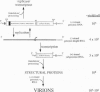
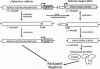
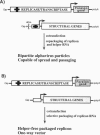
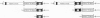Abstract
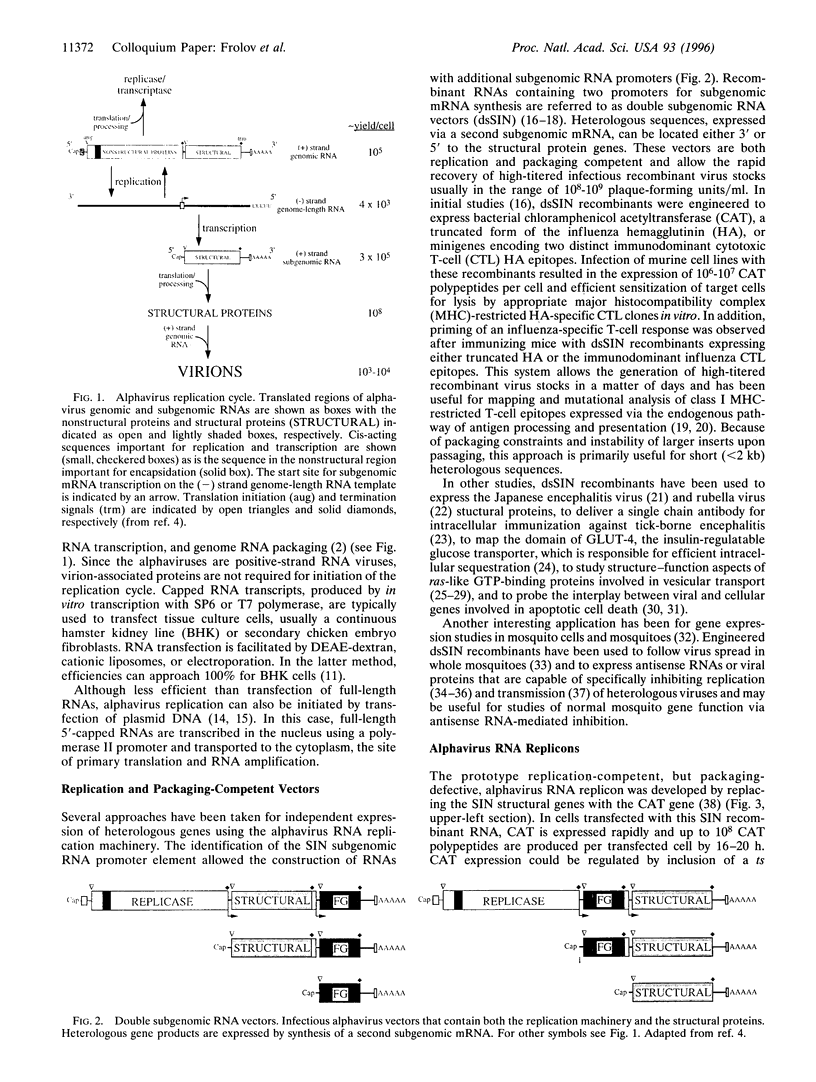
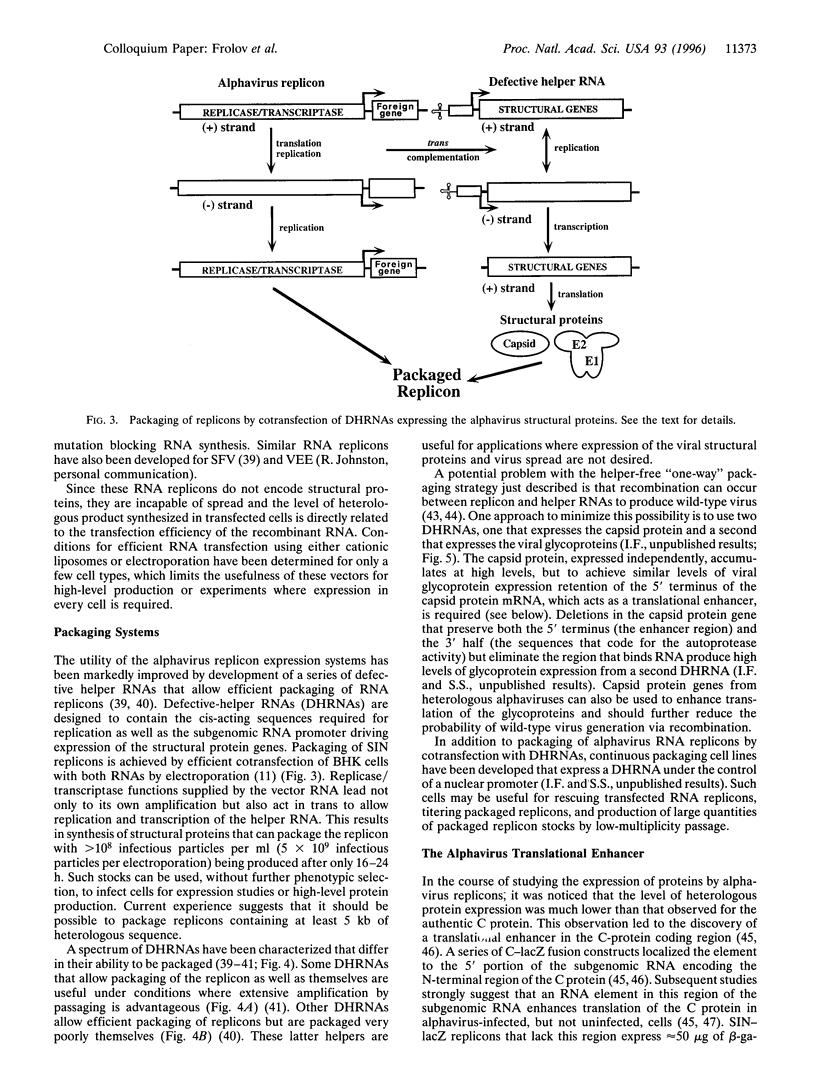
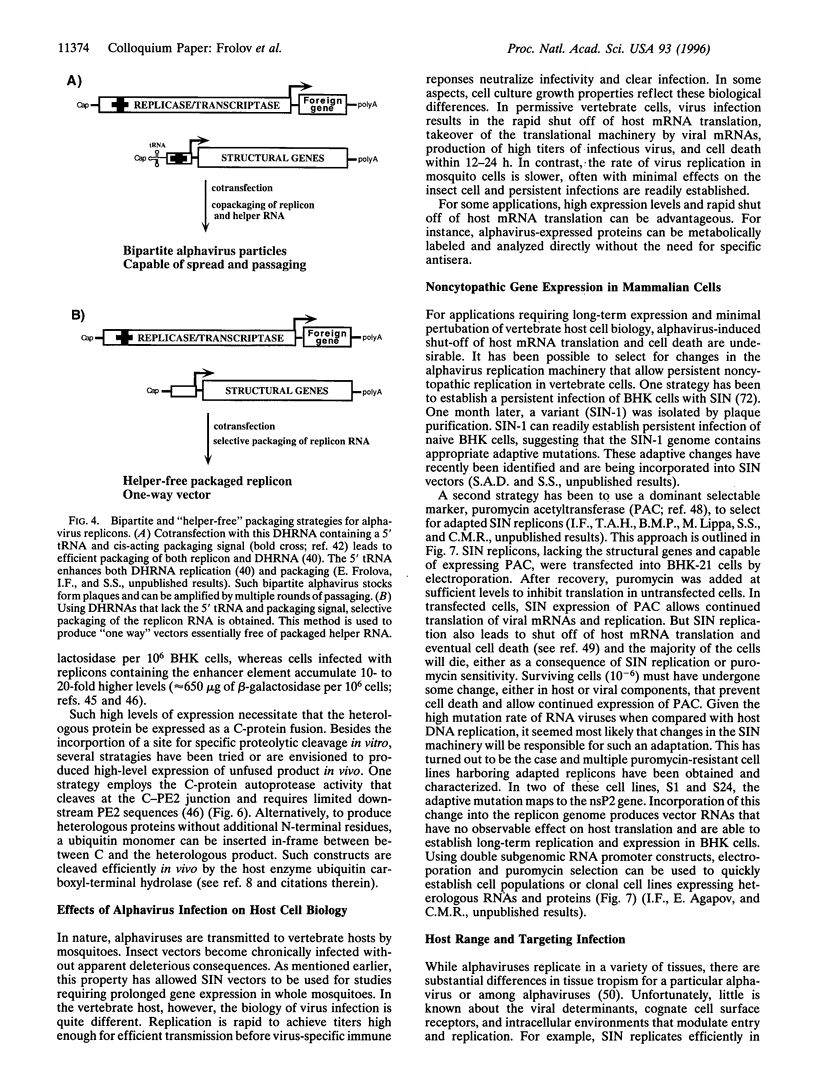
Alphaviruses are positive-strand RNA viruses that can mediate efficient cytoplasmic gene expression in insect and vertebrate cells. Through recombinant DNA technology, the alphavirus RNA replication machinery has been engineered for high-level expression of heterologous RNAs and proteins. Amplification of replication-competent alpha-virus RNAs (replicons) can be initiated by RNA or DNA transfection and a variety of packaging systems have been developed for producing high titers of infectious viral particles. Although normally cytocidal for vertebrate cells, variants with adaptive mutations allowing noncytopathic replication have been isolated from persistently infected cultures or selected using a dominant selectable marker. Such mutations have been mapped and used to create new alphavirus vectors for noncytopathic gene expression in mammalian cells. These vectors allow long-term expression at moderate levels and complement previous vectors designed for short-term high-level expression. Besides their use for a growing number of basic research applications, recombinant alphavirus RNA replicons may also facilitate genetic vaccination and transient gene therapy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berglund P., Tubulekas I., Liljeström P. Alphaviruses as vectors for gene delivery. Trends Biotechnol. 1996 Apr;14(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(96)10019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredenbeek P. J., Frolov I., Rice C. M., Schlesinger S. Sindbis virus expression vectors: packaging of RNA replicons by using defective helper RNAs. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6439–6446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6439-6446.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. P., Miller D., Katow S., Frey T. K. Expression of the rubella virus structural proteins by an infectious Sindbis virus vector. Arch Virol. 1995;140(11):2075–2084. doi: 10.1007/BF01322694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng E. H., Levine B., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Hardwick J. M. Bax-independent inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl-XL. Nature. 1996 Feb 8;379(6565):554–556. doi: 10.1038/379554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng R. H., Kuhn R. J., Olson N. H., Rossmann M. G., Choi H. K., Smith T. J., Baker T. S. Nucleocapsid and glycoprotein organization in an enveloped virus. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90516-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza-Schorey C., Li G., Colombo M. I., Stahl P. D. A regulatory role for ARF6 in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Science. 1995 Feb 24;267(5201):1175–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.7855600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Brown K. W., Greenwald G. F., Zajac A. J., Zacny V. L., Smith J. F., Johnston R. E. Attenuated mutants of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus containing lethal mutations in the PE2 cleavage signal combined with a second-site suppressor mutation in E1. Virology. 1995 Sep 10;212(1):102–110. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Brown K. W., Johnston R. E. A viral vaccine vector that expresses foreign genes in lymph nodes and protects against mucosal challenge. J Virol. 1996 Jun;70(6):3781–3787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.6.3781-3787.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Powell N., Greenwald G. F., Willis L. V., Johnson B. J., Smith J. F., Johnston R. E. Attenuating mutations in the E2 glycoprotein gene of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus: construction of single and multiple mutants in a full-length cDNA clone. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):20–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90114-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Willis L. V., Smith J. F., Johnston R. E. In vitro synthesis of infectious venezuelan equine encephalitis virus RNA from a cDNA clone: analysis of a viable deletion mutant. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):189–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubensky T. W., Jr, Driver D. A., Polo J. M., Belli B. A., Latham E. M., Ibanez C. E., Chada S., Brumm D., Banks T. A., Mento S. J. Sindbis virus DNA-based expression vectors: utility for in vitro and in vivo gene transfer. J Virol. 1996 Jan;70(1):508–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.1.508-519.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuisson J., Hsu H. H., Cheung R. C., Greenberg H. B., Russell D. G., Rice C. M. Formation and intracellular localization of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein complexes expressed by recombinant vaccinia and Sindbis viruses. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6147–6160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6147-6160.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuisson J., Rice C. M. Sindbis virus attachment: isolation and characterization of mutants with impaired binding to vertebrate cells. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3363–3374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3363-3374.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolov I., Schlesinger S. Comparison of the effects of Sindbis virus and Sindbis virus replicons on host cell protein synthesis and cytopathogenicity in BHK cells. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1721–1727. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1721-1727.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolov I., Schlesinger S. Translation of Sindbis virus mRNA: effects of sequences downstream of the initiating codon. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):8111–8117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.8111-8117.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines P. J., Olson K. E., Higgs S., Powers A. M., Beaty B. J., Blair C. D. Pathogen-derived resistance to dengue type 2 virus in mosquito cells by expression of the premembrane coding region of the viral genome. J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2132–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.4.2132-2137.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Wilschut J., Liljeström P., Wahlberg J. M., Bron R., Suomalainen M., Smyth J., Salminen A., Barth B. U., Zhao H. Assembly and entry mechanisms of Semliki Forest virus. Arch Virol Suppl. 1994;9:329–338. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9326-6_33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geigenmüller-Gnirke U., Weiss B., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Complementation between Sindbis viral RNAs produces infectious particles with a bipartite genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3253–3257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Levine B., Tyor W. R., Tucker P. C., Hardwick J. M. Age-dependent susceptibility to fatal encephalitis: alphavirus infection of neurons. Arch Virol Suppl. 1994;9:31–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9326-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Levine B., Ubol S., Hardwick J. M. The effects of alphavirus infection on neurons. Ann Neurol. 1994;35 (Suppl):S23–S27. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Hahn Y. S., Braciale T. J., Rice C. M. Infectious Sindbis virus transient expression vectors for studying antigen processing and presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Hahn C. S., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J., Rice C. M. CD8+ T cell recognition of an endogenously processed epitope is regulated primarily by residues within the epitope. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1335–1341. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heino P., Dillner J., Schwartz S. Human papillomavirus type 16 capsid proteins produced from recombinant Semliki Forest virus assemble into virus-like particles. Virology. 1995 Dec 20;214(2):349–359. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz J. M., Huang H. V. Utilization of heterologous alphavirus junction sequences as promoters by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.857-864.