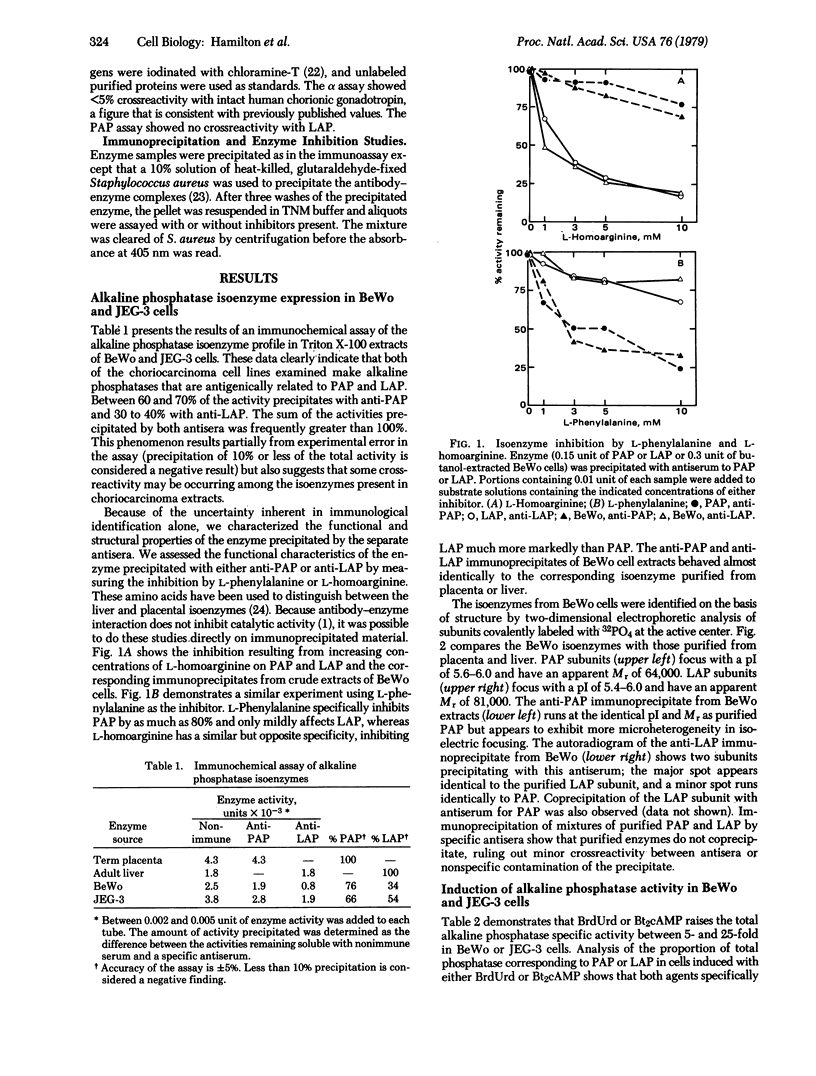
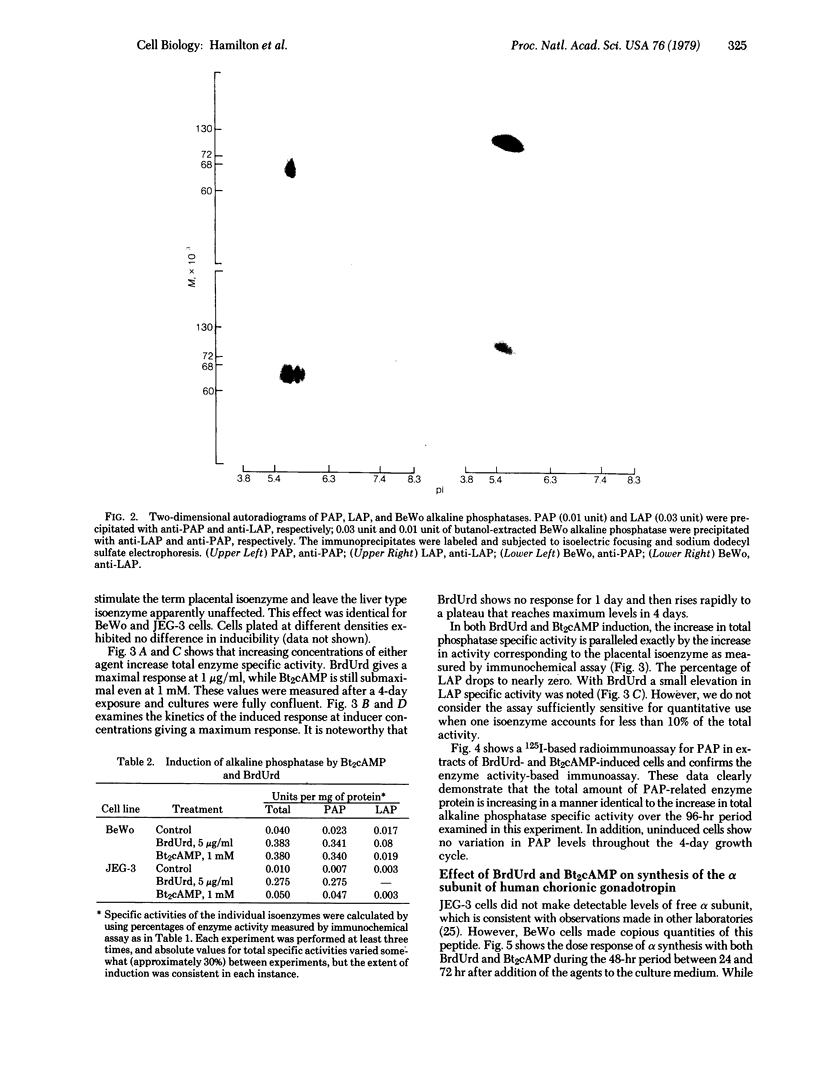
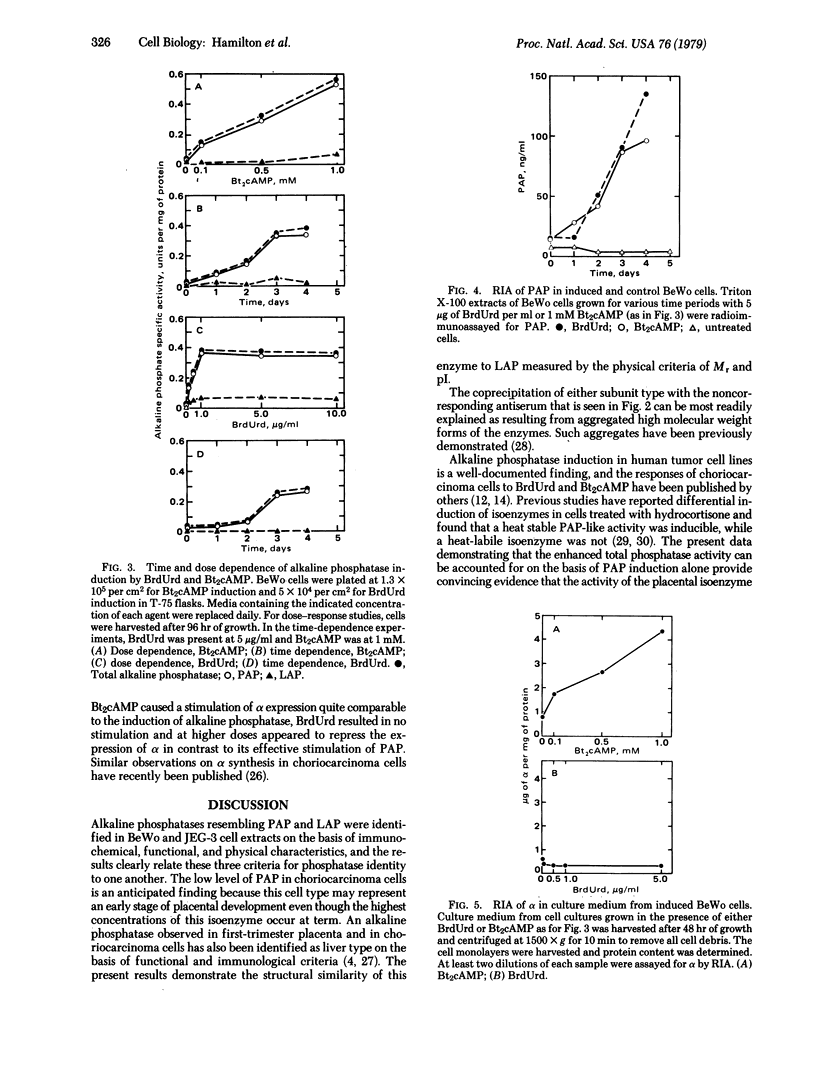
Abstract
The coincident expression of two structurally distinct isoenzymes of human alkaline phosphatase was demonstrated in two independently derived gestational choriocarcinoma cell lines. These proteins were shown to have enzymatic, antigenic, and physical-chemical properties resembling those of isoenzymes from term placenta and adult liver. The regulation of these isoenzymes has been studied during the exposure of both cell lines to 5-bromodeoxyuridine and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. The responses of the alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes to these agents have also been compared with the response of another protein phenotypic to placenta, the alpha subunit of chorionic gonadotropin. The results show that (i) the separate structural genes coding for placental and liver alkaline phosphatases are regulated in a noncoordinate fashion; (ii) both alkaline phosphatase genes respond independently of the alpha subunit; and (iii) the induction of the placental type isoenzyme occurs via at least two independent pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger K. S., Sussman H. H. Structural evidence that human liver and placental alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes are coded by different genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2201–2205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahl O. P. Human chorionic gonadotropin. II. Nature of the carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. P., MACLEOD C. M. Alkaline phosphatase content and the effects of prednisolone on mammalian cells in culture. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jan;45:439–485. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Wada H. G., Sussman H. H. The plasma membrane of human placenta. Isolation of microvillus membrane and characterization of protein and glycoprotein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4139–4146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y. Establishment of clonal human placental cells synthesizing human choriogonadotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1854–1858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Robinson J. C. Induction of alkaline phosphatase in choriocarcinoma cells by 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-cytosine, mitomycin C, phleomycin, and cyclic nucleotides. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Aug;92(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlow J. B., Ota T., Relacion J. R., Kohler P. O., Robinson J. C. Enzymes of normal and malignant trophoblast: phosphoglucose isomerase, phosphoglucomutase, hexokinase, lactate dehydrogenase, and alkaline phosphatase. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar 1;121(5):674–681. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90472-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman L., Miyayama H., Driscoll S. G., Fishman W. H. Developmental phase-specific alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes of human placenta and their occurrence in human cancer. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 1):2268–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Inglis N. I., Stolbach L. L., Krant M. J. A serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme of human neoplastic cell origin. Cancer Res. 1968 Jan;28(1):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H. Perspectives on alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):617–650. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90631-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Sie H. G. Organ-specific inhibition of human alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes of liver, bone, intestine and placenta; L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan and L homoarginine. Enzymologia. 1971 Sep 30;41(3):141–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh N. K., Rukenstein A., Baltimore R., Cox R. P. Studies on hormonal induction of alkaline phosphatase in HeLa cell cultures. Kinetic, thermodynamic and electrophoretic properties of induced and base-level enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. J., Sussman H. H. Structual comparison of ectopic and normal placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. J., Price G. H., Bazzell K. L. A study of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate, sodium butyrate and cortisol as inducers of HeLa alkaline phosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):619–623. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTZ R. Choriocarcinoma of women maintained in serial passage in hamster and rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:77–81. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. O., Bridson W. E. Isolation of hormone-producing clonal lines of human choriocarcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):683–687. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama H., Kato R., Ono T. Induction of alkaline phosphatase by cyclic AMP or its dibutyryl derivative in a hybrid line between mouse and Chinese hamster in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90663-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama H., Ono T. Induction of alkaline phosphatase by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in a hybrid line between mouse and Chinese hamster in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Dec;69(2):468–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J. M., Weintraub B. D., Krauth G. H., Kohler P. O., Rabson A. S., Rosen S. W. Ectopic and eutopic secretion of chorionic gonadotropin and its sub-nits in vitro: comparison of clonal strains from carcinomas of lung and placenta. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 May;56(5):911–917. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.5.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña M. A., Iverson G. M., Sussman H. H. Expression of liver and placental alkaline phosphatases in Chang liver cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Apr;91(1):119–129. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña M. A., Sussman H. H. Characterization of KB cell alkaline phosphatase. Evidence of similarity to placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2620–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi S. Q., Nussey S. S., Shindelman J. E., Kriss J. P. The influence of lipid substitution on thyrotropin-receptor interactions in artificial vesicles. Endocrinology. 1977 Nov;101(5):1406–1412. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-5-1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. The amino acid sequence around the reactive serine residue in alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):410–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0920410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattillo R. A., Gey G. O. The establishment of a cell line of human hormone-synthesizing trophoblastic cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1231–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh I., Tsang K. Y., Blakemore W. S. Placenta-like alkaline phosphatases from human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Jan;38(1):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speeg K. V., Jr, Azizkhan J. C., Stromberg K. Characteristics of alkaline phosphatase from two continuous lines of human choriocarcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman H. H., Small P. A., Jr, Cotlove E. Human alkaline phosphatase. Immunochemical identification of organ-specific isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman H. H., Weintraub B. D., Rosen S. W. Relationship of ectopic placental alkaline phosphatase to ectopic chorionic gonadotropin and placental lactogen. Discordance of three "markers" for cancer. Cancer. 1974 Mar;33(3):820–823. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197403)33:3<820::aid-cncr2820330329>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Weintraub B. D., Barowsky N. J., Rabson A. S., Rosen S. W. Subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin: unbalanced synthesis and secretion by clonal cell strains derived from a bronchogenic carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1419–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H. G., Górnicki Z., Sussman H. H. The sialoglycoprotein subunits of human placental brush border membranes characterized by two-two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(4):473–484. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



