Abstract
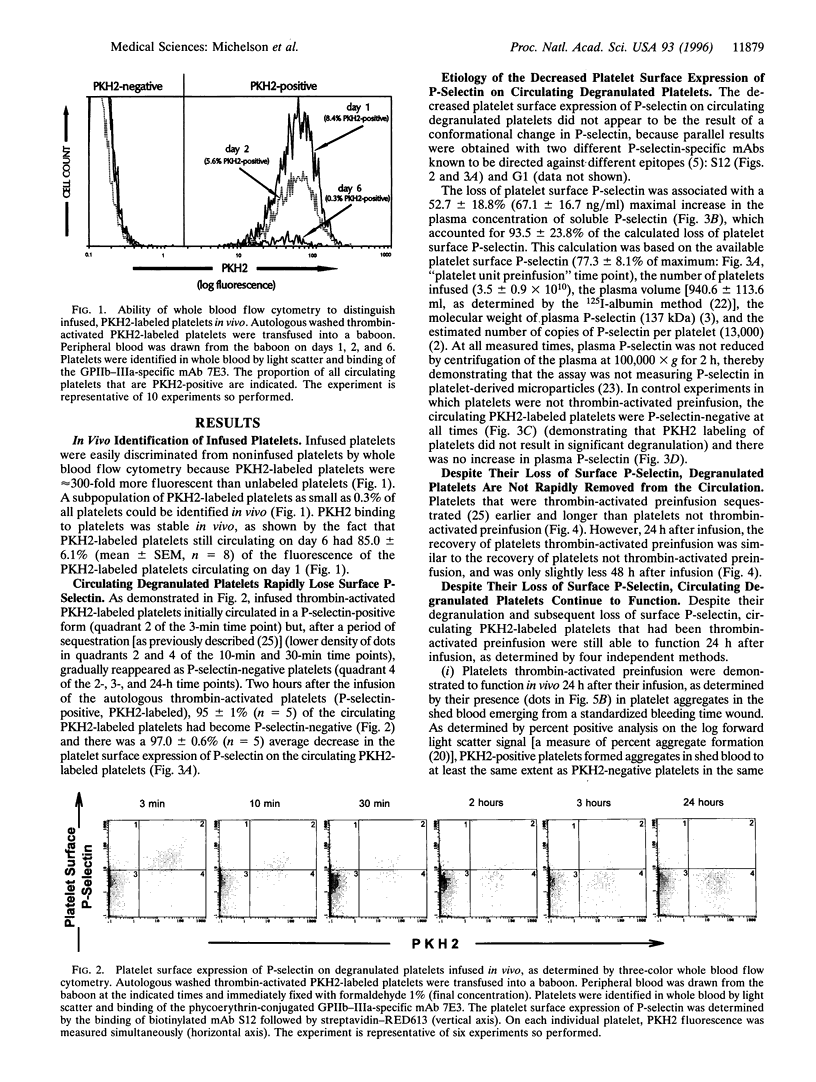
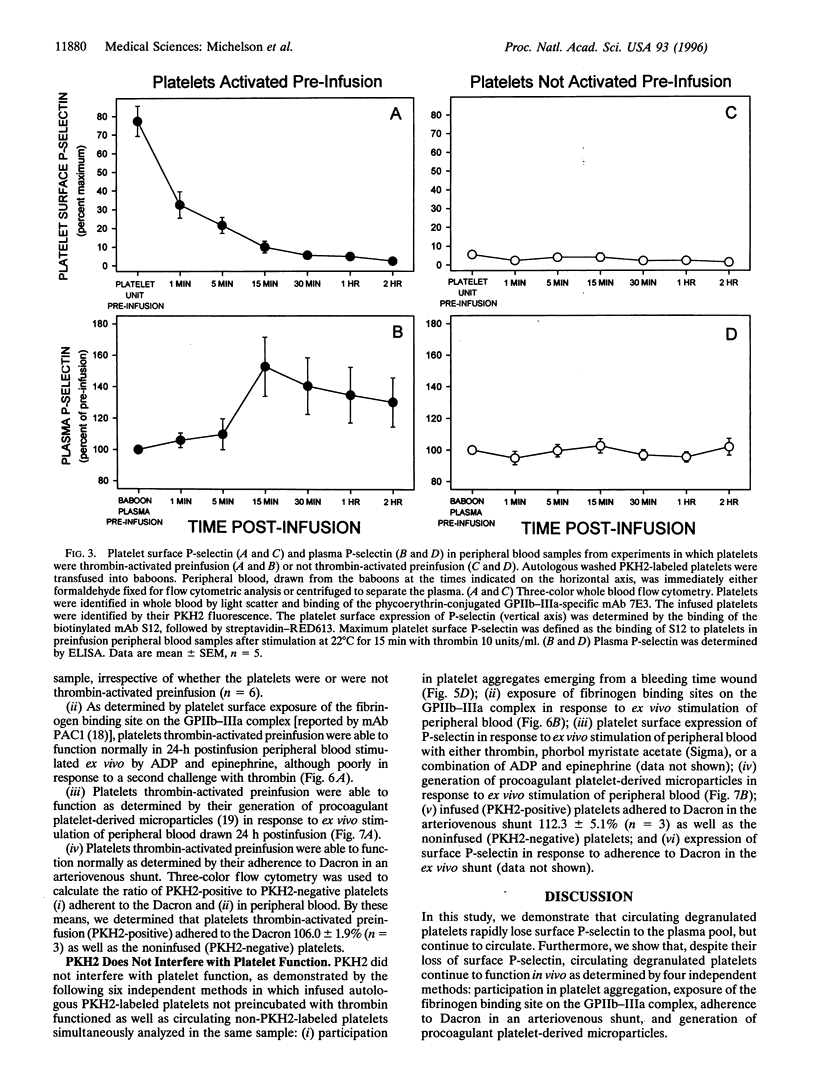
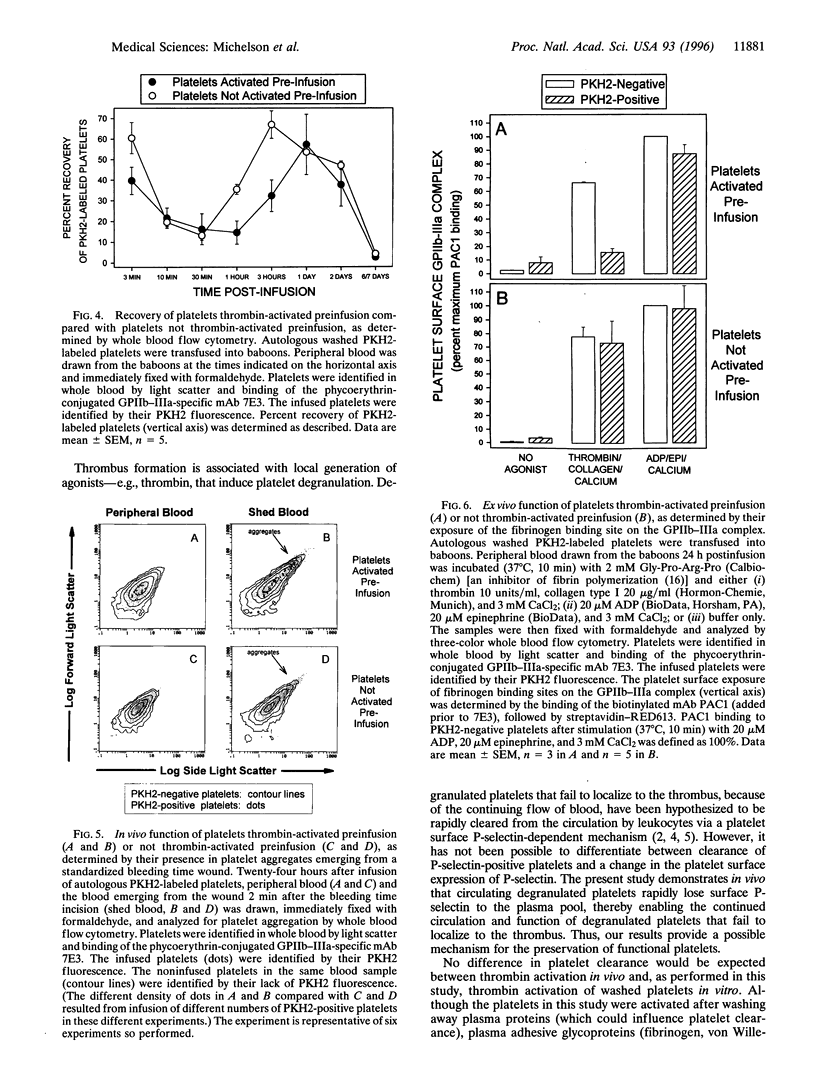
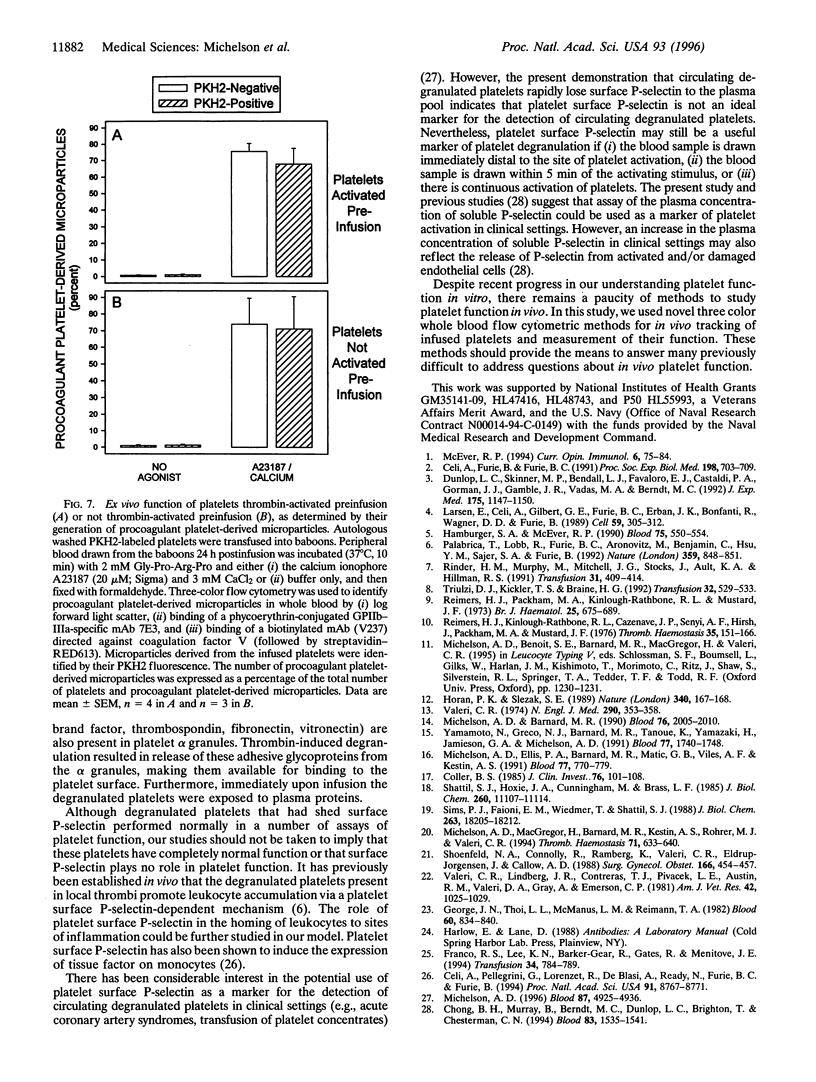
To examine the hypothesis that surface P-selectin-positive (degranulated) platelets are rapidly cleared from the circulation, we developed novel methods for tracking of platelets and measurement of platelet function in vivo. Washed platelets prepared from nonhuman primates (baboons) were labeled with PKH2 (a lipophilic fluorescent dye), thrombin-activated, washed, and reinfused into the same baboons. Three-color whole blood flow cytometry was used to simultaneously (i) identify platelets with a mAb directed against glycoprotein (GP)IIb-IIIa (integrin alpha 11b beta 3), (ii) distinguish infused platelets by their PKH2 fluorescence, and (iii) analyze platelet function with mAbs. Two hours after infusion of autologous thrombin-activated platelets (P-selectin-positive, PKH2-labeled), 95 +/- 1% (mean +/- SEM, n = 5) of the circulating PKH2-labeled platelets had become P-selectin-negative. Compared with platelets not activated with thrombin preinfusion, the recovery of these circulating PKH2-labeled, P-selectin-negative platelets was similar 24 h after infusion and only slightly less 48 h after infusion. The loss of platelet surface P-selectin was fully accounted for by a 67.1 +/- 16.7 ng/ml increase in the plasma concentration of soluble P-selectin. The circulating PKH2-labeled, P-selectin-negative platelets were still able to function in vivo, as determined by their (i) participation in platelet aggregates emerging from a bleeding time wound, (ii) binding to Dacron in an arteriovenous shunt, (iii) binding of mAb PAC1 (directed against the fibrinogen binding site on GPIIb-IIIa), and (iv) generation of procoagulant platelet-derived microparticles. In summary, (i) circulating degranulated platelets rapidly lose surface P-selectin to the plasma pool, but continue to circulate and function; and (ii) we have developed novel three-color whole blood flow cytometric methods for tracking of platelets and measurement of platelet function