Abstract
Malaria parasites and related Apicomplexans are the causative agents of the some of the most serious infectious diseases of humans, companion animals, livestock and wildlife. These parasites must undergo sexual reproduction to transmit from vertebrate hosts to vectors, and their sex ratios are consistently female-biased. Sex allocation theory, a cornerstone of evolutionary biology, is remarkably successful at explaining female-biased sex ratios in multicellular taxa, but has proved controversial when applied to malaria parasites. Here we show that, as predicted by theory, sex ratio is an important fitness-determining trait and Plasmodium chabaudi parasites adjust their sex allocation in response to the presence of unrelated conspecifics. This suggests that P. chabaudi parasites use kin discrimination to evaluate the genetic diversity of their infections, and they adjust their behaviour in response to environmental cues. Malaria parasites provide a novel way to test evolutionary theory, and support the generality and power of a darwinian approach.
The allocation of resources to male versus female offspring is one of the most well understood topics in evolutionary biology, and provides some of the best evidence for darwinian adaptation in the natural world1–5. In many cases, simple theory can successfully predict when, why and by how much organisms should adjust their offspring sex ratio in response to changes in their environment. However, despite over a century of research effort directed at malaria (Plasmodium) and related Apicomplexan (including Haemoproteus and Leucocytozoon) blood parasites, evolutionary biologists have not been able to explain their sex ratios6–10. These parasites replicate asexually, and a proportion of these asexually produced parasites develop into sexual stages, termed gametocytes. When taken up in an insect vector’s blood meal, gametocytes differentiate into gametes and mate. In Plasmodium species, male gametocytes can differentiate into a maximum of eight gametes and each female differentiates into a single gamete. Sex allocation in Plasmodium is consistently female-biased when measured across populations, but sex ratios vary extensively when measured throughout individual infections11–15. Sex is crucial for transmission to vectors, and so there is a drive to identify drugs and develop vaccines that block this process. Yet remarkably little is understood as to why such female-biased and variable sex allocation strategies have evolved.
Hamilton’s theory of ‘local mate competition’ (LMC) predicts that female-biased sex allocation is favoured when genetically related males compete for mates; because males can each fertilize more than one female, an equal sex ratio would result in a wasteful surfeit of male gametes4. For malaria parasites, LMC predicts that the unbeatable sex allocation strategy (investment into males relative to females) depends on the inbreeding rate, and is given by the equation z*=(1–f)/2, where z* is the proportional allocation into males versus females and f is Wright’s coefficient of inbreeding16–19. When inbreeding does not occur, owing to a large number of genotypes represented in mating groups (no inbreeding; f=0), the unbeatable strategy is to produce an equal number of males and females20 (z*=1/2). Conversely, when only one or a small number of genotypes are present (inbreeding; f>0), female-biased sex allocation is favoured4 (z*<1/2).
LMC is one of the most successful theories in evolutionary biology and its explanatory power has been demonstrated in a variety of taxa21 including plants, snakes, insects, mites, worms and fish, but the application of LMC theory to Apicomplexan parasites has proved controversial and inconclusive. There is considerable variation in the inbreeding rate (as allowed by the number of multiple infections) experienced by parasites within and across species of Apicomplexa22–24. LMC is supported by correlations between observed sex ratio and inbreeding rate across several Apicomplexan taxa, with female-biased sex ratios occurring in populations with higher rates of inbreeding19,25,26. However, contradictory data are as numerous: (1) sex ratios in populations of Haemoproteus bird parasites do not correlate with the inferred genetic diversity of their infections and are consistently less female biased than expected9; (2) LMC theory cannot explain the considerable variation in sex ratios observed during experimental infections8,19,26–28; (3) the inbreeding rate is not the only factor shaping sex allocation, because Plasmodium parasites facultatively alter their sex ratio in response to changes in host anaemia11,13; and (4) successful transmission to vectors appears unrelated to mating group sex ratio29,30.
Failure to understand sex allocation in malaria parasites poses problems for both medical science and evolutionary biology. If an evolutionary framework cannot explain a relatively simple trait like parasite sex allocation, there is no reason to believe that it can be usefully applied to more complex traits such as virulence. Also, organisms such as parasites and microbes present a novel and independent test for the explanatory power and generality of an evolutionary theory that has been largely developed to explain the biology of metazoan taxa such as insects, birds and mammals31. Explicitly testing whether sex allocation in malaria parasites is shaped by LMC has not previously been possible, because the required experimental methods and techniques have only just become available.