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herweijer H., Latendresse J. S., Williams P., Zhang G., Danko I., Schlesinger S., Wolff J. A. A plasmid-based self-amplifying Sindbis virus vector. Hum Gene Ther. 1995 Sep;6(9):1161–1167. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.9-1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs S., Powers A. M., Olson K. E. Alphavirus expression systems: applications to mosquito vector studies. Parasitol Today. 1993 Dec;9(12):444–452. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90098-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. J., Summers J. Infection initiated by the RNA pregenome of a DNA virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5435–5439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5435-5439.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Venugopal K., Gould E. A. Intracellular interference of tick-borne flavivirus infection by using a single-chain antibody fragment delivered by recombinant Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):1044–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.1044-1049.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanning F. W., Conry R. M., LoBuglio A. F., Wright M., Sumerel L. A., Pike M. J., Curiel D. T. A Sindbis virus mRNA polynucleotide vector achieves prolonged and high level heterologous gene expression in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 May 11;23(9):1495–1501. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.9.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Niesters H. G., Hong Z., Strauss J. H. Infectious RNA transcripts from Ross River virus cDNA clones and the construction and characterization of defined chimeras with Sindbis virus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90584-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemm J. A., Rümenapf T., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H., Rice C. M. Polypeptide requirements for assembly of functional Sindbis virus replication complexes: a model for the temporal regulation of minus- and plus-strand RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2925–2934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Goldman J. E., Jiang H. H., Griffin D. E., Hardwick J. M. Bc1-2 protects mice against fatal alphavirus encephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4810–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Barbieri M. A., Colombo M. I., Stahl P. D. Structural features of the GTP-binding defective Rab5 mutants required for their inhibitory activity on endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14631–14635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Barbieri M. A., Stahl P. D. Myristoylation cannot functionally replace the isoprenylation of Rab5. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Jan 10;316(1):529–534. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Stahl P. D. Post-translational processing and membrane association of the two early endosome-associated rab GTP-binding proteins (rab4 and rab5). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Aug 1;304(2):471–478. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Stahl P. D. Structure-function relationship of the small GTPase rab5. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24475–24480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Garoff H. A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1356–1361. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Lusa S., Huylebroeck D., Garoff H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: the small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4107–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4107-4113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Lindenbach B. D., Prágai B. M., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Processing in the hepatitis C virus E2-NS2 region: identification of p7 and two distinct E2-specific products with different C termini. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5063–5073. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5063-5073.