Abstract
Peyronie’s disease (PD) is a condition of the penis, characterized by the presence of localized fibrotic plaque in the tunica albuginea. PD is not an uncommon disorder, with recent epidemiologic studies documenting a prevalence of 3–9% of adult men affected. The actual prevalence of PD may be even higher. It is often associated with penile pain, anatomical deformities in the erect penis, and difficulty with intromission. As the definitive pathophysiology of PD has not been completely elucidated, further basic research is required to make progress in the understanding of this enigmatic condition. Similarly, research on effective therapies is limited. Currently, nonsurgical treatments are used for those men who are in the acute stage of PD, whereas surgical options are reserved for men with established PD who cannot successfully penetrate. Intralesional treatments are growing in clinical popularity as a minimally invasive approach in the initial treatment of PD. A surgical approach should be considered when men with PD do not respond to conservative, medical, or minimally invasive therapies for approximately 1 year and cannot have satisfactory sexual intercourse. As scientific breakthroughs in the understanding of the mechanisms of this disease process evolve, novel treatments for the many men suffering with PD are anticipated.
Keywords: oral therapy, intralesional treatment, topical therapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, traction devices, plication, incision and grafting, penile prosthesis
Introduction
Peyronie’s disease (induratio penis plastica; PD) is a condition of the penis, characterized by the presence of localized fibrotic plaques in the tunica albuginea and affecting 3.2–8.9% of the adult male population.1–3 The true prevalence of PD may be even higher as many patients are reluctant to discuss their condition with a physician or may not seek medical help if the symptoms are not disabling.4 At present, most authorities support the hypothesis that PD generally arises from repetitive (micro)trauma to the erect penis during sexual activities. However, not all penile trauma leads to the development of PD. Abnormal wound healing appears to be more common in men with PD and there is evidence for a genetic predisposition.5 Furthermore, studies have shown that risk factors for atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and smoking are more common in men with PD.6–8
The underlying etiology of PD appears to be an imbalance between profibrotic and antifibrotic substances. Profibrotic substances include transforming growth factor β-1 (TGF-β1), fibrin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, and are found to be overexpressed or aberrantly expressed.9 Antifibrotic substances include matrix metalloproteinases, which are a class of molecules responsible for collagen degradation.10 The wound healing cascade begins with exposure of platelets to collagen and the release of chemoattractant molecules such as TGF-β1, platelet-derived growth factor, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1, and fibrin, which act as a matrix for repair.9 Inhibition of the fibrinolytic system or an inability to degrade the intravasated fibrin leads to its persistence in the tunica and continues to exert a proinflammatory response.11 This response ultimately leads to the formation of a palpable plaque secondary to the excessive deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix, with disorganization of collagen fibers and loss of elastic fibers.11 There are other theories on plaque formation which include cytokine and/or growth factor overexpression and free radical production.12
PD usually presents in men aged 40–70 years and has two phases. The acute phase, lasting for 6–18 months, is often characterized by the development of penile curvature and onset of pain with erection. The acute phase is followed by a chronic phase, characterized by negligible penile pain, and the establishment of a stable penile abnormality.6 Patients presenting with PD can exhibit any single or combination of penile plaque, curvature, pain, and erectile dysfunction (ED). Plaques are typically located on the dorsal or lateral aspect of the penis, causing an upward or lateral defection during erection. As many patients are embarrassed by or unaware of their PD, they are unlikely to mention the topic unless specifically questioned by a treating physician.13 PD is generally a progressive disorder that uncommonly resolves completely. It is difficult to predict an individual’s prognosis at the initiation of the disease. Only penile pain, if present, resolves spontaneously within the first year in the majority of patients.14 In most circumstances, PD progressively worsens over time, as reported in 48% of men with PD in a recent study.15 Two-thirds of patients with PD are likely to have risk factors for arterial disease and therefore will develop ED over the long term.8 Treatment options are chosen based upon disease severity, patient preference, and surgeon’s training. Options include oral medications, intralesional injection therapy, plication procedures, incision and grafting, and placement of a penile prosthesis with or without manual modeling or other ancillary straightening techniques.2
Nonsurgical treatment of PD
Numerous nonsurgical treatment options have been utilized since PD was first descriptively named in 1743. The majority of studies evaluating oral medications lack controls or an adequate number of subjects, are of short duration, and focus on reduction of deformity as the critical measurement of outcome.16 Despite various reports in the literature of deformity stabilization and/or reduction outcomes, recent guidelines indicate that the available evidence shows generally no significant benefit from oral therapies for reducing penile deformity.16,17 However, the standard of care still involves an initial trial of either oral or intralesional treatment at first presentation.13 An accepted goal of medical therapy is to shorten the acute phase of PD in order to stabilize the plaque or diminish disease progression.18
Oral therapy
Vitamin E (tocopherol)
Vitamin E is a fat soluble natural antioxidant that theoretically plays a role in DNA repair.13 Its antioxidant properties have been hypothesized to inhibit nitric oxide synthesis as well as oxygen free radical-induced fibrosis in human cavernosal cells.19 Despite double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studies showing no significant improvement, tocopherol remains the most common nonsurgical therapy because of its safety, availability, and low cost.20,21
Potassium para-aminobenzoate (Potaba®)
Potassium para-aminobenzoate was first introduced in 1959 as an oral therapy for PD after it was shown to decrease collagen production in vitro when added to fibroblast cells.22 Its hypothesized mechanism of action involves the enhancement of three endogenous antifibrotic processes: oxygen uptake, glycosaminoglycan secretion, and monoamine oxidase activity.23 Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studies evaluating the efficacy of Potaba have been published. Shah et al in 1983 reported improvement of symptoms, particularly pain, when compared to placebo; however, these findings were not statistically significant.24 In a more recent study in 2005, Weidner et al published results that demonstrated significant stabilization of preexisting penile deviation and reduction of plaque size, but no significant reduction of pain or preexisting curvature.25 Potaba is currently a first-line therapy for PD because of its tolerability and availability.23
Colchicine
The mechanism of action of colchicine remains unknown but it is hypothesized to reduce lactic acid production, which decreases uric acid deposition and decrease collagen synthesis.13 Akkus et al demonstrated a reduction in plaque size, degree of curvature, and pain symptoms in response to colchicine therapy.26 In another uncontrolled study, Kadioglu et al demonstrated that the efficacy of colchicine increases when used in specified patient groups without any vascular disease risk factors, presenting in the first 6 months of disease, a degree of curvature less than 30 degrees, and without ED.27 A recent nonrandomized study demonstrated that using tocopherol with colchicine in the early stages of PD reduced plaque size, curvature, and pain.28 A recent study by Akman et al retrospectively evaluated patients that were treated with colchicine in the acute phase of PD. They found that the predictive factors for curvature alterations in PD patients were mild deformities mainly in those with lateral curvature, which mostly shifted to the dorsal side after treatment.29 However, another double-blind placebo-controlled study by Safarinejad demonstrated no difference in pain relief, plaque size, or penile curvature.30 Further studies are necessary to clarify the beneficial effects of colchicine in the treatment of PD. The side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.13
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is a nonsteroidal antiestrogen. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it is hypothesized to modulate TGF-β1, which reduces fibrosis.13 Two uncontrolled studies, Apaydin et al in 199831 and Ralph et al in 1992,32 reported a decrease of plaque size, penile deviation, and pain. However the results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized study done by Teloken et al reported that the effect on curvature, plaque size, and pain was not significant.33 In the absence of a demonstrable benefit, this drug is not routinely recommended for the treatment of PD.