First, we test the basic assumptions of LMC as applied to malaria parasites. We test whether females are the more limiting sex for mating group productivity and whether the relationship between sex ratio and fitness varies in the manner predicted by theory1,4. Even though LMC has been so successfully applied to other taxa, this fundamental assumption has yet to be properly tested in any species. Such data are lacking owing to the difficulties in manipulating this trait independently of confounding variables, and the very success of LMC theory has suggested that such a test is unnecessary. We also test whether there is genetic variation for patterns of within-infection sex allocation in malaria parasites, and examine whether these patterns follow the predictions of theory32,33. Second, we test the key predictions of LMC by manipulating the number of genotypes present in infections (inbreeding rate) and investigate whether focal genotypes adjust their sex allocation strategy in response13,26,34,35. Facultative sex-ratio adjustment in response to genetic diversity would confirm that sex allocation strategies in malaria parasites are as sophisticated as those observed in multicellular taxa, that they can be explained by evolutionary theory, and that malaria parasites can discriminate kin from non-kin.
Fitness consequences of sex allocation
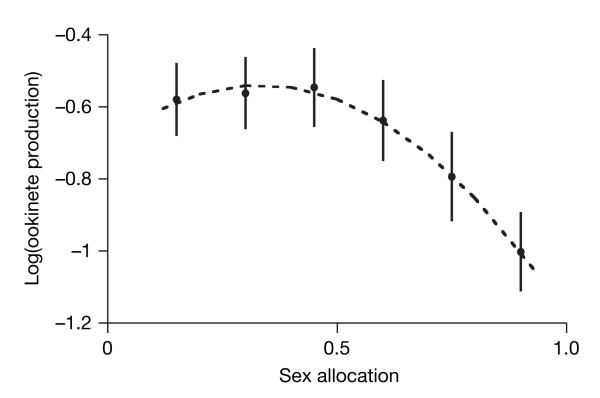
We used two genetically transformed lines of the rodent malaria Plasmodium berghei to examine the fitness consequences of sex ratio variation36,37. One parasite line (pb48/45-ko) cannot express genes essential for male-gamete fertility, so it is limited to female function; the other (pb47-ko) cannot express genes essential for female-gamete fertility, so it has only male function. Otherwise, both lines are genetically identical, exhibit normal infection dynamics and their gametocyte and gamete production is the same as their wild-type ancestor. By mixing parasites from these lines in different proportions and using in vitro fertilization culture methods, we directly manipulated mating-group sex ratio (proportion of male gametocytes) and measured the resulting reproductive success as the number of zygotes (ookinetes) produced38. As predicted by theory, mating success is maximized at intermediate sex ratios, indicating that sex allocation in malaria parasites is likely to be under stabilizing selection (Fig. 1: linear term, F1,90=40.97, P<0.0001; and quadratic term, F1,90=13.81, P=0.004). These data also support LMC theory, as mating group reproductive success is maximized at female-biased sex ratios (maximum 33% males: 95% confidence index (CI), 20–39%; see Supplementary Information). We estimate that each male produces an average of 2.03 viable gametes (95% CI, 1.56–4.00), revealing that, on average, male gametocytes fail to realize their potential fecundity of eight gametes and will become limiting to mating group productivity at extremely female-biased sex ratios. Owing to biological constraints, difficulty controlling for other relevant trade-offs, and genotype-by-environment interactions, mapping fitness across the range of sex allocation strategies has not previously been possible for malaria parasites or any other taxa. Therefore, these data are the first to unequivocally support a fundamental assumption of sex allocation as applied to any species.
Figure 1. The fitness consequences of sex ratio variation.
The relationship between sex allocation (given as proportion male) and fitness (given as log(ookinete production)) varies in the manner predicted by theory, revealing that this life-history trait of malaria parasites is important and under selection. Shown is log-transformed mean ookinetes (×106 ml−1) produced in 19 cross-factored sets of P. berghei cultures spanning 0–100% males (R2=0.77); dashed line is the fitted relationship . As expected, no ookinetes were produced in our control groups of 0% and 100% males, and we excluded these data from our analysis. Error bars, ±s.e.m.
