Abstract
Pseudomonas syringae is a common foliar bacterium responsible for many important plant diseases. We studied the population structure and dynamics of the core genome of P. syringae via multilocus sequencing typing (MLST) of 60 strains, representing 21 pathovars and 2 nonpathogens, isolated from a variety of plant hosts. Seven housekeeping genes, dispersed around the P. syringae genome, were sequenced to obtain 400 to 500 nucleotides per gene. Forty unique sequence types were identified, with most strains falling into one of four major clades. Phylogenetic and maximum-likelihood analyses revealed a remarkable degree of congruence among the seven genes, indicating a common evolutionary history for the seven loci. MLST and population genetic analyses also found a very low level of recombination. Overall, mutation was found to be approximately four times more likely than recombination to change any single nucleotide. A skyline plot was used to study the demographic history of P. syringae. The species was found to have maintained a constant population size over time. Strains were also found to remain genetically homogeneous over many years, and when isolated from sites as widespread as the United States and Japan. An analysis of molecular variance found that host association explains only a small proportion of the total genetic variation in the sample. These analyses reveal that with respect to the core genome, P. syringae is a highly clonal and stable species that is endemic within plant populations, yet the genetic variation seen in these genes only weakly predicts host association.
Pseudomonas syringae is a plant-associated bacterium that can readily be found both as a harmless commensal on leaf surfaces and as a significant plant pathogen of major agricultural and economic concern (27). The species as a whole has an extremely large host range, while individual strains are typically restricted to a fairly small set of potential hosts. P. syringae is responsible for a variety of bacterial spot, speck, and blight diseases in a wide range of important crop species, including bacterial speck of tomato and bacterial blight of soybeans (28). It also has an illustrious career as a biocontrol agent against fungal plant pathogens (31), produces a protein that is central to the artificial-snow-making industry, and received a great deal of notoriety when “Ice-minus” P. syringae became the first genetically engineered organism to be tested in the field (27, 38).
P. syringae strains are subclassified into approximately 50 pathogenic varieties, or pathovars, according to the plant host from which they were originally isolated. Although the pathovar nomenclature system has been useful in an agricultural context, its biological justification is questionable. Many individual clones are known to grow quite well on a number of different plant hosts. Additionally, there are essentially no biochemical or physiological distinctions that reliably differentiate P. syringae pathovars (35). Finally, phylogenetic studies of P. syringae indicate that strains with the same pathovar designation are not always closely related (53).
A previous phylogenetic study of P. syringae by Sawada et al. (53) revealed a remarkable degree of congruence between two housekeeping genes (gyrB and rpoD) and two components of the pathogenesis-associated type III secretion system (hrpS and hrpL), leading to the conclusion that the type III secretion system was acquired prior to the diversification of the P. syringae pathovars. The evolutionary history of the argK gene (involved in phaseolotoxin production), on the other hand, was clearly inconsistent with that of the housekeeping genes, lending strong support for an important role for horizontal transfer at this locus (52). On the basis of the four congruent genes, the species was partitioned into three primary monophyletic groups.
The diversity of P. syringae strains has been further explored by the physical mapping of the ribosomal gene cluster (rrn) (52). This analysis revealed that the size and structure of P. syringae genomes vary greatly by pathovar and that large-scale genomic rearrangements are common.
Gardan et al. (20) have used DNA-DNA hybridization to characterize the taxonomic structure of P. syringae. They concluded that one of the major clades of P. syringae (the Sawada group 3 strains, which include the pathovars savastanoi, phaseolicola, and glycinea) was sufficiently distinct that it should be given separate species status as Pseudomonas savastanoi.
Although all of these studies have been informative, a clearer picture of the population structure of the species would be gained by focusing strictly on housekeeping genes. These genes are components of the “core genome” (see below) and are less likely to undergo horizontal gene transfer. Housekeeping genes are particularly useful for clarifying clonal relationships among strains and for assessing the importance of recombination in driving the evolution of clonal lineages.
Recent comparative studies of bacterial genomes have found bacterial evolution to be a composite of forces acting on two largely independent yet intimately intertwined genomes: the “core” and “flexible” genomes (25). The core genome consists of genes ubiquitously found among strains of a bacterial species. These genes typically encode proteins that are essential for the survival of the organism, such as housekeeping genes. Components of the core genome are generally less likely to undergo horizontal gene transfer, and they either evolve neutrally or are selectively constrained. The core genome can be thought of as the clonal backbone of the species, and its constituents can be used to track the evolutionary history of clonal lineages through time.
