Abstract
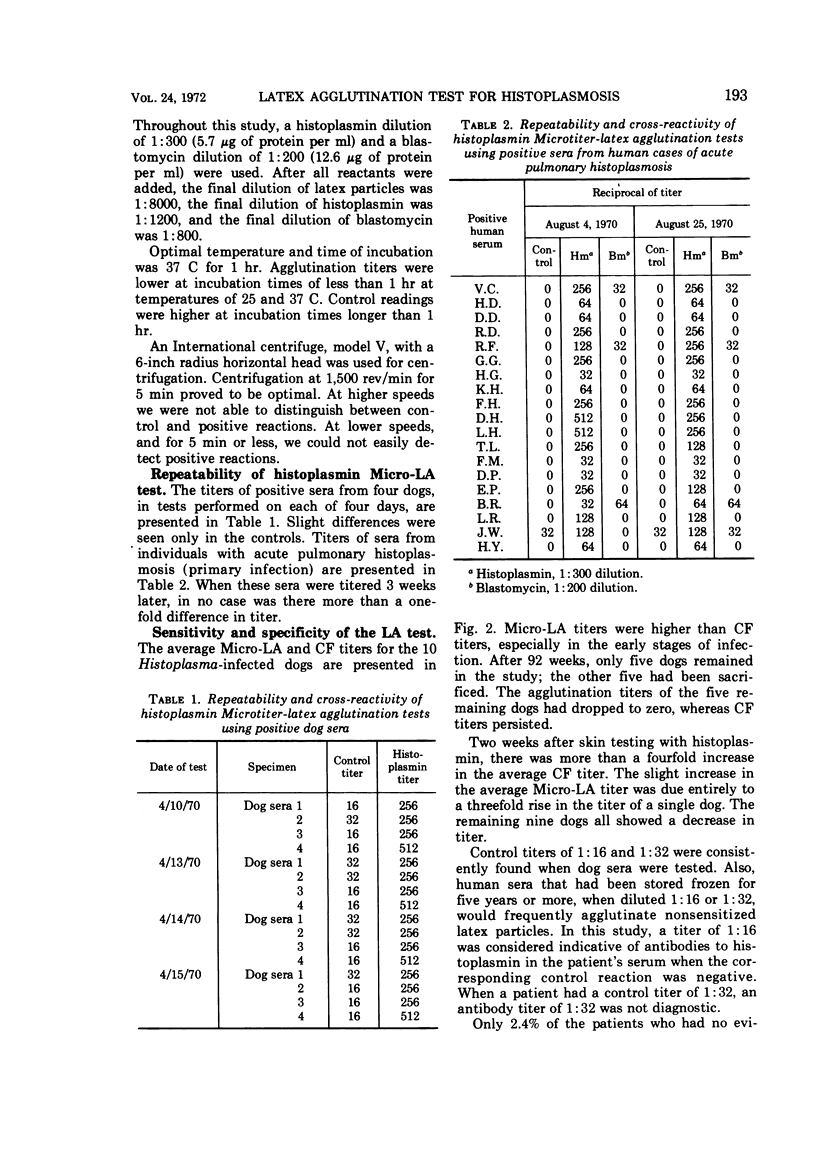
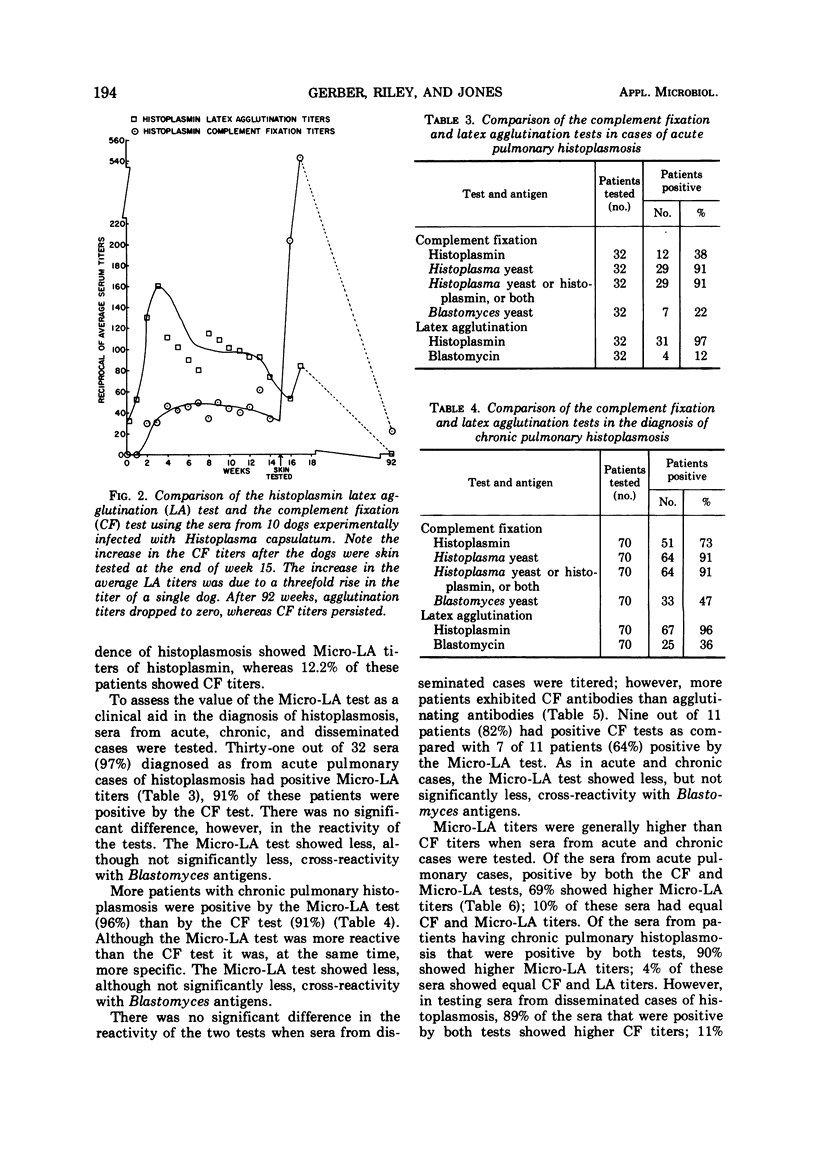
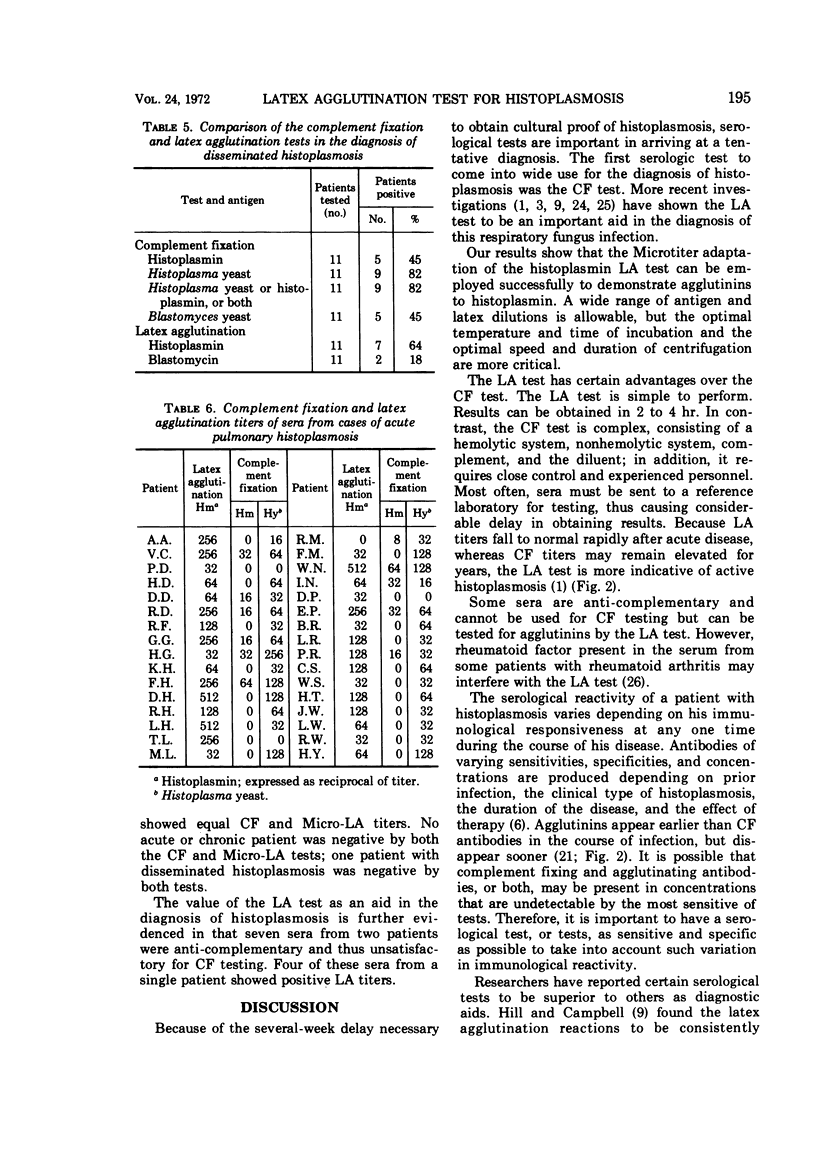
Experiments were designed to evaluate a Microtiter latex agglutination (Micro-LA) test, as a serological aid in the diagnosis of histoplasmosis, and to compare this test with the conventional microtiter-complement fixation (CF) test for histoplasmosis. Sera tested were from cases of acute and chronic pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis, as well as from individuals not having histoplasmosis. Ninety-seven percent of the cases of acute pulmonary histoplasmosis had positive Micro-LA tests, whereas 91% had positive CF tests. Ninety-six percent of the patients having chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis showed positive Micro-LA tests and 91% had positive CF tests. In contrast, 64% of the cases of disseminated histoplasmosis had positive Micro-LA tests, whereas 82% had positive CF tests. None of these differences was statistically significant. Although there were no significant differences in complement fixing and agglutinating antibody cross-reactivity with Blastomyces antigens, more patients demonstrated CF titers than Micro-LA titers. Sera from patients with acute and chronic histoplasmosis showed higher Micro-LA titers than CF titers, whereas sera from cases of disseminated histoplasmosis showed higher CF titers. Histoplasmin skin testing has less of a boosting effect on agglutinating antibodies than on CF antibodies to histoplasmin. Anticomplementary sera can be used in the Micro-LA test. This test is simple to perform, and results can be obtained in 2 to 4 hr.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOMFIELD N., GORDON M. A., ELMENDORF D. F., Jr DETECTION OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS ANTIGEN IN BODY FLUIDS BY LATEX PARTICLE AGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:64–67. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. E. The histoplasmin latex agglutination test: clinical evaluation and a review of the literature. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Feb;251(2):175–183. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196602000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLISLE H. N., SASLAW S. A histoplasmin-latex agglutination test. I. Results with animal sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 May;51(5):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN C. L., MENDEZ-BRYAN R., LARSON D. L. Latex agglutination test for disseminated lupus erythematosus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FESSEL W. J. Nucleoprotein-latex agglutination test in connective tissue diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Sep;18:255–258. doi: 10.1136/ard.18.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURCOLOW M. L. Tests of immunity in histoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1963 Feb 14;268:357–361. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196302142680706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. S., Kaufman L., Koenig M. G. Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. Value of immunologic detection of cryptococcal antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 19;285(8):434–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108192850804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL G. B., CAMPBELL C. C. Commercially available histoplasmin sensitized latex particles in an agglutination test for histoplasmosis. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1962 Nov 10;18:160–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02051586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusinkveld R. S., Tosh F. E., Newberry W. M., Jr, Ciccone P. J., Chin T. D. Antibody response to the histoplasmin skin test. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Nov;96(5):1069–1071. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.5.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipp S. S., Berns D. S., Tompkins V., Buckley H. R. Latex slide agglutination test for Aspergillus antibodies. Sabouraudia. 1970 Nov;8(3):237–241. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. N., Powell S. J., Elsdon-Dew R. Latex agglutination test for invasive amoebiasis. Lancet. 1970 Jun 27;1(7661):1362–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS W. M., WIER J. A., KUHN L. R., CAMPBELL C. C., NOLTE L. B., HILL G. B. Serologic effects of histoplasmin skin testing. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Feb;83:276–279. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.83.2P1.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. B., Stevens R. W., Gaafar H. A. Latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSEN C. R., RANTZ L. A. [The latex fixation test using whole serum and an euglobulin fraction in various arthritic disorders]. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Feb;1(1):54–61. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILP J. R., WEIR D. M., STUART A. E., IRVINE W. J. A latex particle precipitation test in the diagnosis of thyroid disease. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Mar;15:148–152. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIOR J. A., SASLAW S. Effect of repeated histoplasmin skin tests on skin reactivity and collodion agglutination. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Nov;66(5):588–593. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.66.5.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVIN S. B., WEBER R. W., LACKMAN D. B., NISHIO J., MENGES G. Influence of repeated histoplasmin skin tests on precipitins and complement-fixing antibodies. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Jul;44(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASLAW S., CAMPBELL C. C. Effect of histoplasmin skin testing on serologic results. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Apr;82(4):689–691. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASLAW S., CAMPBELL C. C. Studies on the stability of the histoplasmin collodion agglutination test. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 May;35(5):780–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASLAW S., CARLISLE H. N. Histoplasmin-latex agglutination test. II. Results with human sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Mar;97(3):700–703. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., WIGGINS G. L. The evaluation of serologic tests for histoplasmosis in relation to the clinical diagnosis. Am J Hyg. 1963 May;77:240–249. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saslaw S., Campbell C. C. Serologic Studies in Histoplasmosis. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Apr;40(4):427–435. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