Genetic variation for sex allocation
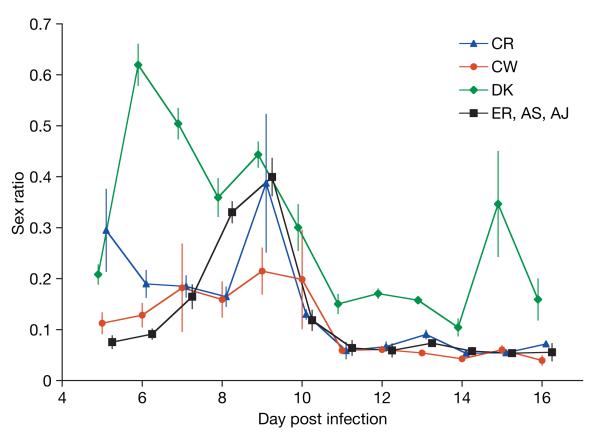
We then used wild-type clonal genotypes of the rodent malaria P. chabaudi to test, for the first time, whether there is within-species genetic variation for patterns of sex allocation in malaria parasites. We sequenced six P. chabaudi genotypes and determined that our recently developed quantitative reverse-transcription PCR assays39 for measuring sex ratios could be applied to all of them (see Supplementary Information). We initiated replicate controlled infections of each of these genotypes and measured infection parameters daily throughout the acute phase. We found that our six genotypes followed four significantly different sex allocation patterns throughout their infections (Fig. 2: χ255=159.55, P<0.0001; see Supplementary Table 1). Such genetic variation is required for selection to act, but could itself be adaptive and reflect differences in the number of gametes produced by males of different genotypes, a parameter which may also vary throughout infections30,32. If this is the case, then we can estimate the fecundity of male gametocytes from sex ratio (see Supplementary Information). In addition to controlling for variation across days, our analyses controlled for infection parameters (including virulence, anaemia, asexual parasite and gametocyte density) that could influence sex ratio and confound differences between the genotypes. Only parasite density remained in the minimal model, which correlated positively with sex ratio (χ21=5.25: P=0.022; slope=(27.35 ± 13.41)×106 ml−1).
Figure 2. Genetic variation in patterns of sex allocation.
P. chabaudi genotypes exhibit significant genetic variation in the sex ratios produced throughout their infections. Genotypes DK, CW and CR all followed significantly different sex allocation patterns but AS, AJ and ER could be grouped together. Here, and in Figs 4–6, sex ratio is given as proportion male. The means from 30 independent infections are presented and the x-axis is jittered for clarity. Error bars, ±s.e.m.
Sex ratio variation during infections
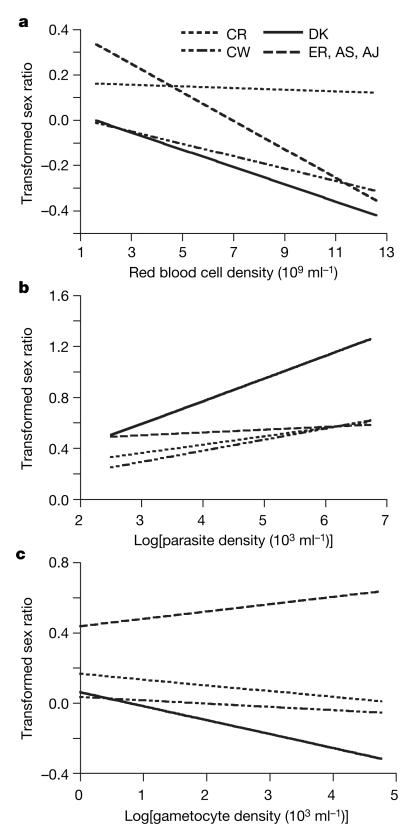
In addition to the presence of co-infecting genotypes, malaria parasites are predicted to allocate sex in response to factors that compromise their fertilization success in blood meals11,26,32,33. Specifically, a lower female-bias is predicted for a given inbreeding rate when the fertility of males is reduced by factors such as low gametocyte density, host anaemia and immunity. There are two broad reasons why these factors are expected to reduce fertilization success. First, when gametocyte density is low and/or hosts are anaemic, there is a stochastic risk of too few male gametocytes being taken up in blood meals to fertilize the females. Second, if the appearance of host factors reduces the ability of male gametocytes to produce viable gametes, there will not be enough male gametes in the blood meal to fertilize the females. When few gametocytes are able to interact in a blood meal and/or male gamete production is low, parasites are expected to increase their investment in male gametocytes to ensure their females are fertilized. Data from our single genotype infections support these predictions, and show that throughout infections sex ratios correlate negatively with red blood cell density (χ23=15.86; P=0.0012) and gametocyte density (χ23=22.11; P<0.0001), but positively with parasite density (which is related to the strength of host immune responses; χ23=35.35; P<0.0001), and that there is genetic variation for these patterns (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 3. Explaining sex ratio variation throughout infections.
Sex ratios (arcsin square-root transformed) of P. chabaudi correlate with the density of: a, red blood cells; b, parasites; and c, gametocytes. Lines are fitted from the estimates predicted by the minimal model using infection parameters observed 48 h before sex ratios (see Supplementary Information). Genotypes are grouped according to the four different sex ratio patterns followed throughout 30 independent infections (Fig. 2).