Unlike the core genome, the flexible genome consists of genes that vary among strains within a species. These genes typically encode proteins that are responsible for adaptation to specific niches, hosts, or environments. The flexible genome may include virulence-associated genes, resistance genes, and genes associated with mobile elements such as bacteriophage, plasmids, or transposons. By definition, the flexible genome evolves largely through horizontal genetic exchange (i.e., through gene acquisition and loss). Since horizontal transfer shuffles and effectively obscures evolutionary histories, the most reliable approach to characterizing bacterial diversity would focus strictly on the core genome.
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) (12, 40) is a recently developed strain-typing system that focuses strictly on the core genome. This highly accurate and reproducible approach uses the DNA sequences from seven housekeeping genes to differentiate strains and clonal lineages. The choice of seven loci ensures adequate variability so that one can distinguish between the most closely related strains and still be able to track global clonal dynamics. The use of housekeeping genes focuses the analysis on the core genome, thereby revealing the clonal history of the species with the highest possible accuracy.
One of the most powerful aspects of MLST analysis is its ability to detect and measure recombination (15, 16). Recombination has a tremendous influence on bacterial evolutionary dynamics (1, 17, 21, 22). It can cause the rapid diversification of clones when genetic material is introduced from other clonal lineages; conversely, it can homogenize genetic variation when it occurs within individual clonal groups. By reshuffling genetic variation, recombination creates new genotypes that may be better adapted to particular hosts or environments. Recombination has been shown to play a central role in the evolution of several important pathogens (17). An appreciation of recombination is central to understanding how bacterial clones and populations evolve and adapt to new environmental and host challenges.
In this study, we have provided the first MLST analysis of a plant-pathogenic bacterium. We find that P. syringae is surprisingly clonal, contrasting sharply with the extremely labile virulence-associated genes (24, 53). We also show that the core genome is only weakly associated with the host of isolation and pathovar designation and that P. syringae is endemic in plant populations. We hope that this study will provide a community resource and form the foundation for future investigations into P. syringae pathogenesis and host adaptation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains.
Members of the research community, and the gene bank of the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, kindly donated 60 strains of P. syringae. Details about the strains are presented in Table 1. Pseudomonas fluorescens K756, a cucumber root isolate, was used as the outgroup. Strains were grown in King's B medium (33) at 30°C.
TABLE 1.
Strains
| Pathovar | Name | Designation | Place of isolation | Yr of isolation | Host | Host family | Sourcea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinidiae | FTRS_L1 | PanFTRS_L1 | Shizuoka, Japan | 1984 | Kiwi | Actinidiaceae | MAFF 302091 |
| Aptata | 601 | Ptt601 | 1966 | Sugar beet | Amaranthaceae | MAFF 301008 | |
| Aptata | G733 | PttG733 | 1976 | Brown rice | Poaceae | MAFF 302831 | |
| Broussonetiae | KOZ8101 | PbrKOZ8101b | Tottori, Japan | 1980 | Paper mulberry | Moraceae | MAFF 810036 |
| Coronafaciens | KN221 | PcnKN221 | 1984 | Oats | Poaceae | MAFF 302787 | |
| Glycinea | KN44 | Pgy1 | Ibaraki, Japan | 1981 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 301683 |
| Glycinea | KN28 | Pgy1 | 1981 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 302676 | |
| Glycinea | 301765 | Pgy1 | 1982 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 301765 | |
| Glycinea | KN127 | Pgy1 | 1982 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 302751 | |
| Glycinea | KN166 | Pgy1 | 1982 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 302770 | |
| Glycinea | BR1 | Pgy1 | 1989 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 210373 | |
