Abstract
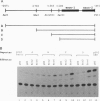
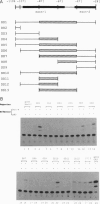
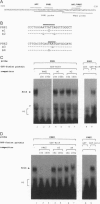
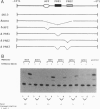
Brn-4 is a member of the POU transcription factor family and is expressed in the central nervous system. In this study, we addressed whether Brn-4 regulates expression of the D1A dopamine receptor gene. We found a functional Brn-4 responsive element in the intron of this gene by means of cotransfection chloramphenical acetyltransferase assays. This region contains two consensus sequences for binding of POU factors. Gel mobility-shift assays using glutathione S-transferase-Brn-4 fusion protein indicated that Brn-4 binds to these sequences. Both these sites are essential for transactivation by Brn-4 because deletion of either significantly reduced this enhancer activity. In situ hybridization revealed colocalization of Brn-4 and D1A mRNAs at the level of a single neuron in the rat striatum where this dopamine receptor is most abundantly expressed. Gel mobility-supershift assay using rat striatal nuclear extract and Brn-4 antibody confirmed the presence of Brn-4 in this brain region and its ability to bind to its consensus sequences in the D1A gene. These data suggest a functional role for Brn-4 in the expression of the D1A dopamine receptor gene both in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach I., Robinson D., Thomas N., Ropers H. H., Cremers F. P. Physical fine mapping of genes underlying X-linked deafness and non fra (X)-X-linked mental retardation at Xq21. Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;89(6):620–624. doi: 10.1007/BF00221950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botfield M. C., Jancso A., Weiss M. A. Biochemical characterization of the Oct-2 POU domain with implications for bipartite DNA recognition. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 30;31(25):5841–5848. doi: 10.1021/bi00140a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collarini E. J., Kuhn R., Marshall C. J., Monuki E. S., Lemke G., Richardson W. D. Down-regulation of the POU transcription factor SCIP is an early event in oligodendrocyte differentiation in vitro. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):193–200. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. N., Koike S., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Maurer R. A. Both Pit-1 and the estrogen receptor are required for estrogen responsiveness of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1964–1971. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Schimmang T., Schuhbaur B., Chambon P., Duboule D. Disruption of the Hoxd-13 gene induces localized heterochrony leading to mice with neotenic limbs. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Hamada H. A CNS-specific POU transcription factor, Brn-2, is required for establishing mammalian neural cell lineages. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90231-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrero M. R., McEvilly R. J., Turner E., Lin C. R., O'Connell S., Jenne K. J., Hobbs M. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Brn-3.0: a POU-domain protein expressed in the sensory, immune, and endocrine systems that functions on elements distinct from known octamer motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10841–10845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90104-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Rovescalli A. C., Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Structure and evolution of four POU domain genes expressed in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3280–3284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Gerrero R., Simmons D. M., Park R. E., Lin C. J., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Tst-1, a member of the POU domain gene family, binds the promoter of the gene encoding the cell surface adhesion molecule P0. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1739–1744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Binding of a Drosophila POU-domain protein to a sequence element regulating gene expression in specific dopaminergic neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):467–470. doi: 10.1038/343467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine C., Young W. S., 3rd RHS2, a POU domain-containing gene, and its expression in developing and adult rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3285–3289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Mark M., Chambon P. Disruption of the Hox-1.6 homeobox gene results in defects in a region corresponding to its rostral domain of expression. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1105–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90034-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. M., Simmons D. M., He X., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Brain 4: a novel mammalian POU domain transcription factor exhibiting restricted brain-specific expression. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2551–2561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowa M. T., Minowa T., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R., Mouradian M. M. Characterization of the 5' flanking region of the human D1A dopamine receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowa M. T., Minowa T., Mouradian M. M. Activator region analysis of the human D1A dopamine receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23544–23551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Brassard D. L., Sibley D. R. Identification and characterization of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in cultured neuroblastoma and retinoblastoma clonal cell lines. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):314–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90915-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Lemke G. Repression of the myelin P0 gene by the POU transcription factor SCIP. Mech Dev. 1993 Jul;42(1-2):15–32. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90095-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Weinmaster G., Trapp B. D., Lemke G. Expression and activity of the POU transcription factor SCIP. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1975954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Weinmaster G., Kuhn R., Lemke G. SCIP: a glial POU domain gene regulated by cyclic AMP. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazawa H., Okamoto K., Ishino F., Ishino-Kaneko T., Takeda S., Toyoda Y., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. The oct3 gene, a gene for an embryonic transcription factor, is controlled by a retinoic acid repressible enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2997–3005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfäffle R. W., DiMattia G. E., Parks J. S., Brown M. R., Wit J. M., Jansen M., Van der Nat H., Van den Brande J. L., Rosenfeld M. G., Ingraham H. A. Mutation of the POU-specific domain of Pit-1 and hypopituitarism without pituitary hypoplasia. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz J. L., Sharp P. A., Pabo C. O. Structure-based design of transcription factors. Science. 1995 Jan 6;267(5194):93–96. doi: 10.1126/science.7809612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radovick S., Nations M., Du Y., Berg L. A., Weintraub B. D., Wondisford F. E. A mutation in the POU-homeodomain of Pit-1 responsible for combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijli F. M., Mark M., Lakkaraju S., Dierich A., Dollé P., Chambon P. A homeotic transformation is generated in the rostral branchial region of the head by disruption of Hoxa-2, which acts as a selector gene. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1333–1349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90620-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain transcription factors: pou-er-ful developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):897–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saugier-Veber P., Abadie V., Moncla A., Mathieu M., Piussan C., Turleau C., Mattei J. F., Munnich A., Lyonnet S. The Juberg-Marsidi syndrome maps to the proximal long arm of the X chromosome (Xq12-q21). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1040–1045. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., West B. L., Baxter J. D. Synergistic activation of the rat growth hormone promoter by Pit-1 and the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):656–665. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1584227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi K., Miyai K., Notomi T., Kaibe K., Amino N., Mizuno Y., Kohno H. Cretinism with combined hormone deficiency caused by a mutation in the PIT1 gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):56–58. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner E. E., Jenne K. J., Rosenfeld M. G. Brn-3.2: a Brn-3-related transcription factor with distinctive central nervous system expression and regulation by retinoic acid. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Alkema M. J., van Weperen W. W., Van Leeuwen H. C., Strating M. J., van der Vliet P. C. The DNA binding specificity of the bipartite POU domain and its subdomains. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4993–5003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Drolet D. W., Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain proteins: structure and function of developmental regulators. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. M., Levey A. I., Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Brann M. R. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor mRNA in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1859–1863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. V., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Modulation of memory fields by dopamine D1 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Nature. 1995 Aug 17;376(6541):572–575. doi: 10.1038/376572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M., Hu X. T., Cooper D. C., Moratalla R., Graybiel A. M., White F. J., Tonegawa S. Elimination of cocaine-induced hyperactivity and dopamine-mediated neurophysiological effects in dopamine D1 receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):945–955. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M., Moratalla R., Gold L. H., Hiroi N., Koob G. F., Graybiel A. M., Tonegawa S. Dopamine D1 receptor mutant mice are deficient in striatal expression of dynorphin and in dopamine-mediated behavioral responses. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):729–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90557-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., McDonough J., Fyodorov D., Morris M., Wang F., Deneris E. S. Characterization of an acetylcholine receptor alpha 3 gene promoter and its activation by the POU domain factor SCIP/Tst-1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10252–10264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Li C., Civelli O. Characterization of gene organization and promoter region of the rat dopamine D1 receptor gene. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1875–1883. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]