Genetic diversity and sex allocation
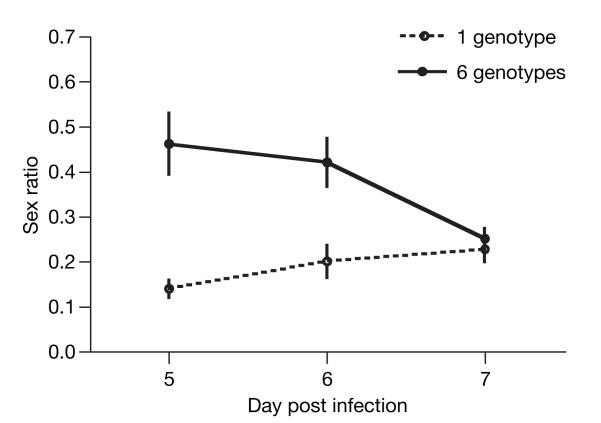
Having verified that the key assumptions of sex allocation theory are appropriate to the biology of malaria parasites, we tested whether they can facultatively respond to LMC. We compared sex ratios produced by our six single-genotype infections to sex ratios in mixed-infections consisting of all six genotypes. Our above analyses support the prediction that parasite sex ratios are influenced by other parameters11,26,32,33, so we predicted that any response to the presence of co-infecting genotypes is most likely to be detected before these factors exert their confounding influences. For all of our treatment groups, day 8 post infection (PI) was the modal day of peak parasite density, and parasite density was subsequently reduced by immune factors, anaemia and competition between genotypes. Therefore, we restricted our analyses to the period between infections becoming patent and reaching their peaks (days 5–7 PI). As predicted by LMC, sex ratios in six-genotype infections were less female-biased than in single-genotype infections, and the magnitude of this effect varied through infections (Fig. 4: χ22=19.93, P<0.0001; see Supplementary Table 3). As with the inbreeding rate and sex ratio, we found a significant negative correlation between gametocyte density and sex ratio (χ21=11.94; P<0.0001; slope=(−28.20 ± 8.18)×10−3 ml−1). Using the model of ref. 25, and assuming that male gametocytes produce up to 8 gametes on average, the predicted evolutionary stable sex ratios for single-and six-genotype infections are 0.11 (proportion male) and 0.42 respectively. At the start of infections, our data support these predictions: on days 5 and 6 PI, sex ratios were respectively 0.14 ± 0.02 and 0.20 ± 0.04 in the single-genotype infections, and 0.46 ± 0.09 and 0.42 ± 0.07 in the six-genotype infections.
Figure 4. Sex ratio varies with the genetic diversity of P. chabaudi infections.
Infections with six genotypes produced significantly less female biased sex ratios than those with one genotype, but only at the start of infections. Means are presented from 40 independent infections. Error bars, ±s.e.m.
Sex allocation in focal genotypes
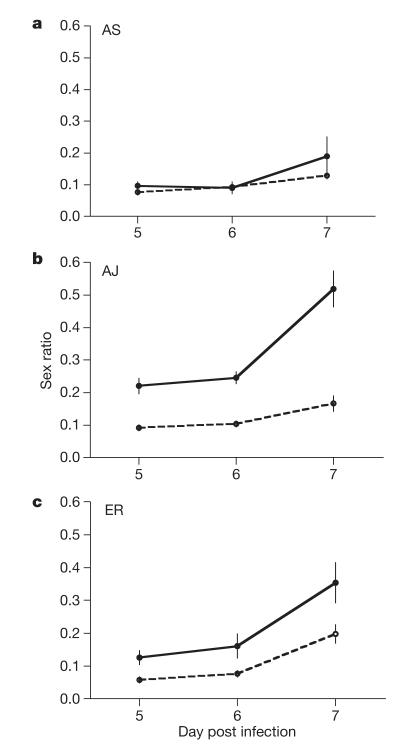
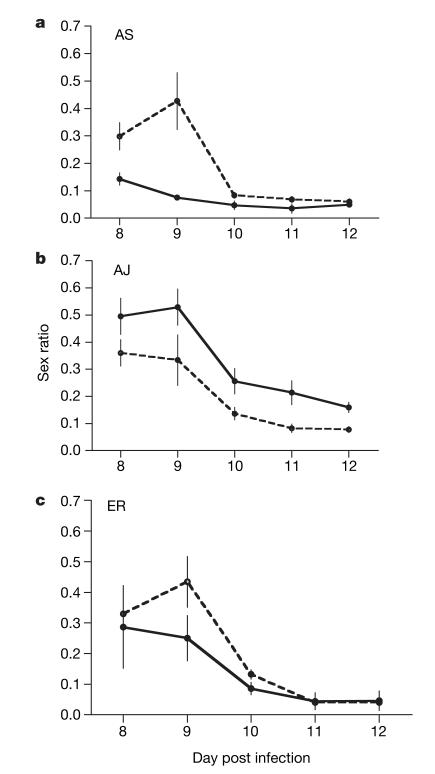
The best way to test whether parasites respond to LMC is to test whether focal genotypes alter their sex allocation in response to the presence of co-infecting genotypes. We were able to examine this for the three P. chabaudi genotypes AJ, AS and ER in single- and double-genotype infections. Our quantitative PCR assays could distinguish genotype AJ from genotypes AS and ER but not between AS and ER (see Supplementary Information). Therefore, we tested whether AS and ER independently altered their sex allocation when co-infecting with AJ, and whether AJ altered its sex allocation when co-infecting with either AS or ER. As we could confirm that parasites from both genotypes were present throughout the mixed infections, we were able to analyse sex ratios when parasites are in the growth phase (parasite density increasing) and post-peak phase (parasite density declining) of their infections. We split our analyses into the pre-peak period (days 5–7 PI) and the post-peak phase (days 8–12 PI). Because sex ratios produced by AJ when co-infecting with AS were not significantly different to those produced when co-infecting with ER (growth phase; χ21=1.66, P=0.198: post-peak phase; χ21=0.25, P=0.617), we grouped these AJ data. In the growth phase of their infections, both AJ and ER increased their investment in males when co-infecting with another genotype, as predicted by LMC, but AS did not (Fig. 5; χ22=9.98, P=0.007; see Supplementary Table 4a). Sex ratio adjustment was greater in AJ than ER and all other infection parameters fitted in the maximal model were non-significant. In contrast, during the post-peak phase only AJ increased investment in males when infecting with a second genotype; AS decreased investment in males and sex ratios were not significantly altered in ER (Fig. 6; χ22=27.33, P<0.0001; see Supplementary Table 5a). All other infection parameters fitted in the maximal model were non-significant apart from red blood cell density, which correlated positively with sex ratio (χ21=6.89, P=0.009; slope=(32.91 ± 13.06)×106 ml−1).