L-carnitine
L-carnitine’s mechanism of action is not fully understood but it is hypothesized to increase mitochondrial respiration, which decreases free radical formation.34 Biagiotti and Cavallini performed a double-blind, randomized study in 2001 that compared acetyl-L-carnitine with tamoxifen, which was previously shown to have no benefit over placebo, and demonstrated that acetyl-L-carnitine was more effective in reducing pain and disease progression.35 Cavallini et al in 2002 compared the efficacy of oral propionyl-L-carnitine or tamoxifen combined with intralesional verapamil injections. They demonstrated that the combination of propionyl-L-carnitine and verapamil was efficacious and suggested it as the treatment of choice for advanced PD.36 Another doubleblind, placebo-controlled, randomized study by Safarinejad et al in 2007 found that oral propionyl-L-carnitine treatment was not superior to placebo.20 It is possible that an insufficient dose of this agent was used in light of a recent review suggesting that the minimum dose necessary for an effect was at least 3–3.5 g per day.37 The drug has a relatively safe profile, with reported side effects of mild euphoria and gastrointestinal upset.34
Pentoxifylline
Pentoxifylline is a nonspecific phosphodiesterase inhibitor with a hypothesized mechanism of action of upregulating cyclic adenosine monophosphate and decreasing type I collagen production, which remedies the abnormal collagen phenomenon.34 Valente et al in 2003 collected data from in vivo and in vitro models that demonstrated decreased levels of profibrotic factors and plaque size after treatment with pentoxifylline.38 Other studies document that pentoxifylline reduced calcium content in the plaque and collagen fiber deposition and altered elastogenesis by antagonizing the effects of TGF-β1.39–41 Safarinejad et al conducted a doubleblind, placebo-controlled, randomized study that reported a significant effect of pentoxifylline therapy on reducing penile curvature and plaque volume particularly in patients in the early stages of established PD.42 These somewhat promising results with pentoxifylline need further confirmation. This drug is associated with relatively mild side effects, most commonly nausea, dizziness, and headache.34
Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors
PDE5 inhibitors have been shown to decrease oxidative stress-associated inflammatory changes, as observed in the pathophysiology of PD. Its mechanism of action results in an increase of cavernosal smooth muscle levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate. PDE5 inhibitors, when given continuously over long periods, induce an elevation of nitric oxide and cyclic guanosine monophosphate which act as antifibrotic agents to reduce collagen deposition, profibrotic factor release, oxidative stress, and myofibroblast numbers.11 Levine and Latchamsetty demonstrated that sildenafil was a safe, effective, and well-tolerated first-line therapy for PD patients with ED.43 In another study by Levine et al, sildenafil reduced the incidence of postoperative ED in patients who underwent surgical correction of PD using pericardial grafting after plaque incision. However these results were not statistically significant.44 Valente et al performed a study in a rat model with a PD-like plaque induced by TGF-β1, demonstrating that sildenafil caused a reduction in plaque size.38 Ferrini et al performed a similar rat model study with a PD-like plaque elicited by TGF-β1 or fibrin injection into the tunica albuginea. Long-term oral treatment with vardenafil slowed and reversed the early stages of the PD-like plaque in this rat model.45 Chung et al reported septal scar resolution and improved International Index of Erectile Function-5 questionnaire symptom scores in a study with low-dose daily tadalafil.46 Palmieri et al concluded that extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in addition to 5 mg of tadalafil once daily produced significant improvement in erectile function and quality of life for patients with PD and ED.47 Further studies are mandated before any of these methods of treatment can be recommended.
