Abstract
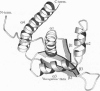
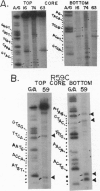
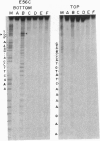
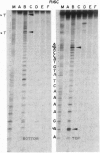
The replication terminator protein (RTP) of Bacillus subtilis is a homodimer that binds to each replication terminus and impedes replication fork movement in only one orientation with respect to the replication origin. The three-dimensional structure of the RTP-DNA complex needs to be determined to understand how structurally symmetrical dimers of RTP generate functional asymmetry. The functional unit of each replication terminus of Bacillus subtilis consists of four turns of DNA complexed with two interacting dimers of RTP. Although the crystal structure of the RTP apoprotein dimer has been determined at 2.6-A resolution, the functional unit of the terminus is probably too large and too flexible to lend itself to cocrystallization. We have therefore used an alternative strategy to delineate the three dimensional structure of the RTP-DNA complex by converting the protein into a site-directed chemical nuclease. From the pattern of base-specific cleavage of the terminus DNA by the chemical nuclease, we have mapped the amino acid to base contacts. Using these contacts as distance constraints, with the crystal structure of RTP, we have constructed a model of the DNA-protein complex. The biological implications of the model have been discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bussiere D. E., Bastia D., White S. W. Crystal structure of the replication terminator protein from B. subtilis at 2.6 A. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrigan C. M., Pack R. A., Smith M. T., Wake R. G. Normal terC-region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome acts in a polar manner to arrest the clockwise replication fork. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90206-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Ebright R. H. Phenyl-azide-mediated photocrosslinking analysis of Cro-DNA interaction. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):453–460. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumoulin P., Oertel-Buchheit P., Granger-Schnarr M., Schnarr M. Orientation of the LexA DNA-binding motif on operator DNA as inferred from cysteine-mediated phenyl azide crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2030–2034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright Y. W., Chen Y., Pendergrast P. S., Ebright R. H. Incorporation of an EDTA-metal complex at a rationally selected site within a protein: application to EDTA-iron DNA affinity cleaving with catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) and Cro. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10664–10670. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermácora M. R., Delfino J. M., Cuenoud B., Schepartz A., Fox R. O. Conformation-dependent cleavage of staphylococcal nuclease with a disulfide-linked iron chelate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks A. H., Griffiths A. A., Wake R. G. Identification and characterization of new DNA replication terminators in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jul;17(1):13–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17010013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul S., Mohanty B. K., Sahoo T., Patel I., Khan S. A., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis functions as a polar contrahelicase in gram-negative Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11143–11147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri G. S., MacAllister T., Sista P. R., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of E. coli is a DNA sequence-specific contra-helicase. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley D. B., Smith M. T., Lewis P. J., Wake R. G. Protein-nucleoside contacts in the interaction between the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and the DNA terminator. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):771–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Ralston G. B., Christopherson R. I., Wake R. G. Identification of the replication terminator protein binding sites in the terminus region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome and stoichiometry of the binding. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90147-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Smith M. T., Wake R. G. A protein involved in termination of chromosome replication in Bacillus subtilis binds specifically to the terC site. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3564–3567. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3564-3567.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manna A. C., Pai K. S., Bussiere D. E., White S. W., Bastia D. The dimer-dimer interaction surface of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3253–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarelli J. M., Ermácora M. R., Fox R. O., Grindley N. D. Mapping interactions between the catalytic domain of resolvase and its DNA substrate using cysteine-coupled EDTA-iron. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):2979–2986. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty B. K., Sahoo T., Bastia D. The relationship between sequence-specific termination of DNA replication and transcription. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2530–2539. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley M. G., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the GCN4 DNA binding domain characterized by affinity cleaving. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.2111578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai K. S., Bussiere D. E., Wang F., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, White S. W., Bastia D. The structure and function of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis: identification of the 'winged helix' DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1996 Jun 17;15(12):3164–3173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan C. Q., Landgraf R., Sigman D. S. DNA-binding proteins as site-specific nucleases. Mol Microbiol. 1994 May;12(3):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Lobert M., Manna A. C., Bastia D. The contrahelicase activities of the replication terminator proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis are helicase-specific and impede both helicase translocation and authentic DNA unwinding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29138–29144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Patel I., Bastia D. Termination of DNA replication in vitro: requirement for stereospecific interaction between two dimers of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and with the terminator site to elicit polar contrahelicase and fork impedance. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):619–628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Langley D. B., Young P. A., Wake R. G. The minimal sequence needed to define a functional DNA terminator in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1994 Aug 19;241(3):335–340. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Wake R. G. Definition and polarity of action of DNA replication terminators in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):648–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. Sequential replication of Bacillus subtilis chromosome. I. Comparison of marker frequencies in exponential and stationary growth phases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:559–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. Sequential replication of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. II. Isotopic transfer experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:806–813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. A., Wake R. G. The Bacillus subtilis replication terminator system functions in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 22;240(4):275–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]