in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celi A., Furie B., Furie B. C. PADGEM: an adhesion receptor for leukocytes on stimulated platelets and endothelial cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Nov;198(2):703–709. doi: 10.3181/00379727-198-43309a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celi A., Pellegrini G., Lorenzet R., De Blasi A., Ready N., Furie B. C., Furie B. P-selectin induces the expression of tissue factor on monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8767–8771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong B. H., Murray B., Berndt M. C., Dunlop L. C., Brighton T., Chesterman C. N. Plasma P-selectin is increased in thrombotic consumptive platelet disorders. Blood. 1994 Mar 15;83(6):1535–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop L. C., Skinner M. P., Bendall L. J., Favaloro E. J., Castaldi P. A., Gorman J. J., Gamble J. R., Vadas M. A., Berndt M. C. Characterization of GMP-140 (P-selectin) as a circulating plasma protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1147–1150. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R. S., Lee K. N., Barker-Gear R., Gates R., Menitove J. E. Use of bi-level biotinylation for concurrent measurement of in vivo recovery and survival in two rabbit platelet populations. Transfusion. 1994 Sep;34(9):784–789. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1994.34994378280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Thoi L. L., McManus L. M., Reimann T. A. Isolation of human platelet membrane microparticles from plasma and serum. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamburger S. A., McEver R. P. GMP-140 mediates adhesion of stimulated platelets to neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Feb 1;75(3):550–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan P. K., Slezak S. E. Stable cell membrane labelling. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):167–168. doi: 10.1038/340167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen E., Celi A., Gilbert G. E., Furie B. C., Erban J. K., Bonfanti R., Wagner D. D., Furie B. PADGEM protein: a receptor that mediates the interaction of activated platelets with neutrophils and monocytes. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P. Selectins. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994 Feb;6(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(94)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. D., Barnard M. R. Plasmin-induced redistribution of platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2005–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. D., Ellis P. A., Barnard M. R., Matic G. B., Viles A. F., Kestin A. S. Downregulation of the platelet surface glycoprotein Ib-IX complex in whole blood stimulated by thrombin, adenosine diphosphate, or an in vivo wound. Blood. 1991 Feb 15;77(4):770–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. D. Flow cytometry: a clinical test of platelet function. Blood. 1996 Jun 15;87(12):4925–4936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. D., MacGregor H., Barnard M. R., Kestin A. S., Rohrer M. J., Valeri C. R. Reversible inhibition of human platelet activation by hypothermia in vivo and in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1994 May;71(5):633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palabrica T., Lobb R., Furie B. C., Aronovitz M., Benjamin C., Hsu Y. M., Sajer S. A., Furie B. Leukocyte accumulation promoting fibrin deposition is mediated in vivo by P-selectin on adherent platelets. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):848–851. doi: 10.1038/359848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimers H. J., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Cazenave J. P., Senyi A. F., Hirsh J., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. In vitro and in vivo functions of thrombin-treated platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):151–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimers H. J., Packham M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Effect of repeated treatment of rabbit platelets with low concentrations of thrombin on their function, metabolism and survival. Br J Haematol. 