The oral pharmacotherapies as evaluated by randomized controlled trials are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Efficacy of oral therapy evaluated by randomized trials
| Treatment | Study | Mode of study | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E (tocopherol) | Safarinejad et al20 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | No significant difference |
| Potaba® | Shah et al24 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | No significant difference |
| Weidner et al25 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | Decreased plaque size in treatment arm | |
| Colchicine | Safarinejad30 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | No significant difference |
| Tamoxifen | Teloken et al33 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | No significant difference |
| L-carnitine | Biagiotti and Cavallini35 | Double-blind | Decreased plaque size, curvature, and penile pain |
| Pentoxifylline | Safarinejad et al42 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | Decreased penile curvature and plaque volume in early chronic Peyronie’s disease |
Intralesional injection therapy
Corticosteroids
The mechanism of action of corticosteroids was hypothesized to inhibit phospholipase A2 and suppress immune response.48 Historically, the first documented use of intralesional corticosteroids for PD was reported by Bodner et al in 1954, which noted a decrease in plaque size and penile pain following therapy.49 Follow-up studies demonstrated that corticosteroid injections had no therapeutic benefit,50,51 as seen in the single-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized study performed by Cipollone et al in 1998, which showed no statistically significant benefit.52 Lack of evidence for benefit and side effects such as local tissue atrophy, fibrosis, and immune suppression currently limit the clinical use of this option. Therefore corticosteroid injections are not currently recommended as an intralesional therapy for PD.23
Collagenase
Collagenase, also classified as specific matrix metal loproteinase-1, 8, and 13, degrades interstitial collagens, specifically type II collagen.13 The therapeutic potential of collagenase was initially introduced more than two decades ago in both in vitro and in vivo studies by Gelbard et al.53,54 These researchers utilized highly purified clostridial collagenases to test their effect on various human tissues in vitro, including human pericardium, human corpus cavernosum, tunica albuginea, and PD plaques. These experiments with collagenase resulted in a remarkable reduction in the size of the PD plaque, along with microscopic fraying and dispersal of collagen bundles, when compared with plaques injected with normal saline. Moreover, elastic fibers, vascular smooth muscle, and axonal myelin sheaths were not affected by collagenase application.53 In the following period, the investigators performed an in vivo pilot study that injected intralesional collagenase in 31 men with PD.54 After 4 weeks of treatment, 65% of patients exhibited objective improvement, 93% reported elimination of pain, and intercourse was restored in 75% of patients. Additionally, the researchers noted that penile plaques were either significantly altered or disappeared in four patients and reduced by 20%–100% in 16 others. Studies have reported that immunoglobulin G antibodies to collagenase were higher in men with PD versus healthy men, implying that intralesional collagenase has a documented benefit.55 A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study demonstrated a significant response with collagenase injections in patients with small plaques and minor penile deformity.56 Although not placebo-controlled, a recent study employing two intralesional collagenase injections within 24–72 hours over three injection cycles demonstrated improvement with decreases in both plaque size and penile curvature in men with PD.57 Collagenase can be used in both the acute and chronic phases of PD. Because of its potential efficacy, intralesional collagenase has just completed phase III clinical trials in men with PD. Collagenase is associated with minimal adverse side effects such as injection site pain, ecchymosis, and rarely corporal rupture.13,23
Verapamil
Verapamil is a calcium channel antagonist that augments collagenase activity, increases cytokine expression associated with early inflammation and wound formation, and inhibits in vitro fibroblast proliferation in PD plaques.58,59 Levine et al in 1994 reported that intralesional verapamil injection resulted in a significant reduction in penile curvature.60 Additional uncontrolled studies have reported a decrease in penile pain, curvature, deformity, an increase in girth and rigidity, improved erectile function, and subjective softening of the plaque.61,62 Rehman et al performed the only randomized placebo-controlled study in 1998 with verapamil injection therapy and demonstrated that there was no statistically significant change in penile curvature reduction.63 Because only one study evaluating the efficacy of verapamil included a placebo arm, more controlled studies are required. Verapamil remains a relatively safe and inexpensive form of therapy with minor adverse effects such as nausea, lightheadedness, penile pain, and ecchymosis.23
Interferons
Interferons are cytokines that play a regulatory role in the inflammatory response of the immune system. Interferon-α-2b inhibits the proliferation of fibroblasts, increases collagenase activity, decreases collagen production, and has been used in a number of studies for intralesional injection treatment of P D. 18 Initial in vitro studies demonstrated the inhibitory role of interferon-α and interferon-β on collagen production in fibroblasts derived from Peyronie’s plaques.64 Since then, several studies confirmed the beneficial effect in men with PD.65–68 Two single-blind, placebo-controlled studies showed a statistically significant benefit of interferon-α-2b with improvements in penile curvature, plaque size and density, penile pain on erection, erectile function, and penile hemodynamics. This therapy is associated with minor side effects such as sinusitis, minor penile swelling with ecchymosis, and flu-like symptoms of fever, chills, and arthralgia.69,70 The use of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory agents prior to intralesional injection can abrogate the flu-like such effect.
Randomized controlled intralesional therapy studies are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Efficacy of intralesional therapy evaluated by randomized trials
| Treatment | Study | Mode of study | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Cipollone et al52 | Placebo-controlled, single-blind | No significant difference between treatment and placebo |
| Collagenase | Gelbard et al56 | Placebo-controlled, double-blind | Decreased curvature and plaque size |
| Verapamil | Rehman et al63 | Placebo-controlled, single-blind | No significant difference between treatment and placebo |