Figure 5. Sex ratios of focal genotypes during the growth phase of infections.
Mean sex ratios throughout the growth phase of infections for P. chabaudi focal genotypes when alone (dashed line) and co-infecting with a second genotype (solid line). a, AS; b, AJ; c, ER. Sex ratios of genotypes AS and ER could be distinguished from sex ratios of AJ but AS and ER could not be distinguished from each other (see Supplementary Information). Sex ratios produced by AJ when co-infecting with AS or ER were not significantly different so these infections are grouped. We followed 5 independent infections for each genotype combination. Error bars, ±s.e.m.
Figure 6. Sex ratios of focal genotypes during the post-peak phase of infections.
As Fig. 5 but for the post-peak phase.
Facultative sex allocation in response to infection genetic diversity of genotypes ER and AJ (when in two different co-infection scenarios) provides unequivocal support for LMC. Given this result, we extended our analysis to test whether sex allocation of focal genotypes correlates with their relative representation in infections. Theory predicts that genotypes making a small relative contribution of gametocytes to the mating group should invest in more males than when making a relatively large contribution40. Using our co-infection data, we show that there is a negative correlation between sex ratio and the proportion of gametocytes contributed by focal genotypes during the pre-peak period (χ21=16.08, P<0.0001; slope=−0.52 ± 0.12; see Supplementary Table 4b), but not during the post-peak period (χ21=2.68, P=0.102; Supplementary Table 5b). Using proportional representation within the mating group as a proxy of inbreeding rate, LMC theory predicts a sex ratio of z*=(1 – f)/2, and hence a slope of dz*/df=−0.5; thus, the pre-peak data are quantitatively consistent with LMC theory. These data support the possibility that genotypes may be able to infer their own relative frequency in infections. It is not clear why genotype AS did not produce less female-biased sex ratios in response to the presence of a co-infecting genotype. However, this genotype is substantially less virulent than genotypes AJ and ER. The least virulent genotype in our panel is DK41, and this genotype produced the least female-biased sex ratios in single infections. Virulence is a life-history trait unique to infectious organisms, and could influence reproductive strategies in malaria parasites. Understanding how malaria parasites evaluate the genetic diversity of their infections may also explain why genotype AS did not behave as predicted by LMC.
Discussion
We have tested and confirmed the assumptions and predictions of sex allocation theory in malaria parasites. The female bias typical of single-genotype infections declines towards an equal sex ratio in multiple infections. We also show that: (1) sex ratio is important and transmission studies must consider this trait alongside gametocyte density; (2) mating group productivity decreases at extremely female-biased sex ratios because male gametes become limiting; (3) within-infection sex ratio patterns are explained by variation in anaemia and parasite densities (patterns for which there is significant genetic variation); and (4) female-biased sex allocation in response to LMC decreases as infections progress and parasite densities decline due to competition, anaemia and the host’s immune response. These data support ‘fertility insurance theory’, which predicts that malaria parasites should adjust their reproductive strategies to maximize transmission opportunities throughout their infections11,26,32,33. Furthermore, our data do not support the hypothesis that malaria parasites preferentially mate with clone-mates, regardless of the genetic make-up of their mating groups42. We have shown that an evolutionary approach can be successfully applied to sex allocation in malaria parasites, suggesting that researchers in pure and applied fields can be optimistic about understanding more complex parasite life-history traits, such as virulence, that are of such economic, medical and veterinary importance43.