| Glycinea | LN10 | Pgy1 | 1989 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 210389 | |
| Glycinea | MOC601 | Pgy1 | 1994 | Soybean | Fabaceae | MAFF 311113 | |
| Glycinea | UnB647 | PgyUnB647c | Kidney bean | Fabaceae | MAFF 210405 | ||
| Japonica | 301072 | PjaM301072 | Tochigi, Japan | 1951 | Barley | Poaceae | MAFF 301072 |
| Lachrymans | N7512 | PlaN7512 | Gunma, Japan | 1975 | Cucumber | Cucurbitaceae | MAFF 301315 |
| Lachrymans | YM7902 | Pla1 | 1979 | Cucumber | Cucurbitaceae | MAFF 730057 | |
| Lachrymans | YM8003 | Pla1 | 1980 | Cucumber | Cucurbitaceae | MAFF 730069 | |
| Maculicola | H7311 | Pma1 | Kanagawa, Japan | 1973 | Chinese cabbage | Brassicaceae | MAFF 301174 |
| Maculicola | H7608 | Pma1 | 1976 | Chinese cabbage | Brassicaceae | MAFF 301175 | |
| Maculicola | KN203 | Pma1 | 1983 | Chinese cabbage | Brassicaceae | MAFF 302783 | |
| Maculicola | AZ85297 | Pma1 | 1985 | Chinese cabbage | Brassicaceae | MAFF 302539 | |
| Maculicola | ES4326 | Pma2 | United States | 1965 | Radish | Brassicaceae | J. Greenberg (10) |
| Maculicola | YM7930 | Pma2 | Japan | 1979 | Radish | Brassicaceae | MAFF 301419 |
| Maculicola | KN84 | PmaKN84 | 1982 | Radish | Brassicaceae | MAFF 302724 | |
| Maculicola | M4 | PmaM4 | United States | 1965 | Radish | Brassicaceae | J. Dangl (8) |
| Maculicola | M6 | PmaM6 | United Kingdom | 1965 | Cauliflower | Brassicaceae | J. Dangl (8) |
| Maculicola | KN91 | PmaKN91 | 1982 | Radish | Brassicaceae | MAFF 302731 | |
| Mellea | N6801 | PmeN6801 | 1968 | Tobacco | Solanaceae | MAFF 302303 | |
| Mori | 301020 | PmoM301020 | Nagano, Japan | 1966 | Mulberry | Moraceae | MAFF 301020 |
| Morsprunorum | FTRS_U7805 | PmpFTRS_U7 | Shiga, Japan | 1978 | Japanese apricot | Rosaceae | MAFF 301436 |
| Myricae | AZ84488 | Pmy1 | 1984 | Bayberry | Myricaceae | MAFF 302460 | |
| Myricae | 302941 | Pmy1 | 1989 | Bayberry | Myricaceae | MAFF 302941 | |
| Oryzae | I_6 | PorI_6 | 1991 | Rice | Poaceae | MAFF 311107 | |
| Oryzae | 36_1 | Por36_1 | 1983 | Rice | Poaceae | MAFF 301538 | |
| Phaseolicola | KN86 | Pph1 | Ibaraki, Japan | 1982 | Kidney bean | Fabaceae | MAFF 301673 |
| Phaseolicola | NS368 | Pph1 | 1992 | Kidney bean | Fabaceae | MAFF 311004 | |
| Phaseolicola | Y5_2 | PphY5_2d | Kudzu | Fabaceae | MAFF 311162 | ||
| Phaseolicola | NPS3121 | PphNPS3121 | United States | Kidney bean | Fabaceae | J. Greenberg (37) | |
| Pisi | H5E1 | Ppi1 | 1993 | Pea | Fabaceae | MAFF 311141 | |
| Pisi | H6E5 | Ppi1 | 1994 | Pea | Fabaceae | MAFF 311144 | |
| Pisi | H7E7 | Ppi1 | 1995 | Pea | Fabaceae | MAFF 311146 | |
| Pisi | PP1 | Ppi2 | Shizuoka, Japan | 1978 | Pea | Fabaceae | MAFF 301208 |
| Pisi | H5E3 | Ppi2 | 1993 | Pea | Fabaceae | MAFF 311143 | |
| Savastanoi | 4352 | Psv4352 | Yugoslavia | Olive | Oleaceae | A. Colmer | |
| Sesami | HC_1 | PseHC_1 | Sesame | Pedaliaceae | MAFF 311181 | ||
| Syringae | L177 | Psy1 | 1983 | Lilac | Oleaceae | MAFF 302085 | |
| Syringae | LOB2_1 | Psy1 | Nagano, Japan | 1986 | Lilac | Oleaceae | MAFF 301861 |
| Syringae | Ps9220 | PsyPs9220 | 1992 | Spring onion | Poaceae | MAFF 730125 | |
| Syringae | B728A | PsyB728A | Wisconsin | Snap bean | Fabaceae | S. Hirano (39) | |
| Syringae | FF5 | PsyFF5 | Oklahoma | 1998 | Ornamental pear | Rosaceae | C. Bender (58) |
| Syringae | FTRS_W6601 | PsyFTRS_W6 | 1966 | Japanese apricot | Rosaceae | MAFF 301429 | |
| Syringae | FTRS_W7835 | PsyFTRS_W7 | 1978 | Japanese apricot | Rosaceae | MAFF 301430 | |
| Thea | K93001 | PthK93001 | 1993 | Tea | Theaceae | MAFF 302851 | |
| Tabaci | 6606 | Pta6606b | Akita, Japan | 1967 | Tobacco | Solanaceae | MAFF 301612 |
| Tomato | KN10 | PtoKN10 | 1981 | Tomato | Solanaceae | MAFF 302665 | |
| Tomato | 2170 | Pto2170 | 1984 | Tomato | Solanaceae | MAFF 301591 | |
| Tomato | DC3000 | PtoDC3000 | Canada | Tomato | Solanaceae | J. Greenberg (6) | |
| Cit7 | PsCit7 | Navel orange | Rutaceae | S. Lindow | |||
| TLP2 | PsTLP2 | Potato | Solanaceae | S. Lindow | |||
| P. fluorescens | K756 | PfK756 | 1981 | Cucumber | Cucurbitaceae | MAFF 520005 |
Strains having designations beginning with MAFF were obtained from the gene bank of the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestries, and Fisheries. Designations are abbreviated strain names indicating nonredundant strain sets.