| Interferons | Judge et al69 | Placebo-controlled, single-blind | Significant improvement in penile curvature, plaque size, penile pain, and erectile function |
| Hellstrom et al70 | Placebo-controlled, single-blind |
Topical therapy and iontophoresis
Aminopropionitrile, hydrocortisone, and verapamil are topical medications with varying results in the treatment of PD.71–74 Iontophoresis is the utilization of electrokinetic transport of charged molecules for the enhancement of transdermal drug delivery to diseased tissue, particularly plaques in PD.75 Martin et al demonstrated that topically administered verapamil gel was not present in the tunica albuginea at excisional surgery the next day,73 but was detected to a small degree in PD plaques after iontophoresis.76 In spite of initial successful reports with iontophoresis of dexamethasone and verapamil,77–79 recent double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trials failed to demonstrate statistically significant improvements in penile curvature. Greenfield et al suggest iontophoresis in patients whose major complaint is pain or those who have mild penile curvature and do not wish to undergo intralesional therapy or surgical correction of their penile curvature.80
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT)
Penile ESWT has been proposed as a possible nonsurgical PD treatment, but few reports have reported any beneficial effects.81,82 Most studies did not observe any significant improvement in penile curvature.83–85 An exploratory meta-analysis in 2004 by Hauck et al did not reveal any significant benefits of ESWT on improvement of penile curvature or plaque size.86 Two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trials have been published. Chitale et al did not observe any significant benefit of ESWT on PD.87 Palmieri et al demonstrated that ESWT appears to expedite pain resolution compared to the natural course of the disease.88 Currently, ESWT is not recommended as a treatment for PD because it has not been shown to improve or even stabilize the plaque or penile curvature.89
Penile traction devices
Gradual expansion of tunica tissue by traction exerted by a penile extender device induces new connective tissue formation.90 Preliminary studies conducted by Levine et al and Gontero et al have demonstrated nonsignificant curvature reduction and increased penile length.91,92 Further long-term controlled studies are necessary. Raheem et al suggested that vacuum pump therapy may have similar effects on improving penile curvature and pain symptoms.93
Surgical options for PD
The ideal candidate for surgical intervention for PD is a patient whose plaque has stabilized (normally at least 12 months since diagnosis) and penile curvature prevents satisfactory sexual intercourse. Attempts at medical management are attempted initially but, with more severe curvature – normally greater than 60 degrees – surgery may be considered as a primary treatment. Concomitant ED is always evaluated when deciding on surgical options for patients with severe PD.94
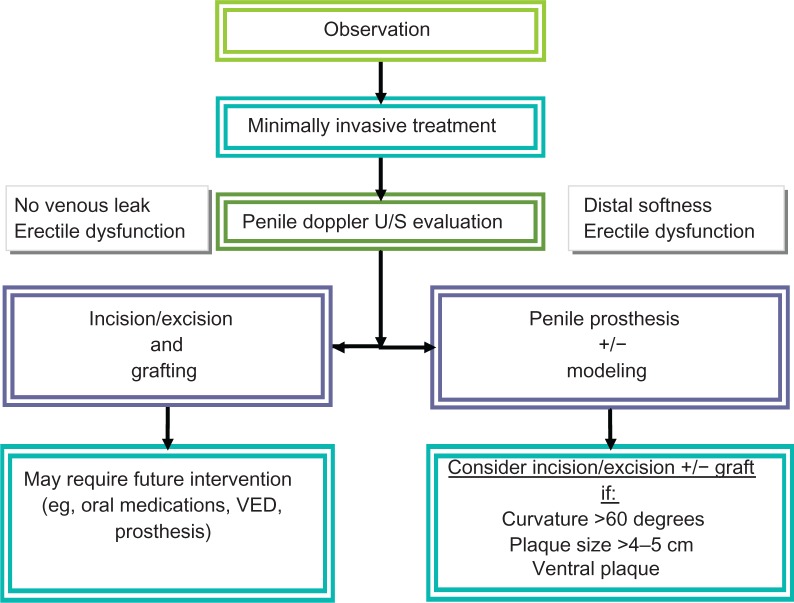
A proposed treatment algorithm for PD is provided in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Algorithm for treatment of Peyronie’s disease.
Abbreviations: U/S, ultrasound; VED, vacuum erection device.
Penile plication
For a patient with less severe penile curvature, one option includes shortening the side directly opposite to the curvature to equalize in length both sides of the penis. The ideal candidate for this is a man with adequate penile length, curvature less than 60 degrees, good preoperative erectile function, and no hourglass defect.95 In one study, patients underwent penile plication and greater than 80% of participants agreed that their residual curvature was decreased to less than 20 degrees and their rigidity was equivalent or better than before the procedure. The intuitive common complaint with this procedure is loss of penile length. Such men had their penile length measured before and after the procedure, with a surprising overall length change of +0.6 cm.96
Tunica albuginea plication can be performed using a variety of techniques. The Yachia procedure involves degloving the penis and making a longitudinal incision in the tunica albuginea opposite the plaque.97 The edges are then brought together horizontally using sutures which shorten the unaffected side and overall straightening of the penis.98 The Essed–Schroeder technique doesn’t involve entry or violation of the venoocclusive mechanism; instead sutures are placed in the tunica albuginea and tightened to effectively plicate and straighten the penis.97,99 Overall, success rates of plication procedures range from 70%–100% with rates of patient satisfaction typically over 80%.96,100–109
Data published about plication techniques are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3.
Data published on plication techniques
| Author | Date of Publication | Patient # | Procedure Type | % Straight | % with ED | Diminished Sensation% | Mean follow up duration (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ralph et al103 | 1995 | 359 | Nesbit | 89 | 2 | 2 | Not reported |
| Daitch et al101 | 1999 | 183 | Modified corporoplasty | 89 | 4 | Not reported | 24.1 |
| Gholami et al104 | 2002 | 132 | 16-dot plication technique | 85 | 3 | Not reported | 31 |
| Syed et al105 | 2003 | 50 | Nesbit | 90 | Not reported | 21 | 84 |
| Savoca et al106 | 2004 | 218 | Nesbit | 86.3 | 13 | 11 | 89 |
| Rolle et al107 | 2005 | 50 | Nesbit | 100 | 0 | Not reported | Not reported |
| Bella et al108 | 2006 | 23 | Minimally invasive plaque excision | 91 | Not reported | 4 | 25 |
| Greenfield et al109 | 2006 | 68 | Tunica albuniea plication (modified Nesbit) | 99 | 7.3 | 4 | 29 |
| Taylor et al96 | 2008 | 90 | Tunica plication | 93 | 12 | 36 | 72 |
Incision and grafting procedures
A more invasive approach involves incising the plaque to release penile curvature and using a graft to augment the missing tunica albuginea. Patients with extensive curvature (greater than 60 degrees), multiple areas of plaque, or those without adequate penile length are candidates for incision and grafting. Similar to penile plication, the penis is degloved exposing Buck’s fascia. The fascia is then entered, avoiding the dorsally located neurovascular bundles. Peyronie’s plaques have a firm texture due to fibrotic changes and can be easily distinguished from the surrounding tunica albuginea. An artificial erection is induced and over the area of the plaque a Y-type or H-type incision is made for tunical release. The tunical defect is then measured and a graft is constructed 10% larger to accommodate possible graft contracture during the healing process.110 The graft is sutured into the defect in a watertight manner and Buck’s fascia is then reapproximated. A final artificial erection is induced to assess for potential vascular leakage. The circumcision is closed in a routine fashion with a mild compression dressing. Most procedures are done on an outpatient basis.