As infections consist of billions of parasites, the ability to distinguish clone-mates from unrelated conspecifics requires kin discrimination44,45. This discovery raises important questions. Does within-infection relatedness influence competitive interactions between genotypes and shape patterns of virulence46–48? Low relatedness between co-infecting malaria parasites is expected to favour the most virulent competitors, but related parasites could also cooperate to facilitate growth or immune evasion and result in more virulent infections. Apoptosis has recently been described in protozoan parasites49, and kin discrimination supports the possibility that this is actually an altruistic behaviour. Whether malaria parasites are using indirect (environmental) or direct (genetic) cues to discriminate kin must now be investigated. Given that P. chabaudi parasites are able to detect the presence of conspecifics in a non-natural host environment (see Supplementary Information), they may be using direct cues rather than changes to their environment. Genetic kin discrimination is rare, but can evolve in situations where marker diversity will be maintained by extrinsic processes45,50. Host–parasite interactions may provide a strong enough source of balancing selection; does pressure to evade immune recognition also enable malaria parasites to employ their sophisticated social behaviour?
METHODS
The fitness consequences of sex ratio variation
To produce P. berghei parasites for experimental cultures, we i.p. inoculated doses of 1×107 parasites into mice that had been pre-treated with phenylhydrazine (60 mg kg−1), to increase gametocyte production, 3 days before receiving their parasites. Parasites were harvested on day 3 PI to set up experimental cultures and also initiate the next set of infections. Each pb48/45-ko infection was paired with a pb47-ko infection and within each pair, parasites from the two lines were mixed in the appropriate ratios to produce each of our eight sex allocation treatments. Each pair of infections contributed parasites to one replicate of each of the following sex ratios (% male gametocytes): 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 70, 90 and 100. We paired infections based on their similarity in gametocyte densities and sex ratio to keep haematocrit at 2% for all cultures. We initiated 24 pairs of infections, over 6 blocks, and chose the 19 closest matched pairs to set up our experimental cultures. By cross-factoring each pair of infections with all sex ratio treatments we avoided confounding sex ratio with infection specific factors that could influence fertilization success (for example, gametocyte age, asexual parasite density, anaemia and immune factors in serum) and could control for pair identity (F18,90=15.39; P<0.0001). To calculate the volume of blood required from every pb47-ko infection (to contribute males), we calculated the density (per ml of mouse blood) of exflagellating males using a haemocytometer. To calculate the volume of blood required from every pb48/45-ko infection (to contribute females) we used blood smear and red blood cell density data (proportion of red blood cells containing female gametocytes×red cells per ml). Cultures contained an average of (0.5 ± 0.04)×106 gametocytes ml−1 and this variation was controlled for in our analysis (F1,90=60.93; P<0.0001). We cultured 100 μl blood in RPMI with 10% calf serum, pH 8, for 20 h at 20 °C. To count ookinetes, we vortex mixed each culture before counting the number observed in a haemocytometer.
Sequencing qRT–PCR target genes in P. chabaudi parasite lines
We have previously developed qRT–PCR to quantify total parasites, total gametocytes and male gametocytes, based on the detection of the P. chabaudi common gametocyte gene 1 (CG1) and male gametocyte gene 1 (MG1). To determine what combinations of genotypes in genetically diverse infections would enable us to follow a focal genotype we sequenced CG1 and MG1 genes in CR, ER, DK and CW P. chabaudi parasite lines. A 659 bp region of the CG1 gene and a 924 bp region of the MG1 gene were then amplified from DNA extracted from each clone and sequenced. Our AJ specific primer sets could discriminate and quantify AJ parasites, gametocytes and male gametocytes in infections with AS and ER. Our AS specific primer sets could discriminate and quantify either AS or ER parasites, gametocytes and male gametocytes in infections with AJ but could not distinguish AS from ER parasites because AS and ER share the same CG1 and MG1 alleles. The other 3 genotypes each had an AS/ER allele and an AJ allele so could not be distinguished from any others, in any combination.
