Abstract
Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) share a wide range of diverse biological activities. To date, low levels of FGF have not been correlated with a pathophysiologic state. We report that blood vessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats are shown to be associated with a marked decrement in endothelial basic FGF content. This decrement correlates both with hypertension and with a decrease in the endothelial content of nitric oxide synthase. Restoration of FGF to physiological levels in the vascular wall, either by systemic administration or by in vivo gene transfer, significantly augmented the number of endothelial cells with positive immunostaining for nitric oxide synthase, corrected hypertension, and ameliorated endothelial-dependent responses to vasoconstrictors. These results suggest an important role for FGFs in blood pressure homeostasis and open new avenues for the understanding of the etiology and treatment of hypertension.
Full text
PDF
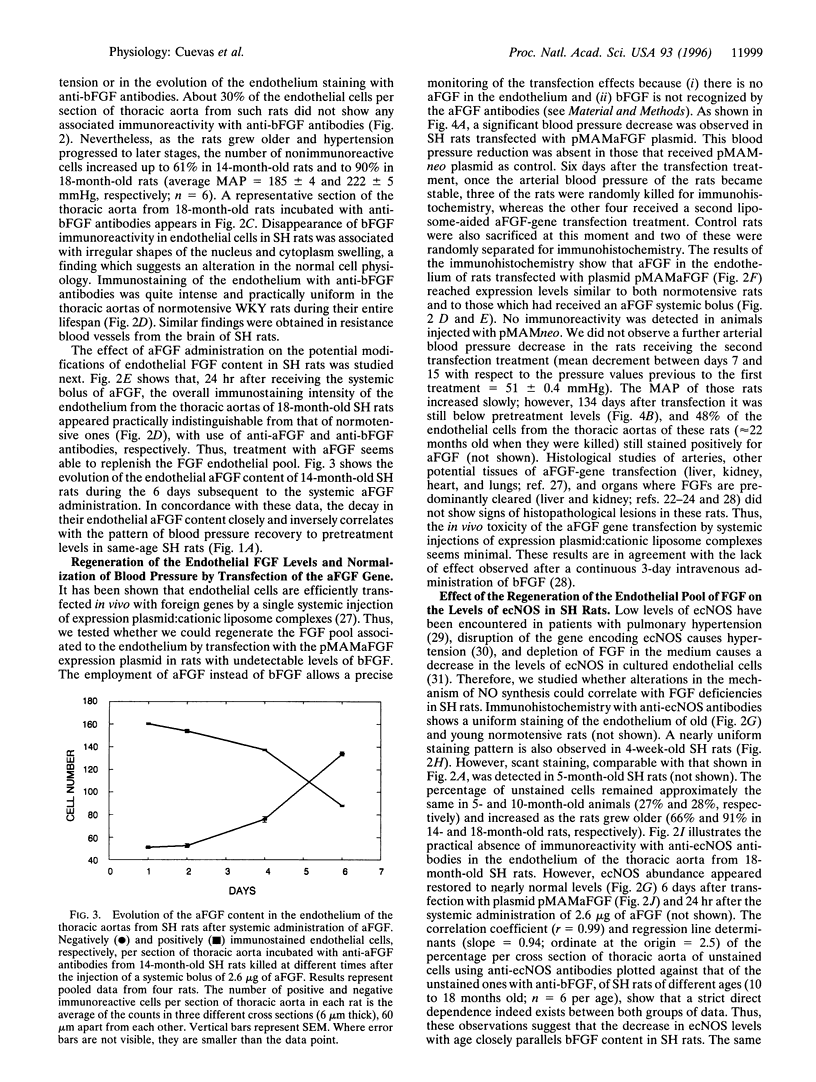
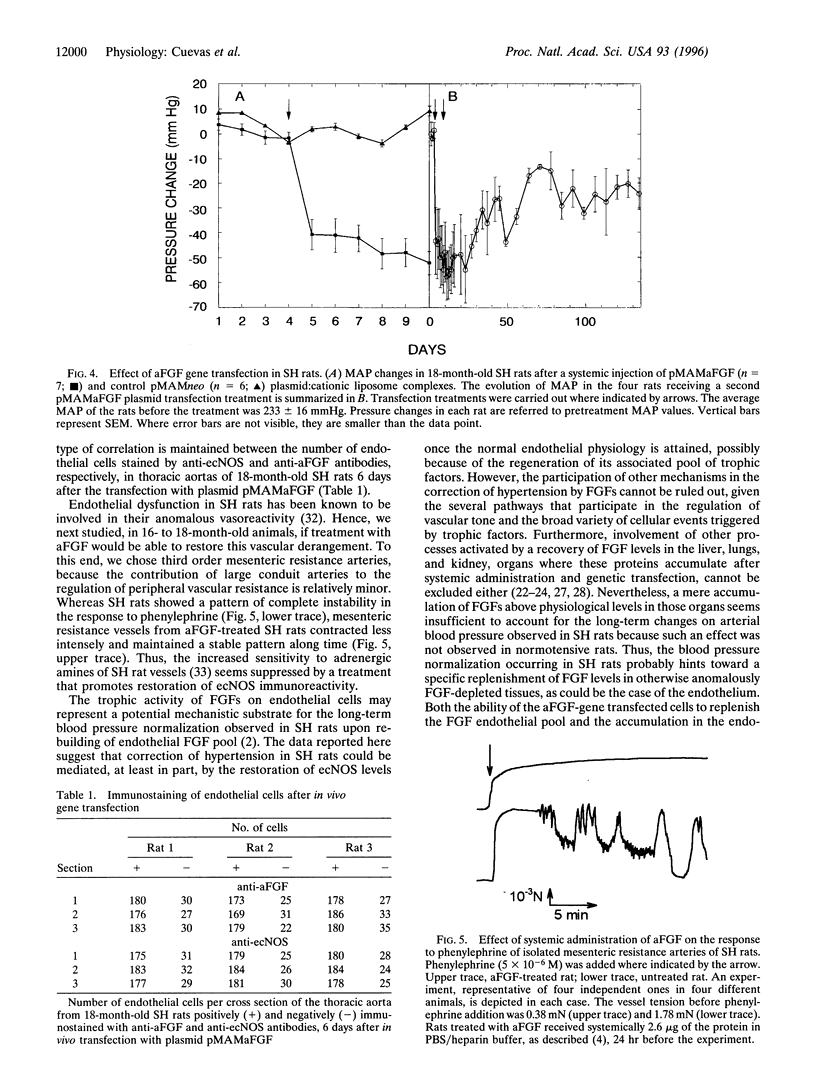

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avidor R., Eilam R., Malach R., Gozes I. VIP-mRNA is increased in hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 4;503(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91679-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busconi L., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase. N-terminal myristoylation determines subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8410–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriaco E., Abbate F., Ferrante F., Laurà R., Amenta F. Structural changes in the endothelium of the femoral artery of spontaneously hypertensive rats: sensitivity to isradipine treatment. J Hypertens. 1993 May;11(5):515–522. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199305000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Vlodavsky I., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Hicklin D., Fuks Z. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):832–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas P., Carceller F., Ortega S., Zazo M., Nieto I., Giménez-Gallego G. Hypotensive activity of fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1208–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.1957172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debs R. J., Freedman L. P., Edmunds S., Gaensler K. L., Düzgünes N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulation of gene expression in vivo by liposome-mediated delivery of a purified transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10189–10192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohi Y., Thiel M. A., Bühler F. R., Lüscher T. F. Activation of endothelial L-arginine pathway in resistance arteries. Effect of age and hypertension. Hypertension. 1990 Aug;16(2):170–179. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante F., Abbate F., Ciriaco E., Laurà R., Amenta F. Influence of isradipine treatment on the morphology of the aorta in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1994 May;12(5):523–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X., Huang L. A novel cationic liposome reagent for efficient transfection of mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):280–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91366-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaid A., Saleh D. Reduced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 27;333(4):214–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507273330403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Gallego G., Cuevas P. Fibroblast growth factors, proteins with a broad spectrum of biological activities. Neurol Res. 1994 Aug;16(4):313–316. doi: 10.1080/01616412.1994.11740246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H. J., Fiedler U., Blödner R. Pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Eur Heart J. 1995 Feb;16(2):243–252. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. L., Huang Z., Mashimo H., Bloch K. D., Moskowitz M. A., Bevan J. A., Fishman M. C. Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):239–242. doi: 10.1038/377239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishai-Michaeli R., Svahn C. M., Weber M., Chajek-Shaul T., Korner G., Ekre H. P., Vlodavsky I. Importance of size and sulfation of heparin in release of basic fibroblast growth factor from the vascular endothelium and extracellular matrix. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):2080–2088. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyk S. K., Kourembanas S., Wheeler E. L., Medeiros D., McQuillan L. P., D'Amore P. A., Braunhut S. J. Basic fibroblast growth factor increases nitric oxide synthase production in bovine endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1995 Nov;269(5 Pt 2):H1583–H1589. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1995.269.5.H1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Rascher W., Unger T., Ganten D. Reduced content of vasopressin in the brain of spontaneously hypertensive as compared to normotensive rats. Neurosci Lett. 1981 May 6;23(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher T. F., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent contractions to acetylcholine in the aorta of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1986 Apr;8(4):344–348. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.4.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M., Keller M. A specific deficiency in paraventricular vasopressin and oxytocin in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 7;249(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M., Wren J. A., Sundberg D. K. Central neural peptides and catecholamines in spontaneous and DOCA/salt hypertension. Peptides. 1981 Summer;2(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(81)80035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka A., Lovenberg W. Regional changes in the activities of aminergic biosynthetic enzymes in the brains of hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 15;43(4):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., AOKI K. Development of a strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Jpn Circ J. 1963 Mar;27:282–293. doi: 10.1253/jcj.27.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer J. M., Pfeffer M. A., Frohlich E. D. Validity of an indirect tail-cuff method for determining systolic arterial pressure in unanesthetized normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Dec;78(6):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengart T. K., Kuperschmid J. P., Maciag T., Clark R. E. Pharmacokinetics and distribution of heparin-binding growth factor I (endothelial cell growth factor) in the rat. Circ Res. 1989 Feb;64(2):227–234. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen G. F., Shing Y., Folkman J. The fate of intravenously administered bFGF and the effect of heparin. Growth Factors. 1989;1(2):157–164. doi: 10.3109/08977198909029125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zazo M., Lozano R. M., Ortega S., Varela J., Díaz-Orejas R., Ramírez J. M., Giménez-Gallego G. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of shortened and full-length human acidic fibroblast growth factor and purification in a form stable in aqueous solutions. Gene. 1992 Apr 15;113(2):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90400-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N., Liggitt D., Liu Y., Debs R. Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):209–211. doi: 10.1126/science.7687073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]