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London S. D., Schmaljohn A. L., Dalrymple J. M., Rice C. M. Infectious enveloped RNA virus antigenic chimeras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):207–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett A. E., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Frey T. K., Wolinsky J. S. Rubella virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses: identification of the capsid as a target of major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted lysis and definition of two epitopes. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):5849–5858. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.5849-5858.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundström K., Mills A., Buell G., Allet E., Adami N., Liljeström P. High-level expression of the human neurokinin-1 receptor in mammalian cell lines using the Semliki Forest virus expression system. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Sep 15;224(3):917–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossman S. P., Bex F., Berglund P., Arthos J., O'Neil S. P., Riley D., Maul D. H., Bruck C., Momin P., Burny A. Protection against lethal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsmmPBj14 disease by a recombinant Semliki Forest virus gp160 vaccine and by a gp120 subunit vaccine. J Virol. 1996 Mar;70(3):1953–1960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.3.1953-1960.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olkkonen V. M., Dupree P., Simons K., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Expression of exogenous proteins in mammalian cells with the Semliki Forest virus vector. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43(Pt A):43–53. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60597-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. E., Higgs S., Gaines P. J., Powers A. M., Davis B. S., Kamrud K. I., Carlson J. O., Blair C. D., Beaty B. J. Genetically engineered resistance to dengue-2 virus transmission in mosquitoes. Science. 1996 May 10;272(5263):884–886. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5263.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. E., Higgs S., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Carlson J. O., Beaty B. J. The expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in Aedes albopictus (C6/36) cells and Aedes triseriatus mosquitoes using a double subgenomic recombinant Sindbis virus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1994 Jan;24(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(94)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul N. L., Marsh M., McKeating J. A., Schulz T. F., Liljeström P., Garoff H., Weiss R. A. Expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins by Semliki Forest virus vectors. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Oct;9(10):963–970. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Slot J. W., Li G., Stahl P. D., James D. E. Recombinant Sindbis virus as an expression system for cell biology. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43(Pt A):55–78. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Tai C., Slot J. W., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Huang H., James D. E. The efficient intracellular sequestration of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT-4) is conferred by the NH2 terminus. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):729–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. M., Kamrud K. I., Olson K. E., Higgs S., Carlson J. O., Beaty B. J. Molecularly engineered resistance to California serogroup virus replication in mosquito cells and mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4187–4191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. M., Olson K. E., Higgs S., Carlson J. O., Beaty B. J. Intracellular immunization of mosquito cells to LaCrosse virus using a recombinant Sindbis virus vector. Virus Res. 1994 Apr;32(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(94)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugachev K. V., Mason P. W., Shope R. E., Frey T. K. Double-subgenomic Sindbis virus recombinants expressing immunogenic proteins of Japanese encephalitis virus induce significant protection in mice against lethal JEV infection. Virology. 