Experimental design
Male MF1 mice (in-house supplier, University of Edinburgh) were infected with the clonal P. chabaudi genotypes AS, AJ, ER, CR, CW or DK (WHO Registry of Standard Malaria Parasites, The University of Edinburgh). We initiated infections with each of our six P. chabaudi genotypes on their own, in combinations of two genotypes, three genotypes and all together. We infected five mice for each of 11 treatment groups as follows: (1) six groups of single-genotype infections, consisting of 1×106 AJ, AS, ER, CR, CW or DK parasites; (2) two groups of two-genotype infections, one group with 1×106 AJ + 1×106 AS parasites and a second group with 1×106 AJ + 1×106 ER parasites; (3) one group of three-genotype infections with 1×106 AJ + 1×106 AS + 1×106 ER parasites; and (4) two identical groups of six-genotype infections with 1×105 AJ + 1×105 AS + 1×105 ER + 1×105 CR + 1×105 CW + 1×105 DK parasites. All infections were sampled in the morning when the circulating parasites were in ring or early trophozoite stages from days 5 to16 PI. Red blood cell densities were estimated using flow cytometry and reticulocyte densities were estimated from thin blood smears as previously described.
Analyses
We used R version 2.5.0 (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing; http://www.R-project.org) for all analyses. In all analyses sex ratios were arcsine square root transformed. Owing to the number of host deaths in mixed-genotype infections we maximized data resolution by restricting analyses of these data to days 5–12 PI. Statistics are presented from linear mixed-effects models of sex ratio variation throughout infections to overcome problems associated with pseudoreplication in longitudinal analysis. We evaluated the significance of fixed effects by comparing models using log-likelihood ratio tests following stepwise deletion of the least significant term. Specifically, we compared the change in model deviance, following term deletion, to χ2 distributions with degrees of freedom corresponding to the difference in number of terms in the models. We simplified maximal models using maximum likelihood techniques, until only significant terms remained in the model (α<0.05). We then re-ran minimal models using restricted maximum likelihood to estimate the effect sizes reported in the text. We do not present results for the main effects of terms contained in significant interactions.
Models included the identity of genotypes, the number of genotypes in infections and day PI as factors (as sex ratio variation over time is nonlinear), as well as relevant interactions between these terms. Where possible we grouped genotypes together when there was no significant difference in their sex ratio patterns across infections. Covariates known or suspected to influence sex ratio were fitted, including: (1) measures of virulence and anaemia (mass, red blood cells and reticulocytes); (2) relative and absolute contributions of focal genotypes’ gametocytes and asexuals to their infections; and (3) absolute number of gametocytes and asexuals in infections.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank A. P. Waters, C. Janse and M. R. van Dijk for the genetically modified parasites, and D. H. Nussey, S. A. West, A. F. Read and A. Buckling for discussions. The Wellcome Trust, NERC, BBSRC and Royal Society provided funding.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information is also linked to the online version of the paper at www.nature.com/nature.
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints.
References
- 1.Charnov EL. The Theory of Sex Allocation. Princeton Univ. Press; Princeton: 1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Frank SA. Sex allocation theory for birds and mammals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1990;21:13–55. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Frank SA. A touchstone in the study of adaptation. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution. 2002;56:2561–2564. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hamilton WD. Extraordinary sex ratios. Science. 1967;156:477–488. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hardy ICW. Sex Ratios: Concepts and Research Methods. Cambridge Univ. Press; Cambridge, UK: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ferguson DJP. Toxoplasma gondii and sex: Essential or optional extra. Trends Parasitol. 2002;18:355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ferguson DJP. More on Toxoplasma gondii, sex and premature rejection. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19:157–158. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(03)00033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Paul REL, Ariey F, Robert V. The evolutionary ecology of Plasmodium. Ecol. Lett. 2003;6:866–880. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shutler D, Bennett GF, Mullie A. Sex proportions of Haemoproteus blood parasites and local mate competition. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:6748–6752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.West SA, Reece SE, Read AF. Toxoplasma gondii, sex and premature rejection. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19:155–157. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(03)00033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reece SE, Duncan AB, West SA, Read AF. Host cell preference and variable transmission strategies in malaria parasites. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2005;272:511–517. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robert V, et al. Sex ratio of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes in inhabitants of Dielmo, Senegal. Parasitology. 2003;127:1–8. doi: 10.1017/s0031182003003299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Paul REL, Coulson TN, Raibaud A, Brey PT. Sex determination in malaria parasites. Science. 2000;287:128–131. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5450.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Paul REL, Raibaud A, Brey PT. Sex ratio adjustment in Plasmodium gallinaceum. Parassitologia. 1999;41:153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Osgood SM, Eisen RJ, Schall JJ. Gametocyte sex ratio of a malaria parasite: Experimental test of heritability. J. Parasitol. 2002;88:494–498. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2002)088[0494:GSROAM]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dye C, Godfray HCF. On sex ratio and inbreeding in malaria parasite populations. J. Theor. Biol. 1993;161:131–134. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1993.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nee S, West SA, Read AF. Inbreeding and parasite sex ratios. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2002;269:755–760. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Read AF, Anwar M, Shutler D, Nee S. Sex allocation and population-structure in malaria and related parasitic protozoa. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1995;260:359–363. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1995.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.West SA, Smith TG, Read AF. Sex allocation and population structure in apicomplexan (protozoa) parasites. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2000;267:257–263. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2000.0995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fisher RA. The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection. Clarendon; Oxford, UK: 1930. [Google Scholar]
