adeno-associated virus as a response to cellular genotoxic stress. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3123–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. Z., Cooper S., Kang L. Y., Ruggieri L., Heimfeld S., Srivastava A., Broxmeyer H. E. Adeno-associated virus 2-mediated high efficiency gene transfer into immature and mature subsets of hematopoietic progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1867–1875. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]