1995 Oct 1;212(2):587–594. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju R., Huang H. V. Analysis of Sindbis virus promoter recognition in vivo, using novel vectors with two subgenomic mRNA promoters. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2501–2510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2501-2510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju R., Subramaniam S. V., Hajjou M. Genesis of Sindbis virus by in vivo recombination of nonreplicative RNA precursors. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7391–7401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7391-7401.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolls M. M., Haglund K., Rose J. K. Expression of additional genes in a vector derived from a minimal RNA virus. Virology. 1996 Apr 15;218(2):406–411. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolls M. M., Webster P., Balba N. H., Rose J. K. Novel infectious particles generated by expression of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein from a self-replicating RNA. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Wahlberg J. M., Lobigs M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Membrane fusion process of Semliki Forest virus. II: Cleavage-dependent reorganization of the spike protein complex controls virus entry. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):349–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirako Y., Strauss J. H. Regulation of Sindbis virus RNA replication: uncleaved P123 and nsP4 function in minus-strand RNA synthesis, whereas cleaved products from P123 are required for efficient plus-strand RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1874–1885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1874-1885.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg E. M., Garoff H. The translation-enhancing region of the Semliki Forest virus subgenome is only functional in the virus-infected cell. J Gen Virol. 1996 Jun;77(Pt 6):1323–1327. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg E. M., Suomalainen M., Garoff H. A significantly improved Semliki Forest virus expression system based on translation enhancer segments from the viral capsid gene. Biotechnology (N Y) 1994 Nov;12(11):1127–1131. doi: 10.1038/nbt1194-1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. The alphaviruses: gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Sep;58(3):491–562. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.3.491-562.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. G., Schlesinger S. Recombination between Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4017–4025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4017-4025.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Rosenthal R., Schlesinger S. Establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sindbis virus in BHK cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):463–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.463-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong C., Levis R., Shen P., Schlesinger S., Rice C. M., Huang H. V. Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1188–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.2922607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Bates P., Willert K., Varmus H. E. Efficient incorporation of human CD4 protein into avian leukosis virus particles. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2175047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X., Berglund P., Rhodes G., Parker S. E., Jondal M., Liljeström P. Self-replicating Semliki Forest virus RNA as recombinant vaccine. Vaccine. 1994 Dec;12(16):1510–1514. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X., Berglund P., Zhao H., Liljeström P., Jondal M. Generation of cytotoxic and humoral immune responses by nonreplicative recombinant Semliki Forest virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Luna S., Soria I., Pulido D., Ortín J., Jiménez A. Efficient transformation of mammalian cells with constructs containing a puromycin-resistance marker. Gene. 1988;62(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90585-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]