Abstract
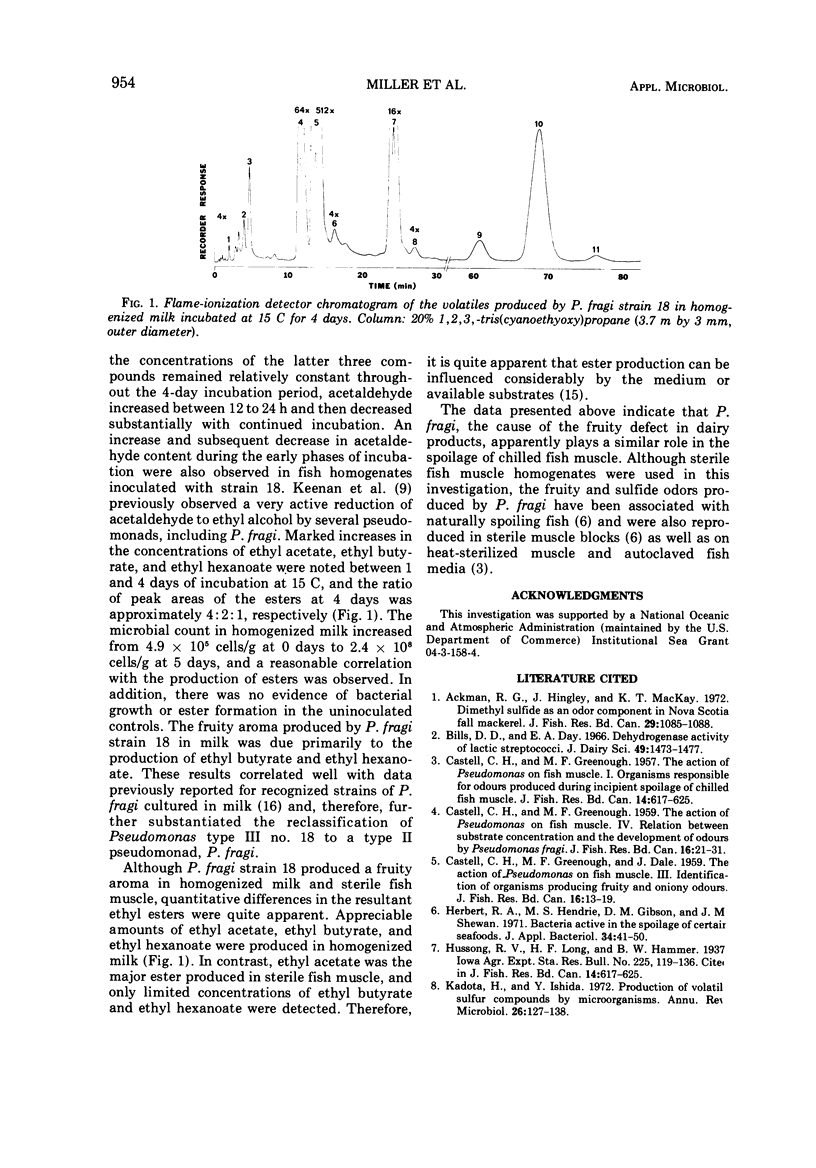
Volatile compounds produced by Pseudomonas fragi strain 18 in sterile fish muscle (Sebastes melanops) were identified by combined gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Compounds positively identified included dimethyl sulfide, acetaldehyde, ethyl acetate, ethyl alcohol, and dimethyl disulfide. Methyl mercaptan, ethyl butyrate, ethyl hexanoate, and butanone were tentatively identified by relative retention times of the authentic compounds. The fruity odor that developed in fish muscle during incipient spoilage was attributed to a synergistic flavor interaction involving the ethyl esters of acetate, butyrate, and hexanoate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bills D. D., Day E. A. Dehydrogenase activity of lactic streptococci. J Dairy Sci. 1966 Dec;49(12):1473–1477. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(66)88120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert R. A., Hendrie M. S., Gibson D. M., Shewan J. M. Symposium on microbial changes in foods. Bacteria active in the spoilage of certain sea foods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;34(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota H., Ishida Y. Production of volatile sulfur compounds by microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:127–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan T. W., Bills D. D., Lindsay R. C. Dehydrogenase activity of pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1216–1218. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1216-1218.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobben J. C., Lee J. S. Roles of microorganisms in the deterioration of rockfish. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1320-1325.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., 3rd, Scanlan R. A., Lee J. S., Libbey L. M., Morgan M. E. Volatile compounds produced in sterile fish muscle (Sebastes melanops) by Pseudomonas perolens. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):257–261. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.257-261.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., 3rd, Scanlan R. A., Lee J. S., Libbey L. M. Quantitative and selective gas chromatographic analysis of dimethyl- and trimethylamine in fish. J Agric Food Chem. 1972 May-Jun;20(3):709–710. doi: 10.1021/jf60181a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. C., Bills D. D., Lindsay R. C. Ester production by Pseudomonas fragi. II. Factors influencing ester levels in milk cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):779–782. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.779-782.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


