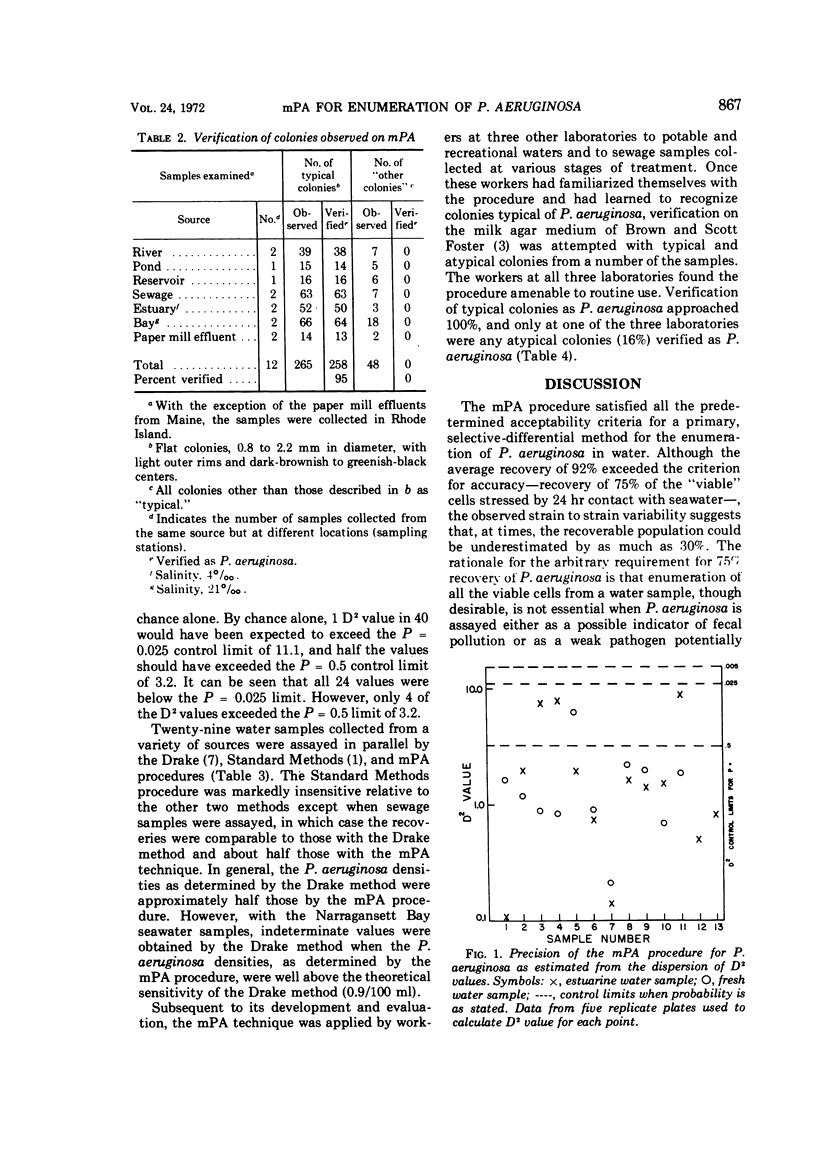
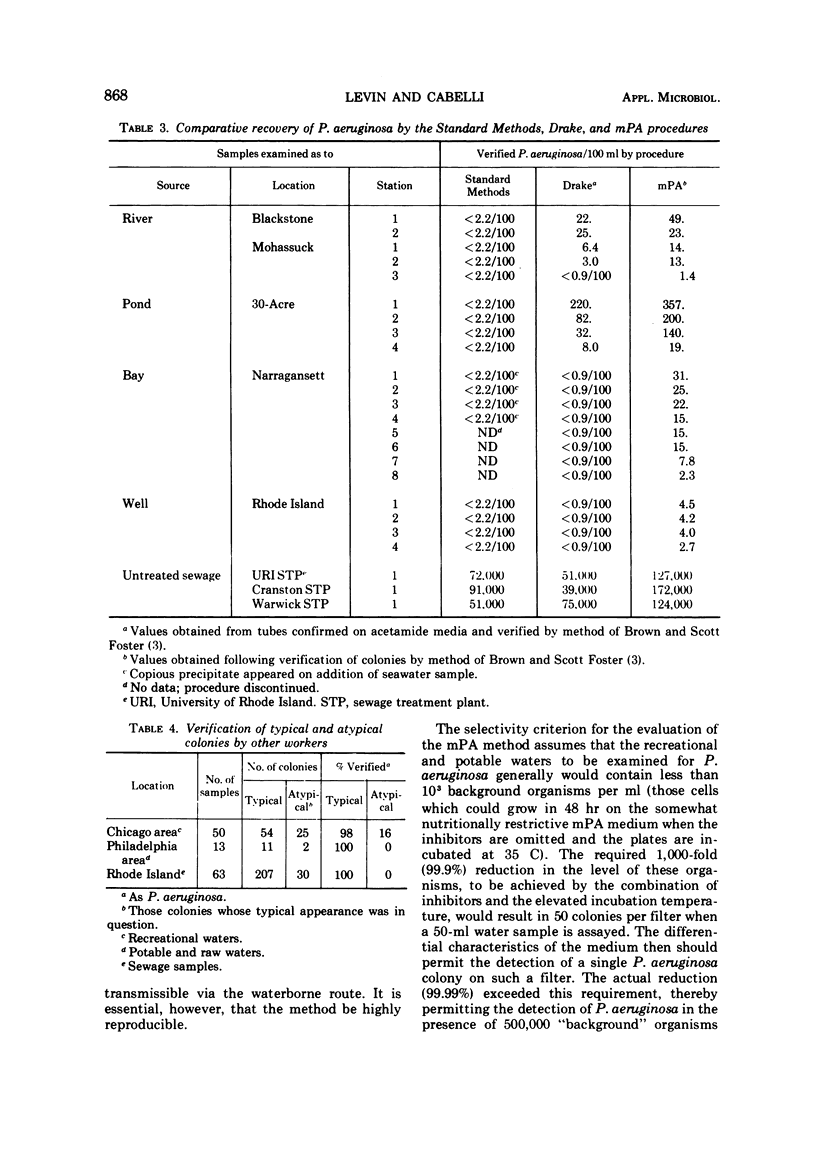
Abstract
A membrane filter procedure for the quantitation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (mPA procedure) has been developed. Through the use of inhibitors and an elevated incubation temperature, the level of background microbial flora was decreased approximately 10,000-fold. Using P. aeruginosa cells suspended in sea water and held for 24 hr, between 70 and 100% of the „viable” cells could be recovered by the mPA procedure. Assay variability was found to be insignificant. The recoveries of P. aeruginosa from surface (fresh and salt) waters, potable waters, and sewage by the mPA procedure exceeded those obtainable by current methods. Subsequent to its development and evaluation, the mPA procedure was used at three other laboratories for the enumeration of P. aeruginosa in potable and recreational waters and in sewage samples. It was found amenable to routine use, and confirmation of typical colonies approached 100%.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASAY L. D., KOCH R. Pseudomonas infections in infants and children. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 26;262:1062–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005262622104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Foster J. H. A simple diagnostic milk medium for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;23(2):172–177. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. A. The detection of various bacteria indicative of water pollution by a presence-absence (P-A) procedure. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):771–780. doi: 10.1139/m69-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell N. D., Morisetti M. D. Microbiological techniques--some statistical aspects. J Sci Food Agric. 1969 Oct;20(10):573–579. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740201001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake C. H. Evaluation of culture media for the isolation and enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Health Lab Sci. 1966 Jan;3(1):10–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhart C., Wilson P. W. STATISTICAL METHODS AND CONTROL IN BACTERIOLOGY. Bacteriol Rev. 1943 Jun;7(2):57–137. doi: 10.1128/br.7.2.57-137.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORRILL R. H., McNEIL E. M. The effect of cold diluent on the viable count of Pseudomonas pyocyanea. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Apr;22:437–442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-2-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Jeter H. L., Winter J. A. Technical considerations in applying the membrane filter procedure. Health Lab Sci. 1967 Apr;4(2):113–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Enomoto S. Nalidixic acid cetrimide agar. A new selective plating medium for the selective isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieble H. G., Colton F. R., Bird T. J., Toigo A., Griffith L. G. Fine-particle humidifiers. Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in a respiratory-disease unit. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 5;282(10):531–535. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003052821003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Ziegler N. R. Application of Statistics to Problems in Bacteriology: I. A Means of Determining Bacterial Population by the Dilution Method. J Bacteriol. 1933 Feb;25(2):101–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.25.2.101-121.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Hurst V., Lane C. W. Quantification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in feces of healthy human adults. Health Lab Sci. 1967 Oct;4(4):245–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L. Identification of Pseudomonas species isolated from hospital environment and human sources. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1532–1538. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1532-1538.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


