Abstract
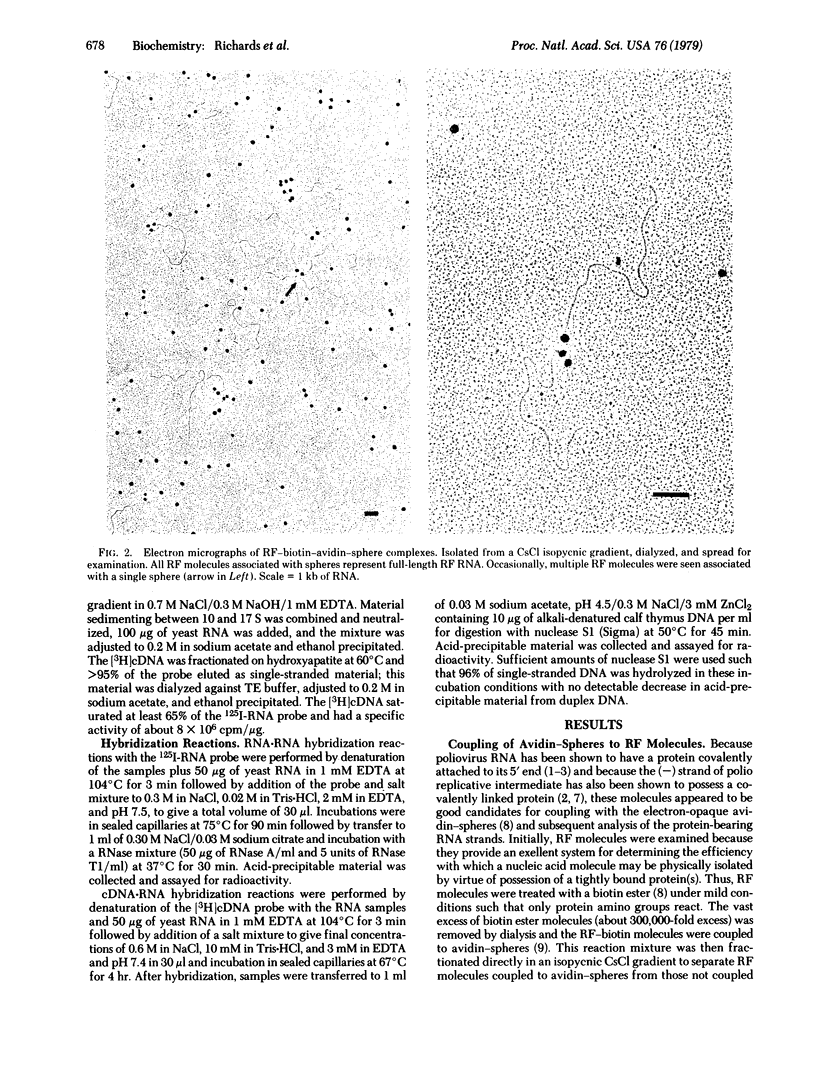
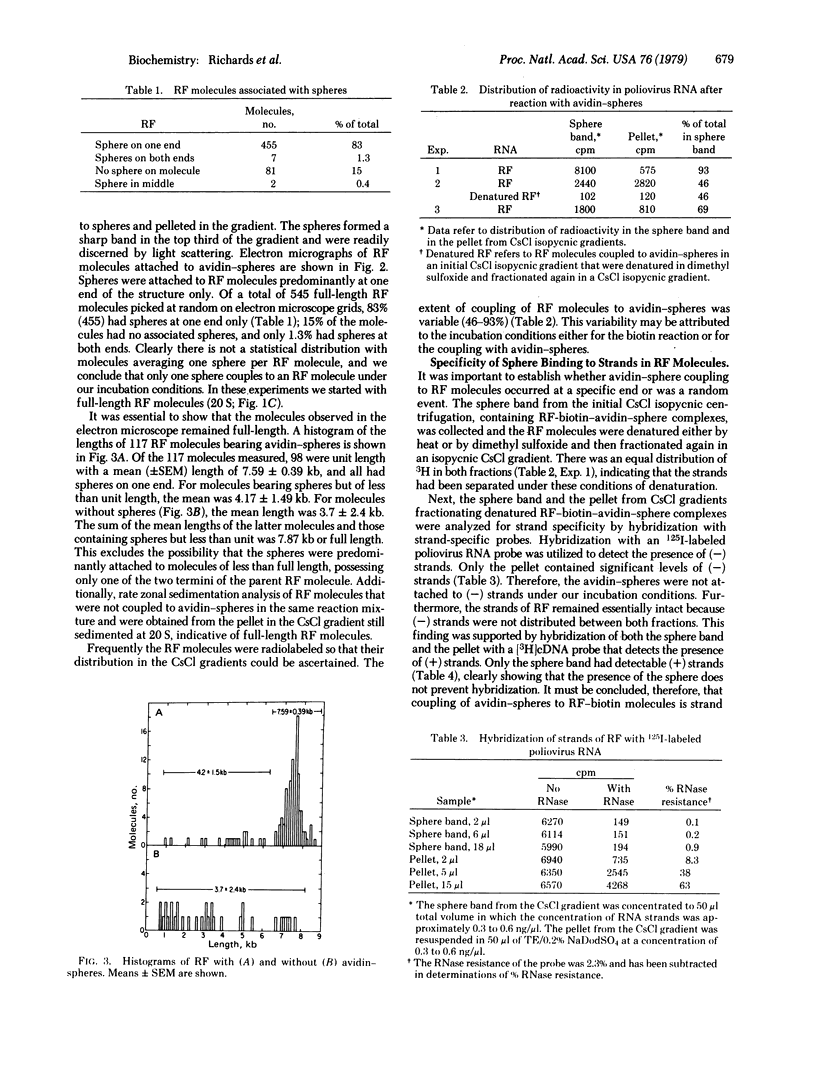
Poliovirus-specific double-stranded RNA molecules containing covalently attached protein were coupled with a biotin ester through the protein moiety. Subsequent interaction of the RNA-biotin with avidin attached to electronopaque plastic spheres led to the formation of complexes that were easily visualized in the electron microscope. Avidinspheres were associated only with one end of the RNA-biotin molecules, as seen in the electron microscope. Avidin-sphere attachment to poliovirus double-stranded RNA is strand specific, as shown by molecular hybridization of strand-specific probes to the separated strands of denatured complexes. [3H]DNA complementary to polio virion RNA hybridized exclusively to the strands bearing associated spheres [(+) strands] whereas 125I-labeled virion RNA hybridized predominantly with strands without spheres [(-)strands]. This biotin-avidin labeling technique provides a means for the isolation of full-length poliovirus (-) strands and may provide a general means for isolation of double-stranded polynucleotides containing tightly attached protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Infectious replicative intermediate of poliovirus: purification and characterization. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Anderson P. J., Bauer W. R. Resolution of single- and double-stranded RNAs in buoyant cesium trichloroacetate. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: detection of two different initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):761–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Boyer H. Susceptibility of the phiX-like phages G4 and G14 to R-EcoRi endonuclease. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. IV. Difference in the VPg's of encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus as evidence that the genome-linked proteins are virus-coded. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. III. Presence of a genome-associated protein. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):413–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.413-415.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Myers J. C. Synthesis of extensive, possibly complete, DNA copies of poliovirus RNA in high yields and at high specific activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2191–2195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J., Pellegrini M., Davidson N. A method for gene enrichment based on the avidin-biotin interaction. Application to the Drosophila ribosomal RNA genes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1364–1370. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Spiegelman S., Kacian D. L. Synthesis of full-length DNA copies of avian myeloblastosis virus RNA in high yields. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2840–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Holmes D. S., Manning J. Application of the avidin-biotin method of gene enrichment to the isolation of long double-stranded DNA containing specific gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):2961–2973. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky W. The radioiodination of RNA and DNA to high specific activities. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:121–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61800-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Bishop D. H. Isolation and properties of poliovirus minus strand ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):604–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.604-609.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Protein covalently linked to foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):648–650. doi: 10.1038/268648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Teng M. H., Wimmer E. Poly(U) in poliovirus minus RNA is 5'-terminal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1101–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




