Abstract
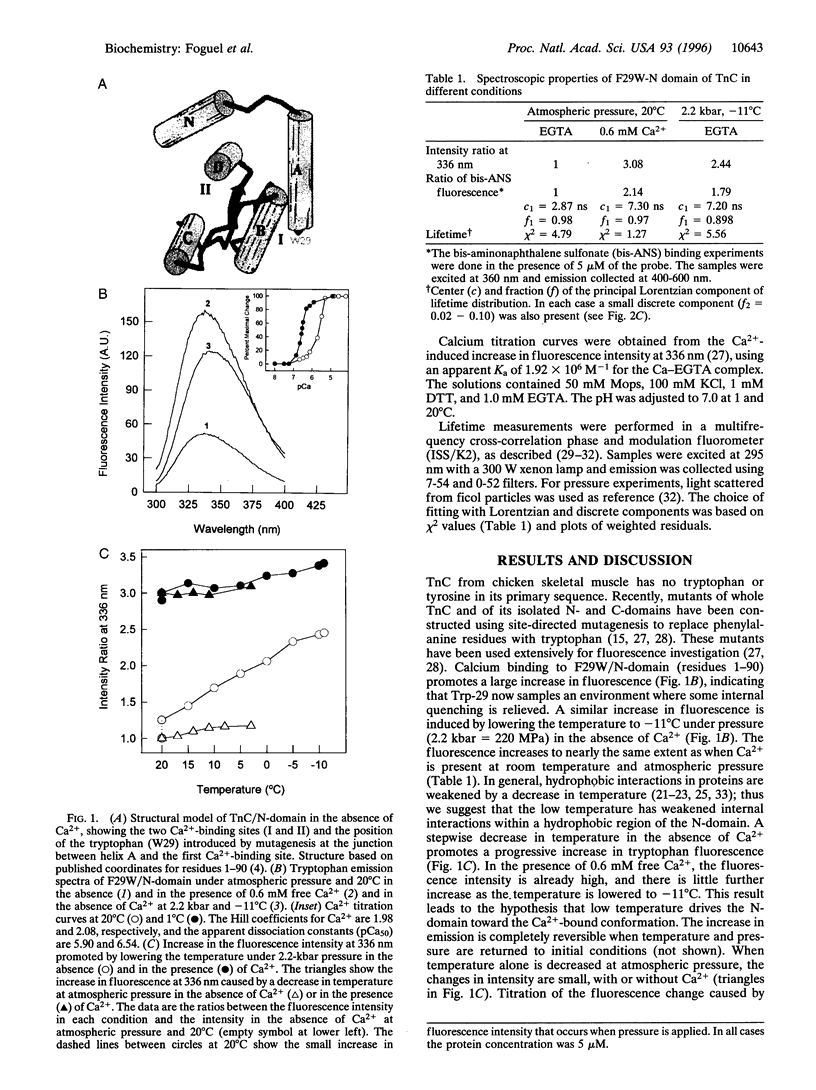
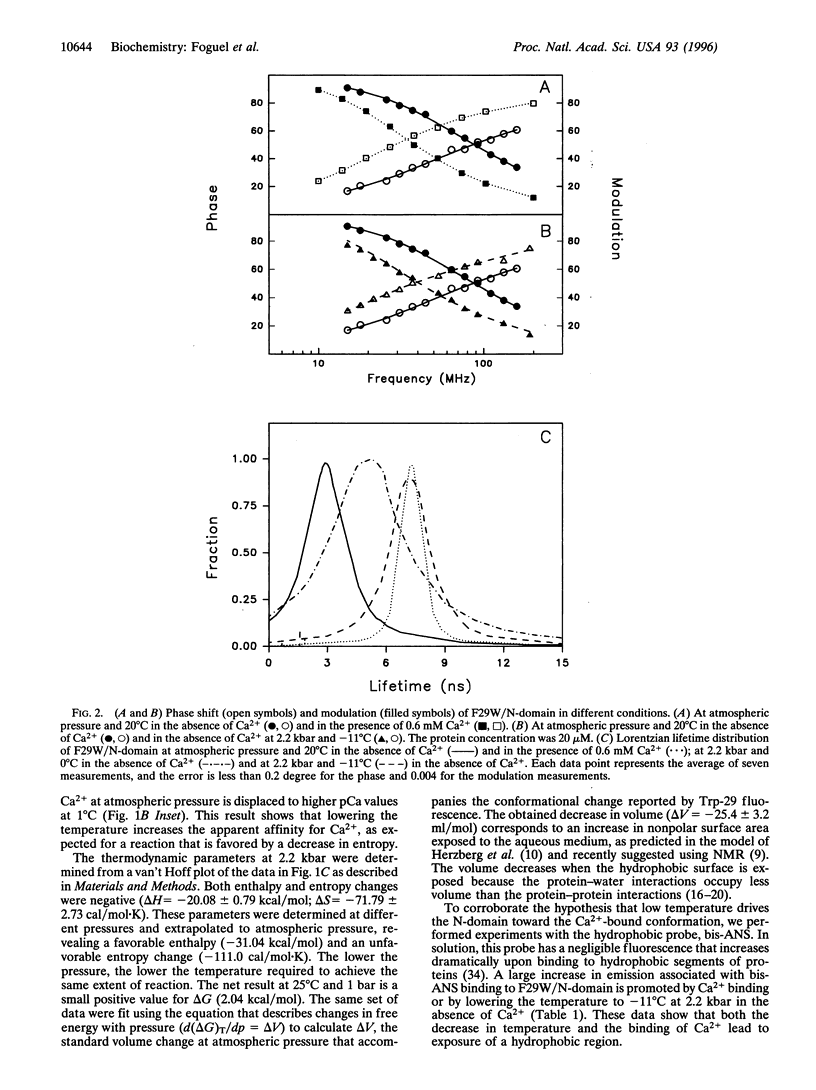
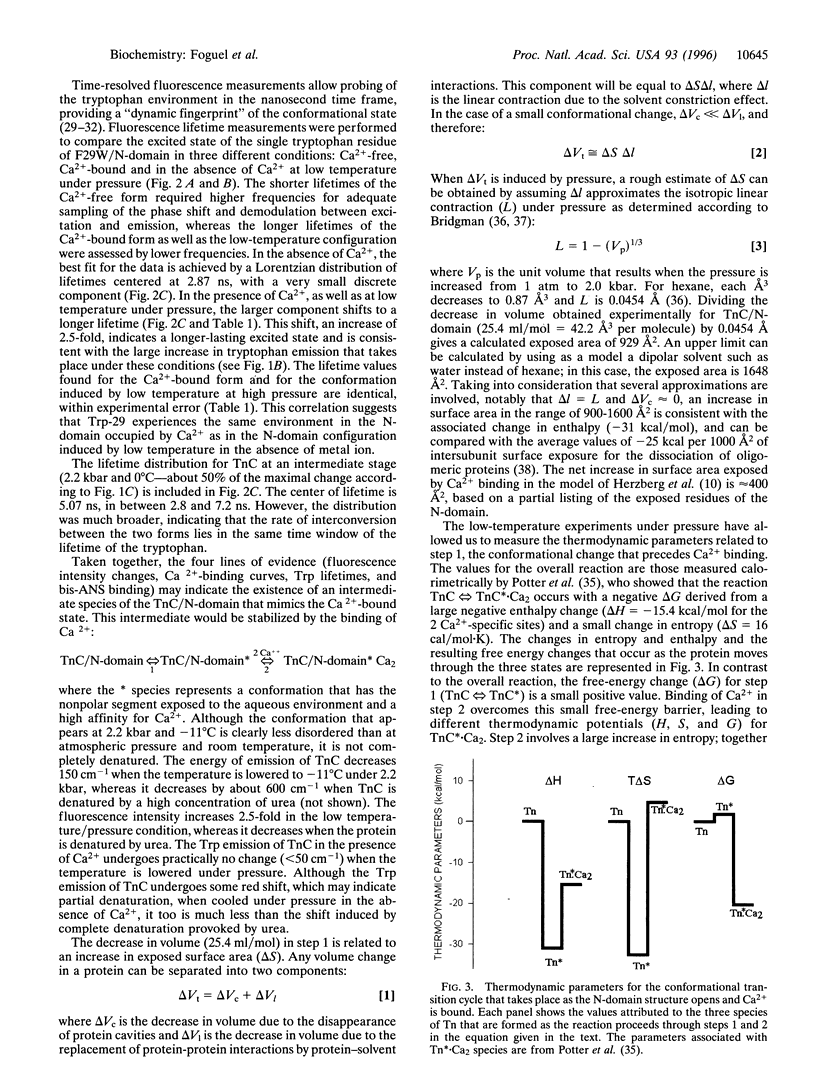
Calcium binding to the N-domain of troponin C initiates a series of conformational changes that lead to muscle contraction. Calcium binding provides the free energy for a hydrophobic region in the core of N-domain to assume a more open configuration. Fluorescence measurements on a tryptophan mutant (F29W) show that a similar conformational change occurs in the absence of Ca2+ when the temperature is lowered under pressure. The conformation induced by subzero temperatures binds the hydrophobic probe bis-aminonaphthalene sulfonate, and the tryptophan has the same fluorescence lifetime (7 ns) as in the Ca2+-bound form. The decrease in volume (delta V = -25.4 ml/mol) corresponds to an increase in surface area. Thermodynamic measurements suggest an enthalpy-driven conformational change that leads to an intermediate with an exposed N-domain core and a high affinity for Ca2+.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcala J. R., Gratton E., Prendergast F. G. Fluorescence lifetime distributions in proteins. Biophys J. 1987 Apr;51(4):597–604. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83384-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah C. S., Reinach F. C. The troponin complex and regulation of muscle contraction. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):755–767. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.9.7601340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foguel D., Silva J. L. Cold denaturation of a repressor-operator complex: the role of entropy in protein-DNA recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8244–8247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foguel D., Teschke C. M., Prevelige P. E., Jr, Silva J. L. Role of entropic interactions in viral capsids: single amino acid substitutions in P22 bacteriophage coat protein resulting in loss of capsid stability. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 31;34(4):1120–1126. doi: 10.1021/bi00004a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foguel D., Weber G. Pressure-induced dissociation and denaturation of allophycocyanin at subzero temperatures. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 1;270(48):28759–28766. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori K., Sorenson M., Herzberg O., Moult J., Reinach F. C. Probing the calcium-induced conformational transition of troponin C with site-directed mutants. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):182–184. doi: 10.1038/345182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné S. M., Tsuda S., Li M. X., Chandra M., Smillie L. B., Sykes B. D. Quantification of the calcium-induced secondary structural changes in the regulatory domain of troponin-C. Protein Sci. 1994 Nov;3(11):1961–1974. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné S. M., Tsuda S., Li M. X., Smillie L. B., Sykes B. D. Structures of the troponin C regulatory domains in the apo and calcium-saturated states. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Sep;2(9):784–789. doi: 10.1038/nsb0995-784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Tan R. Y., Wang J., Tao T., Gergely J. Inhibition of mutant troponin C activity by an intra-domain disulphide bond. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):132–135. doi: 10.1038/345132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Tao T., Gergely J. Molecular mechanism of troponin-C function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Aug;13(4):383–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01738034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4226–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Jaenicke R. Proteins under pressure. The influence of high hydrostatic pressure on structure, function and assembly of proteins and protein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 15;221(2):617–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C. W., Hunziker W. Intracellular calcium-binding proteins: more sites than insights. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90041-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J., James M. N. A model for the Ca2+-induced conformational transition of troponin C. A trigger for muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2638–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J., Jonas A. High-pressure NMR spectroscopy of proteins and membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:287–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Laczko G., Cherek H., Gratton E., Limkeman M. Analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics from variable-frequency phase shift and modulation data. Biophys J. 1984 Oct;46(4):463–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84043-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. X., Chandra M., Pearlstone J. R., Racher K. I., Trigo-Gonzalez G., Borgford T., Kay C. M., Smillie L. B. Properties of isolated recombinant N and C domains of chicken troponin C. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 1;33(4):917–925. doi: 10.1021/bi00170a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. X., Gagné S. M., Tsuda S., Kay C. M., Smillie L. B., Sykes B. D. Calcium binding to the regulatory N-domain of skeletal muscle troponin C occurs in a stepwise manner. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8330–8340. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., Borgford T., Chandra M., Oikawa K., Kay C. M., Herzberg O., Moult J., Herklotz A., Reinach F. C., Smillie L. B. Construction and characterization of a spectral probe mutant of troponin C: application to analyses of mutants with increased Ca2+ affinity. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6545–6553. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Hsu F. J., Pownall H. J. Thermodynamics of Ca2+ binding to troponin-C. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2452–2454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Cold denaturation of proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(4):281–305. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C. R., Sligar S. G. Hydrostatic and osmotic pressure as tools to study macromolecular recognition. Methods Enzymol. 1995;259:395–427. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)59054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. G., Weber G. Dimer formation from 1-amino-8-naphthalenesulfonate catalyzed by bovine serum albumin. A new fluorescent molecule with exceptional binding properties. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3915–3920. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyshur K. A., Rao S. T., Pyzalska D., Drendel W., Greaser M., Sundaralingam M. Refined structure of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C in the two-calcium state at 2-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1628–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. L., Foguel D., Da Poian A. T., Prevelige P. E. The use of hydrostatic pressure as a tool to study viruses and other macromolecular assemblages. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996 Apr;6(2):166–175. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(96)80071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. L., Silveira C. F., Correia Júnior A., Pontes L. Dissociation of a native dimer to a molten globule monomer. Effects of pressure and dilution on the association equilibrium of arc repressor. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 20;223(2):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90669-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. L., Weber G. Pressure stability of proteins. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1993;44:89–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.44.100193.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Bergstrom R., Strasburg G., Rao S. T., Roychowdhury P., Greaser M., Wang B. C. Molecular structure of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle at 3-angstrom resolution. Science. 1985 Feb 22;227(4689):945–948. doi: 10.1126/science.3969570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva A. C., de Araujo A. H., Herzberg O., Moult J., Sorenson M., Reinach F. C. Troponin-C mutants with increased calcium affinity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):599–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]