- 21.West SA, Shuker DM, Sheldon BC. Sex-ratio adjustment when relatives interact: A test of constraints on adaptation. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution. 2005;59:1211–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paul REL, et al. Mating patterns in malaria parasite populations of Papua New Guinea. Science. 1995;269:1709–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.7569897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Conway DJ, et al. High recombination rate in natural populations of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:4506–4511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Walliker D, Babiker HA, Ranford-Cartwright LC. In: Malaria: Parasite Biology, Pathogenesis and Protection. Sherman I, editor. ASM; Washington DC: 1998. pp. 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Read AF, et al. Gametocyte sex-ratios as indirect measures of outcrossing rates in malaria. Parasitology. 1992;104:387–395. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000063630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.West SA, Reece SE, Read AF. Evolution of gametocyte sex ratios in malaria and related Apicomplexan (protozoan) parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2001;17:525–531. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(01)02058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Read AF, Smith TG, Nee S, West SA. In: Sex Ratio Handbook. Hardy ICW, editor. Cambridge Univ. Press; Cambridge, UK: 2002. pp. 314–332. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Robert V, et al. Malaria transmission in urban Sub-Saharan Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003;68:169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Robert V, et al. Effect of gametocyte sex ratio on infectivity of Plasmodium falciparum to Anopheles gambiae. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996;90:621–624. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(96)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schall JJ. Transmission success of the malaria parasite Plasmodium mexicanum into its vector: Role of gametocyte density and sex ratio. Parasitology. 2000;121:575–580. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000006818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.West SA, Griffin AS, Gardner A, Diggle SP. Social evolution theory for microorganisms. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2006;4:597–607. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gardner A, Reece SE, West SA. Even more extreme fertility insurance and the sex ratios of protozoan blood parasites. J. Theor. Biol. 2003;223:515–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(03)00142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.West SA, Smith TG, Nee S, Read AF. Fertility insurance and the sex ratios of malaria and related hemospororin blood parasites. J. Parasitol. 2002;88:258–263. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2002)088[0258:FIATSR]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pickering J, Read AF, Guerrero S, West SA. Sex ratio and virulence in two species of lizard malaria parasites. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2000;2:171–184. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Reece SE, Read AF. Malaria sex ratios. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000;15:259–260. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(00)01893-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.van Dijk MR, et al. A central role for p48/45 in malaria parasite male gamete fertility. Cell. 2001;104:153–164. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Khan SM, et al. Proteome analysis of separated male and female gametocytes reveals novel sex-specific Plasmodium biology. Cell. 2005;121:675–687. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Janse CJ, et al. In vitro formation of ookinetes and functional maturity of Plasmodium-berghei gametocytes. Parasitology. 1985;91:19–29. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Drew DR, Reece SE. Development of reverse-transcription PCR techniques to analyse the density and sex ratio of gametocytes in genetically diverse Plasmodium chabaudi infections. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007;156:199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Werren JH. Sex ratio adaptations to local mate competition in a parasitic wasp. Science. 1980;208:1157–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4448.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mackinnon MJ, Read AF. Genetic relationships between parasite virulence and transmission in the rodent malaria Plasmodium chabaudi. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution. 1999;53:689–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1999.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Razakandrainibe FG, et al. “Clonal” population structure of the malaria agent Plasmodium falciparum in high-infection regions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:17388–17393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508871102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nesse RM, Williams GC. Why We Get Sick: The New Science of Darwinian Medicine. Times Books; New York: 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mehdiabadi NJ, et al. Kin preference in a social microbe. Nature. 2006;442:881–882. doi: 10.1038/442881a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Crozier RH. Genetic clonal recognition abilities in marine-invertebrates must be maintained by selection for something else. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution. 1986;40:1100–1101. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1986.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Frank SA. A kin selection model for the evolution of virulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1992;250:195–197. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Frank SA. Kin selection and virulence in the evolution of protocells and parasites. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1994;258:153–161. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1994.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Herre EA. Population structure and the evolution of virulence in nematode parasites of fig wasps. Science. 1993;259:1442–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.259.5100.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Al-Olayan EM, Williams GT, Hurd H. Apoptosis in the malaria protozoan, Plasmodium berghei: A possible mechanism for limiting intensity of infection in the mosquito. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002;32:1133–1143. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(02)00087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rousset F, Roze D. Constraints on the origin and maintenance of genetic kin recognition. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution. 2007;61:2320–2330. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.