Abstract
Cell-mediated immune responses are essential for protection against many intracellular pathogens. For Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), protection requires the activity of T cells that recognize antigens presented in the context of both major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and I molecules. Since MHC class I presentation generally requires antigen to be localized to the cytoplasmic compartment of antigen-presenting cells, it remains unclear how pathogens that reside primarily within endocytic vesicles of infected macrophages, such as MTB, can elicit specific MHC class I-restricted T cells. A mechanism is described for virulent MTB that allows soluble antigens ordinarily unable to enter the cytoplasm, such as ovalbumin, to be presented through the MHC class I pathway to T cells. The mechanism is selective for MHC class I presentation, since MTB infection inhibited MHC class II presentation of ovalbumin. The MHC class I presentation requires the tubercle bacilli to be viable, and it is dependent upon the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP), which translocates antigenic peptides from the cytoplasm into the endoplasmic reticulum. The process is mimicked by Listeria monocytogenes and soluble listeriolysin, a pore-forming hemolysin derived from it, suggesting that virulent MTB may have evolved a comparable mechanism that allows molecules in a vacuolar compartment to enter the cytoplasmic presentation pathway for the generation of protective MHC class I-restricted T cells.
Full text
PDF

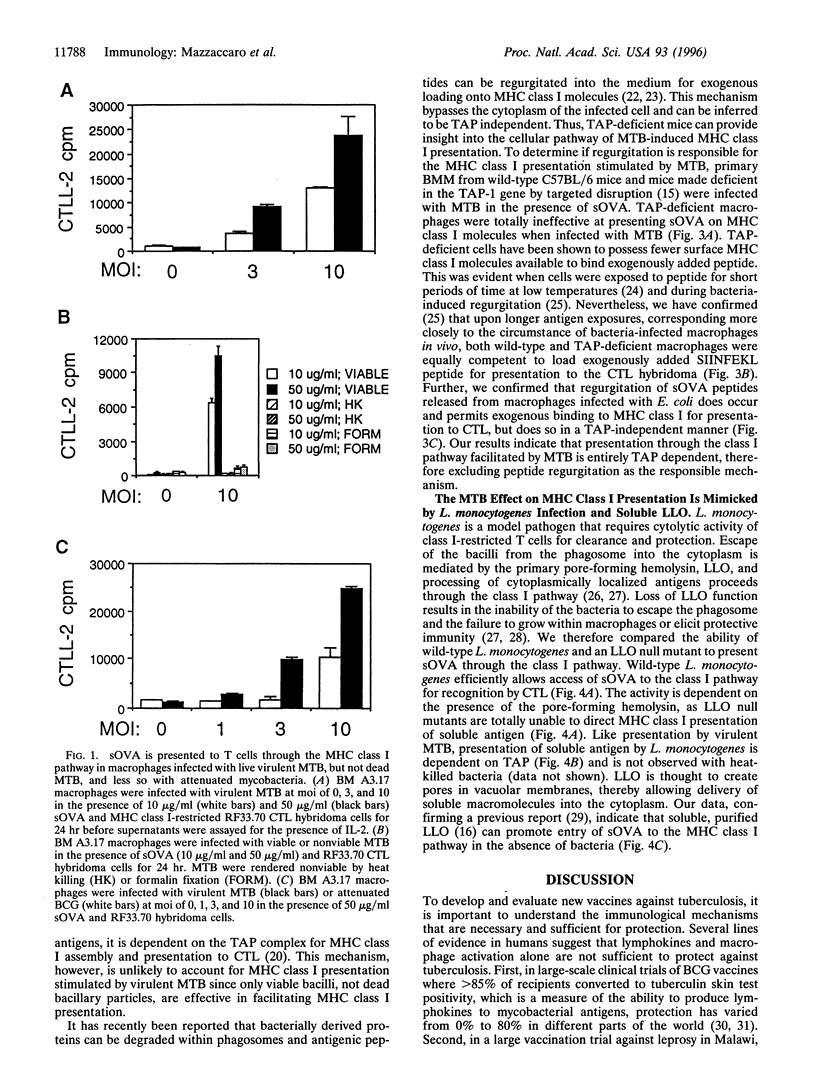
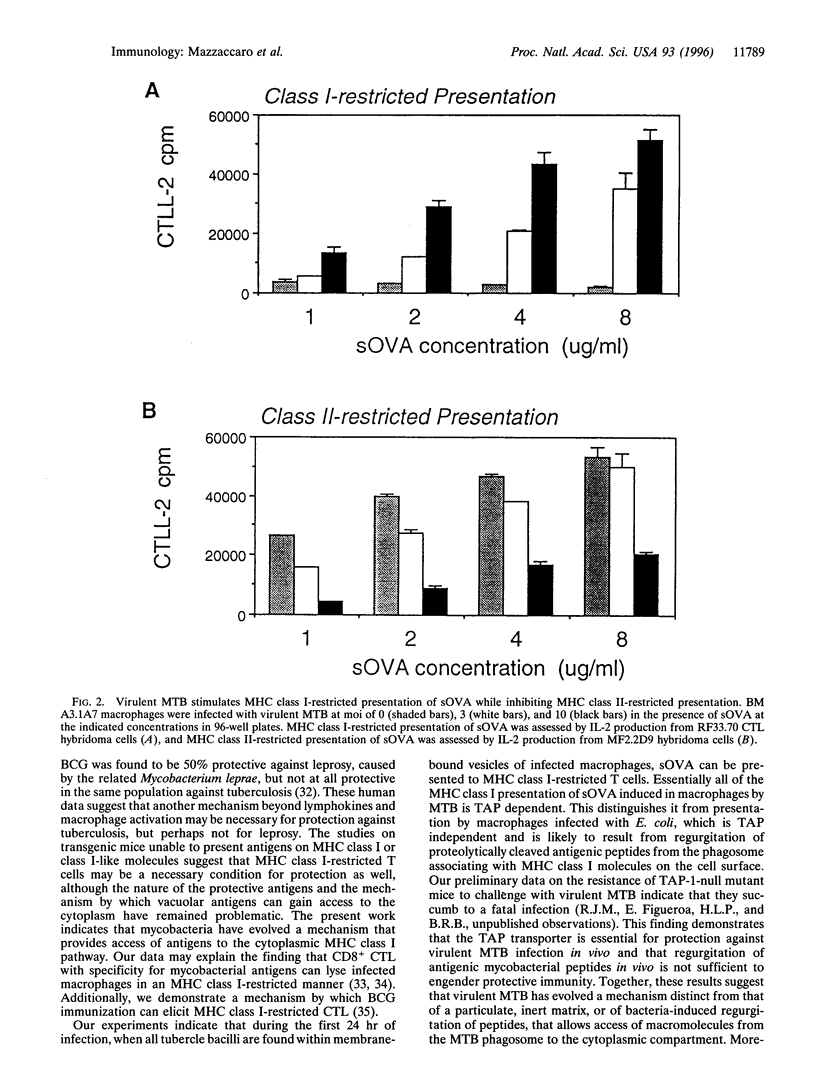
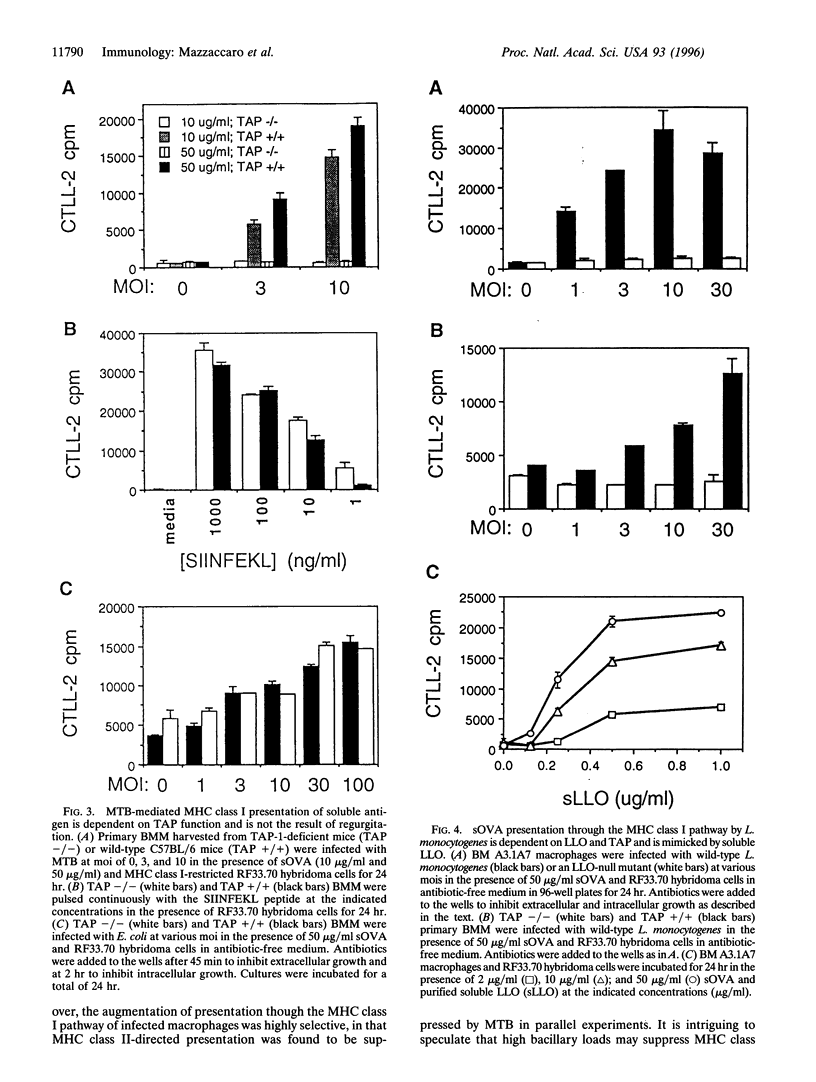

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. A., Bouwer H. G., Portnoy D. A., Hinrichs D. J. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1625–1632. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1625-1632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunt L. M., Portnoy D. A., Unanue E. R. Presentation of Listeria monocytogenes to CD8+ T cells requires secretion of hemolysin and intracellular bacterial growth. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3540–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Horwitz M. A. Characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome and evidence that phagosomal maturation is inhibited. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. M., Dalton D. K., Stewart T. A., Griffin J. P., Russell D. G., Orme I. M. Disseminated tuberculosis in interferon gamma gene-disrupted mice. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2243–2247. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darji A., Chakraborty T., Wehland J., Weiss S. Listeriolysin generates a route for the presentation of exogenous antigens by major histocompatibility complex class I. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Oct;25(10):2967–2971. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day P. M., Esquivel F., Lukszo J., Bennink J. R., Yewdell J. W. Effect of TAP on the generation and intracellular trafficking of peptide-receptive major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Immunity. 1995 Feb;2(2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(95)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Chan J., Triebold K. J., Dalton D. K., Stewart T. A., Bloom B. R. An essential role for interferon gamma in resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2249–2254. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Goldstein M. M., Chan J., Triebold K. J., Pfeffer K., Lowenstein C. J., Schreiber R., Mak T. W., Bloom B. R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is required in the protective immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Immunity. 1995 Jun;2(6):561–572. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Goldstein M. M., Triebold K. J., Koller B., Bloom B. R. Major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells are required for resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12013–12017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gercken J., Pryjma J., Ernst M., Flad H. D. Defective antigen presentation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected monocytes. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3472–3478. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3472-3478.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Song R. Phagocytic processing of exogenous particulate antigens by macrophages for presentation by class I MHC molecules. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 1;153(11):4925–4933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Sutherland I. BCG and vole bacillus vaccines in the prevention of tuberculosis in adolescence and early adult life. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 30;2(6082):293–295. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6082.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemels M. T., Ploegh H. Generation, translocation, and presentation of MHC class I-restricted peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:463–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High N., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Sansonetti P. J. IpaB of Shigella flexneri causes entry into epithelial cells and escape from the phagocytic vacuole. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1991–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics-Bankowski M., Clark K., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Efficient major histocompatibility complex class I presentation of exogenous antigen upon phagocytosis by macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics-Bankowski M., Rock K. L. A phagosome-to-cytosol pathway for exogenous antigens presented on MHC class I molecules. Science. 1995 Jan 13;267(5195):243–246. doi: 10.1126/science.7809629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. D., Oh Y. K., Portnoy D. A., Swanson J. A. Delivery of macromolecules into cytosol using liposomes containing hemolysin from Listeria monocytogenes. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 29;271(13):7249–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Robbins E. S., Nussenzweig V., Andrews N. W. The exit of Trypanosoma cruzi from the phagosome is inhibited by raising the pH of acidic compartments. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):401–413. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough K. A., Kress Y., Bloom B. R. Pathogenesis of tuberculosis: interaction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with macrophages. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2763–2773. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2763-2773.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvik Q. N., Leake E. S., Wright M. J. Disruption of phagosomal membranes of normal alveolar macrophages by the H37Rv strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A correlate of virulence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The kinetics of emergence and loss of mediator T lymphocytes acquired in response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi P., Mirza A., Bhardwaj N., Steinman R. M. Sequestration from immune CD4+ T cells of mycobacteria growing in human macrophages. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):984–986. doi: 10.1126/science.8098550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer J. D., Wick M. J., Roberts R. L., Findlay K., Normark S. J., Harding C. V. Phagocytic processing of bacterial antigens for class I MHC presentation to T cells. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):359–362. doi: 10.1038/361359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönnighaus J. M., Fine P. E., Sterne J. A., Wilson R. J., Msosa E., Gruer P. J., Jenkins P. A., Lucas S. B., Liomba N. G., Bliss L. Efficacy of BCG vaccine against leprosy and tuberculosis in northern Malawi. Lancet. 1992 Mar 14;339(8794):636–639. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis e Sousa C., Germain R. N. Major histocompatibility complex class I presentation of peptides derived from soluble exogenous antigen by a subset of cells engaged in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):841–851. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Rothstein L., Gamble S., Fleischacker C. Characterization of antigen-presenting cells that present exogenous antigens in association with class I MHC molecules. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):438–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. C., Beckers C. J., Joiner K. A. The parasitophorous vacuole membrane surrounding intracellular Toxoplasma gondii functions as a molecular sieve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):509–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H., Slifka M. K., Matloubian M., Jensen E. R., Ahmed R., Miller J. F. Recombinant Listeria monocytogenes as a live vaccine vehicle for the induction of protective anti-viral cell-mediated immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. L., Silva M. F., Pietro R. C., Lowrie D. B. Protection against tuberculosis by passive transfer with T-cell clones recognizing mycobacterial heat-shock protein 65. Immunology. 1994 Nov;83(3):341–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song R., Harding C. V. Roles of proteasomes, transporter for antigen presentation (TAP), and beta 2-microglobulin in the processing of bacterial or particulate antigens via an alternate class I MHC processing pathway. J Immunol. 1996 Jun 1;156(11):4182–4190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., de la Cruz V. F., Fuerst T. R., Burlein J. E., Benson L. A., Bennett L. T., Bansal G. P., Young J. F., Lee M. H., Hatfull G. F. New use of BCG for recombinant vaccines. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):456–460. doi: 10.1038/351456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J., Dockrell H. M. Stimulation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with live Mycobacterium bovis BCG activates cytolytic CD8+ T cells in vitro. Immunology. 1996 Mar;87(3):339–342. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1996.512590.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kaer L., Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Ploegh H. L., Tonegawa S. TAP1 mutant mice are deficient in antigen presentation, surface class I molecules, and CD4-8+ T cells. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1205–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Cooper A., Sturgill-Koszycki S., van Heyningen T., Chatterjee D., Orme I., Allen P., Russell D. G. Intracellular trafficking in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-infected macrophages. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2568–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