1973 Nov;25(5):675–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinder H. M., Murphy M., Mitchell J. G., Stocks J., Ault K. A., Hillman R. S. Progressive platelet activation with storage: evidence for shortened survival of activated platelets after transfusion. Transfusion. 1991 Jun;31(5):409–414. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1991.31591263195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld N. A., Connolly R., Ramberg K., Valeri C. R., Eldrup-Jorgensen J., Callow A. D. The systemic activation of platelets by Dacron grafts. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 May;166(5):454–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Faioni E. M., Wiedmer T., Shattil S. J. Complement proteins C5b-9 cause release of membrane vesicles from the platelet surface that are enriched in the membrane receptor for coagulation factor Va and express prothrombinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18205–18212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triulzi D. J., Kickler T. S., Braine H. G. Detection and significance of alpha granule membrane protein 140 expression on platelets collected by apheresis. Transfusion. 1992 Jul-Aug;32(6):529–533. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1992.32692367196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeri C. R. Hemostatic effectiveness of liquid-preserved and previously frozen human platelets. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):353–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeri C. R., Lindberg J. R., Contreras T. J., Pivacek L. E., Austin R. M., Valeri D. A., Gray A., Emerson C. P. Measurement of red blood cell volume, plasma volume, and total blood volume in baboons. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Jun;42(6):1025–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Greco N. J., Barnard M. R., Tanoue K., Yamazaki H., Jamieson G. A., Michelson A. D. Glycoprotein Ib (GPIb)-dependent and GPIb-independent pathways of thrombin-induced platelet activation. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1740–1748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]