Postoperatively, patients may be advised to use a penile stretching device on a daily basis, possibly with oral medications such as a low-dose PDE5 inhibitor.13,91,111 The use of a PDE5 inhibitor hypothetically increases penile blood flow. Patient satisfaction ranges from 35%–75% with the main complaints postoperatively being decreased penile length and new onset ED.95
The type of graft used often depends on the surgeon’s preference. Saphenous vein, buccal mucosa, acellular porcine dermal matrix, pericardium, and small intestine submucosa are just some of the many available grafts. Buccal mucosa exhibits good elasticity but concerns about oral numbness and mouth tightness demand more long-term follow-up with this approach.95,112 Small intestine submucosa contains collagen, fibroblast growth factor, and fibronectin, which are vital in the healing process.113–114 Recurrence (up to 33% within 3 months), hematoma, infection, and penile shortening have brought this graft material into question.115 Preputial dermal flaps were initially promising but high recurrence, presence of inclusion cysts, and poor patient satisfaction have since been reported.116 Pericardial grafts have the benefit of not requiring a harvest site and exhibit substantial tensile strength.117 The pericardium acts as a scaffold that tunica albuginea grows into and with time the graft is enzymatically dissolved.118
Penile prosthesis implantation
Because PD is often associated with ED, preoperative penile vascular studies using color duplex Doppler ultrasound is recommended.94,110 If a venous leak is identified it is suggested that a PDE5 inhibitor be tried prior to penile prosthesis placement.13 In one study, up to 61% of patients with venous leak responded to oral drugs, changing the need for an inflatable penile prosthesis.119 Penile prosthesis has the advantage of both straightening the curvature and providing patients with ED a functional erection. Both malleable and inflatable devices can be used, however higher satisfaction rates are achieved with the inflatable version. The success rate of penile straightening using penile prosthesis for patients with concomitant PD is higher if the curvature is less than 30 degrees. In men with more severe penile curvatures, incision and grafting or plication procedures may be necessary with simultaneous placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis. When comparing inflatable penile prosthesis to incision and grafting, postoperative erectile function domain scores were significantly higher for patients who had undergone inflatable penile prosthesis implantation. While this approach to surgery offers very good outcomes, there are also still risks that need to be fully discussed with the patient. These include infection, device malfunction, repeat operation, and erosion complications.120
In patients with minimal curvature (less than 30 degrees), placement of the prosthesis alone results in penile straightening by acting as a tissue expander and softening the plaque over time. Commonly, manual modeling is used in combination with a penile prosthesis to correct mild to moderate curvatures.120 Once the prosthesis is inserted, the device is inflated and the surgeon can assess the degree of penile straightening. When the device alone cannot straighten the penis, force is applied to bend the penis in the direction opposite to the curvature.117 This helps to stretch or fracture the plaque and straighten the penis. The success rate with the modeling technique is very high.121 In patients with bottleneck deformities or with severe curvature (greater than 60 degrees), manual modeling alone is less likely to be effective; in such cases incision in the plaque with or without grafting can be performed as previously described.117
Conclusion
PD is not an uncommon disorder, with recent epidemiologic studies documenting a prevalence of 3–9% of adult men affected. The actual prevalence of PD may be even higher. As the definitive pathophysiology of PD has not been completely elucidated, further basic research is required to make progress in the understanding of this enigmatic condition. Currently, nonsurgical treatments are used for those men who are in the acute stage of PD, whereas surgical options are reserved for men with established PD who cannot successfully penetrate. Future oral treatment options may be directed toward increasing tissue expression of matrix metalloproteinases or inhibition of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase activity. This area of research will evolve rapidly as the molecular mechanisms underlying PD are further elucidated. Intralesional treatments are growing in clinical popularity as a minimally invasive approach for the initial treatment of PD. Surgical approaches are considered only when men with PD do not respond to medical or minimally invasive therapies for at least 1 year and when patients cannot have satisfactory sexual intercourse. As scientific breakthroughs in the understanding of the mechanisms of this disease evolve, novel treatments for the many men suffering with PD are anticipated.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Mulhall JP, Creech SD, Boorjian SA, et al. Subjective and objective analysis of the prevalence of Peyronie’s disease in a population of men presenting for prostate cancer screening. J Urol. 2004;171:2350–2353. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000127744.18878.f1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bella AJ, Perelman MA, Brant WO, Lue TF. Peyronie’s disease (CME) J Sex Med. 2007;4:1527–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Taylor FL, Levine LA. Peyronie’s Disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2007;34:517–534.vi. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2007.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rosen R, Catania J, Lue T, et al. Impact of Peyronie’s disease on sexual and psychosocial functioning: qualitative findings in patients and controls. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1977–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chung E, De Young L, Brock GB. Rat as an animal model for Peyronie’s disease research: a review of current methods and the peer-reviewed literature. Int J Impot Res. 2011;23:235–241. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2011.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Usta MF, Bivalacqua TJ, Jabren GW, et al. Relationship between the severity of penile curvature and the presence of comorbidities in men with Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2004;171:775–779. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000097498.34847.7c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bjekic MD, Vlajinac HD, Sipetic SB, Marinkovic JM. Risk factors for Peyronie’s disease: a case-control study. BJU Int. 2006;97:570–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kadioglu A, Tefekli A, Erol B, Oktar T, Tunc M, Tellaloglu S. A retrospective review of 307 men with Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2002;168:1075–1079. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.El-Sakka AI, Hassoba HM, Chui RM, Bhatnagar RS, Dahiya R, Lue TF. An animal model of Peyronie’s-like condition associated with an increase of transforming growth factor beta mRNA and protein expression. J Urol. 1997;158:2284–2290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)68236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Del Carlo M, Cole AA, Levine LA. Differential calcium independent regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases by interleukin-1beta and transforming growth factor-beta in Peyronie’s plaque fibroblasts. J Urol. 2008;179:2447–2455. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with PDE5 inhibitors: an antifibrotic strategy. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7:215–221. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lin CS, Lin G, Wang Z, Maddah SA, Lue TF. Upregulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and effects of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in Peyronie’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;295:1014–1019. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00765-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hellstrom WJ. Medical management of Peyronie’s disease. J Androl. 2009;30:397–405. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.006221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gelbard MK, Dorey F, James K. The natural history of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1990;144:1376–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39746-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mulhall JP, Schiff J, Guhring P. An analysis of the natural history of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2006;175:2115–2118. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(06)00270-9. discussion 2118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ralph D, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Mirone V, et al. The management of Peyronie’s disease: evidence-based 2010 guidelines. J Sex Med. 2010;7:2359–2374. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Montorsi F, Adaikan G, Becher E, et al. Summary of the recommendations on sexual dysfunctions in men. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3572–3588. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.02062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gur S, Limin M, Hellstrom WJ. Current status and new developments in Peyronie’s disease: medical, minimally invasive and surgical treatment options. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011;12:931–944. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.544252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ahuja SK, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ. Stimulation of collagen production in an in vitro model for Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:207–212. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Safarinejad MR, Hosseini SY, Kolahi AA. Comparison of vitamin E and propionyl-L-carnitine, separately or in combination, in patients with early chronic Peyronie’s disease: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study. J Urol. 2007;178:1398–1403. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.05.162. discussion 1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shindel AW, Bullock TL, Brandes S. Urologist practice patterns in the management of Peyronie’s disease: a nationwide survey. J Sex Med. 2008;5:954–964. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zarafonetis CJ, Horrax TM. Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with potassium para-aminobenzoate (potaba) J Urol. 1959;81:770–772. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)66108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Trost LW, Gur S, Hellstrom WJ. Pharmacological Management of Peyronie’s Disease. Drugs. 2007;67:527–545. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767040-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shah PJR GN, Adib RS, Pryor JP. A multicentre double-blind controlled clinical trial of potassium-paraaminobenzoate (Potaba) in Peyronie’s disease. Prog Reprod Biol Med. 1983:61–67. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weidner W, Hauck EW, Schnitker J. Potassium paraaminobenzoate (POTABA) in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Eur Urol. 2005;47:530–535. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2004.12.022. discussion 535–536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Akkus E, Carrier S, Rehman J, Breza J, Kadioglu A, Lue TF. Is colchicine effective in Peyronie’s disease? A pilot study. Urology. 1994;44:291–295. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(94)80155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kadioglu A, Tefekli A, Koksal T, Usta M, Erol H. Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with oral colchicine: long-term results and predictive parameters of successful outcome. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:169–175. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Prieto Castro RM, Leva Vallejo ME, Regueiro Lopez JC, et al. Combined treatment with vitamin E and colchicine in the early stages of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2003;91:522–524. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Akman T, Sanli O, Uluocak N, et al. The most commonly altered type of Peyronie’s disease deformity under oral colchicine treatment is lateral curvature that mostly shifts to the dorsal side. Andrologia. 2011;43:28–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Safarinejad MR. Therapeutic effects of colchicine in the management of Peyronie’s disease: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Impot Res. 2004;16:238–243. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Apaydin E, Semerci B, Kefi A, Cikili N, Gursan A, Mulazimoglu N. The use of tamoxifen in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 1998;10:S57. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ralph DJ, Brooks MD, Bottazzo GF, Pryor JP. The treatment of Peyronie’s disease with tamoxifen. Br J Urol. 1992;70:648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1992.tb15836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Teloken C, Rhoden EL, Grazziotin TM, Ros CT, Sogari PR, Souto CA. Tamoxifen versus placebo in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1999;162:2003–2005. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)68087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Smith JF, Walsh TJ, Lue TF. Peyronie’s disease: a critical appraisal of current diagnosis and treatment. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20:445–459. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2008.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Biagiotti G, Cavallini G. Acetyl-L-carnitine vs tamoxifen in the oral therapy of Peyronie’s disease: a preliminary report. BJU Int. 2001;88:63–67. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cavallini G, Biagiotti G, Koverech A, Vitali G. Oral propionyl-l-carnitine and intraplaque verapamil in the therapy of advanced and resistant Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2002;89:895–900. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2002.02738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Karlic H, Lohninger A. Supplementation of L-carnitine in athletes: does it make sense? Nutrition. 2004;20:709–715. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2004.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Valente EG, Vernet D, Ferrini MG, Qian A, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF. L-arginine and phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors counteract fibrosis in the Peyronie’s fibrotic plaque and related fibroblast cultures. Nitric Oxide. 2003;9:229–244. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2003.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Smith JF, Shindel AW, Huang YC, et al. Pentoxifylline treatment and penile calcifications in men with Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2011;13:322–325. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shindel AW, Lin G, Ning H, et al. Pentoxifylline attenuates transforming growth factor-beta1-stimulated collagen deposition and elastogenesis in human tunica albuginea-derived fibroblasts part 1: impact on extracellular matrix. J Sex Med. 2010;7:2077–2085. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lin G, Shindel AW, Banie L, et al. Pentoxifylline attenuates transforming growth factor-beta1-stimulated elastogenesis in human tunica albuginea-derived fibroblasts part 2: Interference in a TGF-beta1/Smad-dependent mechanism and downregulation of AAT1. J Sex Med. 2010;7:1787–1797. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Safarinejad MR, Asgari MA, Hosseini SY, Dadkhah F. A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of pentoxifylline in early chronic Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2010;106:240–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.09041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Levine LA, Latchamsetty KC. Treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with Peyronie’s disease using sildenafil citrate. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:478–482. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Levine LA, Greenfield JM, Estrada CR. Erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease and a pilot study of the use of sildenafil citrate rehabilitation for postoperative erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2005;2:241–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.20234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ferrini MG, Kovanecz I, Nolazco G, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF. Effects of long-term vardenafil treatment on the development of fibrotic plaques in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2006;97:625–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chung E, Deyoung L, Brock GB. The role of PDE5 inhibitors in penile septal scar remodeling: assessment of clinical and radiological outcomes. J Sex Med. 2011;8:1472–1477. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Palmieri A, Imbimbo C, Creta M, Verze P, Fusco F, Mirone V. Tadalafil once daily and extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the management of patients with Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: results from a prospective randomized trial. Int J Androl. 2011 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tranchant C, Braun S, Warter JM. [Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids: role of lipocortins] Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145:813–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bodner H, Howard AH, Kaplan JH. Peyronle’s disease: cortisone-hyaluronidase-hydrocortisone therapy. J Urol. 1954;72:400–403. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67602-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Winter CC, Khanna R. Peyronie’s disease: results with dermo-jet injection of dexamethasone. J Urol. 1975;114:898–900. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)67169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Williams G, Green NA. The non-surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Br J Urol. 1980;52:392–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1980.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cipollone G, Nicolai M, Mastroprimiano G, Iantorno R, Longeri D, Tenaglia R. [Betamethasone versus placebo in Peyronie’s disease] Arch Ital Urol Androl. 1998;70:165–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gelbard MK, Walsh R, Kaufman JJ. Collagenase for Peyronie’s disease experimental studies. Urol Res. 1982;10:135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00255956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gelbard MK, Lindner A, Kaufman JJ. The use of collagenase in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1985;134:280–283. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)47123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hamilton RG, Mintz GR, Gelbard MK. Humoral immune responses in Peyronie’s disease patients receiving clostridial collagenase therapy. J Urol. 1986;135:641–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)45768-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gelbard MK, James K, Riach P, Dorey F. Collagenase versus placebo in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a double-blind study. J Urol. 1993;149:56–58. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35998-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jordan GH. The use of intralesional clostridial collagenase injection therapy for Peyronie’s disease: a prospective, single-center, non-placebo-controlled study. J Sex Med. 2008;5:180–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Roth M, Eickelberg O, Kohler E, Erne P, Block LH. Ca2+ channel blockers modulate metabolism of collagens within the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mulhall JP, Anderson MS, Lubrano T, Shankey TV. Peyronie’s disease cell culture models: phenotypic, genotypic and functional analyses. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:397–405. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Levine LA, Merrick PF, Lee RC. Intralesional verapamil injection for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1994;151:1522–1524. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lasser A, Vandenberg TL, Vincent MJ, Hellstrom WJ. Intraplaque verapamil injection for treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J La State Med Soc. 1998;150:431–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Levine LA, Goldman KE, Greenfield JM. Experience with intraplaque injection of verapamil for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2002;168:621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(05)64691-5. discussion 625–626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rehman J, Benet A, Melman A. Use of intralesional verapamil to dissolve Peyronie’s disease plaque: a long-term single-blind study. Urology. 1998;51:620–626. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(97)00700-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Duncan MR, Berman B, Nseyo UO. Regulation of the proliferation and biosynthetic activities of cultured human Peyronie’s disease fibroblasts by interferons-alpha, -beta and -gamma. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1991;25:89–94. doi: 10.3109/00365599109024539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Polat O, Gul O, Ozbey I, Ozdikici M, Bayraktar Y. Peyronie’s disease: intralesional treatment with interferon alpha-2 A and evaluation of the results by magnetic resonance imaging. Int Urol Nephrol. 1997;29:465–471. doi: 10.1007/BF02551115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ahuja S, Bivalacqua TJ, Case J, Vincent M, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ. A pilot study demonstrating clinical benefit from intralesional interferon alpha 2B in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Androl. 1999;20:444–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Astorga R, Cantero O, Contreras D, et al. Intralesional recombinant interferon alpha-2b in Peyronie’s disease. Arch Esp Urol. 2000;53:665–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brake M, Loertzer H, Horsch R, Keller H. Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with local interferon-alpha 2b. BJU Int. 2001;87:654–657. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Judge IS, Wisniewski ZS. Intralesional interferon in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a pilot study. Br J Urol. 1997;79:40–42. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1997.02849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hellstrom WJ, Kendirci M, Matern R, et al. Single-blind, multicenter, placebo controlled, parallel study to assess the safety and efficacy of intralesional interferon alpha-2B for minimally invasive treatment for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2006;176:394–398. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(06)00517-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gelbard M, Lindner A, Chvapil M, Kaufman J. Topical beta-aminopropionitrile in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1983;129:746–748. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Miller HC, Ardizzone J. Peyronie disease treated with ultrasound and hydrocortisone. Urology. 1983;21:584–585. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(83)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Martin DJ, Badwan K, Parker M, Mulhall JP. Transdermal application of verapamil gel to the penile shaft fails to infiltrate the tunica albuginea. J Urol. 2002;168:2483–2485. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Fitch W, 3rd, Easterling WJ, Talbert RL, Bordovsky MJ, Mosier M. Topical verapamil HCl, topical trifluoperazine, and topical magnesium sulfate for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease--a placebo-controlled pilot study. J Sex Med. 2007;4:477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Singh J, Maibach HI. Topical iontophoretic drug delivery in vivo: historical development, devices and future perspectives. Dermatology. 1993;187:235–238. doi: 10.1159/000247255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Levine LA, Estrada CR, Shou W, Cole A. Tunica albuginea tissue analysis after electromotive drug administration. J Urol. 2003;169:1775–1778. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000056153.47716.d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Riedl CR, Plas E, Engelhardt P, Daha K, Pfluger H. Iontophoresis for treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2000;163:95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Di Stasi SM, Giannantoni A, Stephen RL, Capelli G, Giurioli A, Jannini EA, Vespasiani G. A prospective, randomized study using transdermal electromotive administration of verapamil and dexamethasone for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2004;171:1605–1608. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000116450.82816.2c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Di Stasi SM, Giannantoni A, Capelli G, et al. Transdermal electromotive administration of verapamil and dexamethasone for Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2003;91:825–829. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Greenfield JM, Shah SJ, Levine LA. Verapamil versus saline in electromotive drug administration for Peyronie’s disease: a double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Urol. 2007;177:972–975. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.10.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Skolarikos A, Alargof E, Rigas A, Deliveliotis C, Konstantinidis E. Shockwave therapy as first-line treatment for Peyronie’s disease: a prospective study. J Endourol. 2005;19:11–14. doi: 10.1089/end.2005.19.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Srirangam SJ, Manikandan R, Hussain J, Collins GN, O’Reilly PH. Long-term results of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for Peyronie’s disease. J Endourol. 2006;20:880–884. doi: 10.1089/end.2006.20.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Michel MS, Ptaschnyk T, Musial A, et al. Objective and subjective changes in patients with Peyronie’s disease after management with shockwave therapy. J Endourol. 2003;17:41–44. doi: 10.1089/089277903321196788. discussion 44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Strebel RT SS, Sautter T, Hauri D. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for Peyronie’s disease does not correct penile deformity. Int J Impot Res. 2004;16:448–451. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hauck EW, Hauptmann A, Bschleipfer T, Schmelz HU, Altinkilic BM, Weidner W. Questionable efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for Peyronie’s disease: results of a prospective approach. J Urol. 2004;171:296–299. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000099891.68488.4e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hauck EW, Mueller UO, Bschleipfer T, Schmelz HU, Diemer T, Weidner W. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for Peyronie’s disease: exploratory meta-analysis of clinical trials. J Urol. 2004;171:740–745. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000108060.30363.8d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Chitale S, Morsey M, Swift L, Sethia K. Limited shock wave therapy vs sham treatment in men with Peyronie’s disease: results of a prospective randomized controlled double-blind trial. BJU Int. 2010;106:1352–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Palmieri A, Imbimbo C, Longo N, et al. A first prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol. 2009;56:363–369. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hauck EW, Diemer T, Schmelz HU, Weidner W. A critical analysis of non-surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol. 2006;49:987–997. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2006.02.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Taylor FL, Levine LA. Non-surgical therapy of Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2008;10:79–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Levine LA, Newell M, Taylor FL. Penile traction therapy for treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a single-center pilot study. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1468–1473. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gontero P, Di Marco M, Giubilei G, et al. Use of penile extender device in the treatment of penile curvature as a result of Peyronie’s disease. Results of a phase II prospective study. J Sex Med. 2009;6:558–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Raheem AA, Garaffa G, Raheem TA, et al. The role of vacuum pump therapy to mechanically straighten the penis in Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2010;106:1178–1180. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ralph DJ. Long-term results of the surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with plaque incision and grafting. Asian J Androl. 2011;13:797. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Djinovic R. Penile corporoplasty in Peyronie’s disease: which technique, which graft? Curr Opin Urol. 2011;21:470–477. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e32834b31fc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Taylor FL, Levine LA. Surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease via tunica albuginea plication or partial plaque excision with pericardial graft: long-term follow up. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2221–2228. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00941.x. discussion 2229–2230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Serefoglu EC, Hellstrom WJ. Treatment of Peyronie’s Disease: 2012 Update. Curr Urol Rep. 2011;12:444–452. doi: 10.1007/s11934-011-0212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kadioglu A, Kucukdurmaz F, Sanli O. Current status of the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Nat Rev Urol. 2011;8:95–106. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Essed E, Schroeder FH. New surgical treatment for Peyronie disease. Urology. 1985;25:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(85)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Yachia D. Modified corporoplasty for the treatment of penile curvature. J Urol. 1990;143:80–82. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39871-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Daitch JA, Angermeier KW, Montague DK. Modified corporoplasty for penile curvature: long-term results and patient satisfaction. J Urol. 1999;162:2006–2009. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)68088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Rehman J, Benet A, Minsky LS, Melman A. Results of surgical treatment for abnormal penile curvature: Peyronie’s disease and congenital deviation by modified Nesbit plication (tunical shaving and plication) J Urol. 1997;157:1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)64953-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ralph DJ, al-Akraa M, Pryor JP. The Nesbit operation for Peyronie’s disease: 16-year experience. J Urol. 1995;154:1362–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Gholami SS, Lue TF. Correction of penile curvature using the 16-dot plication technique: a review of 132 patients. J Urol. 2002;167:2066–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Syed AH, Abbasi Z, Hargreave TB. Nesbit procedure for disabling Peyronie’s curvature: a median follow-up of 84 months. Urology. 2003;61:999–1003. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02549-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Savoca G, Scieri F, Pietropaolo F, Garaffa G, Belgrano E. Straightening corporoplasty for Peyronie’s disease: a review of 218 patients with median follow-up of 89 months. Eur Urol. 2004;46:610–614. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2004.04.027. discussion 613–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Rolle L, Tamagnone A, Timpano M, Destefanis P, Fiori C, Ceruti C, Fontana D. The Nesbit operation for penile curvature: an easy and effective technical modification. J Urol. 2005;173:171–173. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000147160.53124.1a. discussion 173–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Bella AJ, Beasley KA, Obied A, Brock GB. Minimally invasive intracorporeal incision of Peyronie’s plaque: initial experiences with a new technique. Urology. 2006;68:852–857. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Greenfield JM, Lucas S, Levine LA. Factors affecting the loss of length associated with tunica albuginea plication for correction of penile curvature. J Urol. 2006;175175:238–241. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Richardson B, Pinsky MR, Hellstrom WJ. Incision and grafting for severe Peyronie’s disease (CME) J Sex Med. 2009;6:2084–2087. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01385.x. quiz 2088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Moncada-Iribarren I JJ, Martinez-Salamanca JI, Cabello R, Hernandez C. Managing penile shortening after Peyronie’s disease surgery. J Urol. 2007;177:252. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Dublin N, Stewart LH. Oral complications after buccal mucosal graft harvest for urethroplasty. BJU Int. 2004;94:867–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Santucci RA, Barber TD. Resorbable extracellular matrix grafts in urologic reconstruction. Int Braz J Urol. 2005;31:192–203. doi: 10.1590/s1677-55382005000300002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sievert KD, Tanagho EA. Organ-specific acellular matrix for reconstruction of the urinary tract. World J Urol. 2000;18:19–25. doi: 10.1007/s003450050004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Breyer BN, Brant WO, Garcia MM, Bella AJ, Lue TF. Complications of porcine small intestine submucosa graft for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2007;177:589–591. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.09.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tornehl CK, Carson CC. Surgical alternatives for treating Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2004;94:774–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kendirci M, Hellstrom WJ. Critical analysis of surgery for Peyronie’s disease. Curr Opin Urol. 2004;14:381–388. doi: 10.1097/00042307-200411000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Leungwattanakij S, Bivalacqua TJ, Reddy S, Hellstrom WJ. Long-term follow-up on use of pericardial graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 2001;13:183–186. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Mulhall J, Anderson M, Parker M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: functional and satisfaction outcomes. J Sex Med. 2005;2:132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.20113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wilson SK, Delk JR., 2nd A new treatment for Peyronie’s disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1994;152:1121–1123. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)32519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Wilson SK, Cleves MA, Delk JR., 2nd Long-term followup of treatment for Peyronie’s disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 2001;165:825–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]