PbrKOZ8101 and Pta6606 are identical but have different hosts.
PgyUnB647 and Pgy1 have identical MLST profiles but have different hosts.
PphY5_2 and Pph1 have identical MLST profiles but have different hosts.
PCR amplification and DNA sequencing.
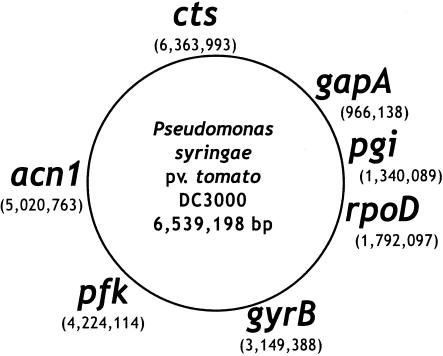
Genomic DNA was prepared by using the PureGene DNA isolation protocol (Gentra Systems) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Seven housekeeping genes were sequenced: those encoding sigma factor 70 (rpoD), gyrase (gyrB), aconitate hydratase B (acnB), citrate synthase (cts), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gap), phosphoglucoisomerase (pgi), and phosphofructokinase (pfk) (Fig. 1). These loci were chosen either because they play key roles in carbohydrate metabolism or because they have been used previously as phylogenetic markers (53). Initial primers for all but gyrB and rpoD (53) were designed based on alignments of coding sequences from P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (NCBI accession no. NC_004578),Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (NCBI accession no. NC_002516), P. fluorescens PfO-1 (Department of Energy—Joint Genome Initiative [DOE JGI]), and Pseudomonas putida KT2440 (NCBI accession no. NC_002947). Except for gyrB and cts, two pairs of primers were designed for each locus (Table 2). The external pair was used for high-stringency PCR amplification. The internal pair was used for cycle sequencing. Only a single pair of primers per locus was used for gyrB and cts.
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the positions of the seven housekeeping genes used in this study, based on the sequenced P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 genome (NCBI accession no. NC_004578). The position of each locus (in base pairs) is given below the gene name.
TABLE 2.
MLST primers
| Primera | Tm (°C)b | Length (bp) | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| acn-Fp | 60 | 23 | ACATCCCGCTGCACGCYCTGGCC |
| acn-Rp | 60 | 24 | GTGGTGTCCTGGGAACCGACGGTG |
| acn-Fs | 53 | 26 | ATGAARCAGATMGAAGAAATGCGCGG |
| acn-Rs | 53 | 23 | GCCRACCATCTTYTGCGCMAGGG |
| cts-Fp | 56 | 23 | AGTTGATCATCGAGGGCGCWGCC |
| cts-Rp | 56 | 22 | TGATCGGTTTGATCTCGCACGG |
| cts-Fs | 53 | 22 | CCCGTCGAGCTGCCAATWCTGA |
| cts-Rs | 50 | 24 | ATCTCGCACGGSGTRTTGAACATC |
| gapA-Fps | 62 | 16 | CGCCATYCGCAACCCG |
| gapA-Rps | 62 | 19 | CCCAYTCGTTGTCGTACCA |
| gyrB-Fpsc | 63 | 24 | MGGCGGYAAGTTCGATGACAAYTC |
| gyrB-Rpsc | 63 | 25 | TRATBKCAGTCARACCTTCRCGSGC |
| pfk-Fp | 63 | 20 | ACCMTGAACCCKGCGCTGGA |
| pfk-Rp | 63 | 20 | ATRCCGAAVCCGAHCTGGGT |
| pfk-Fs | 50 | 20 | AGCAAYATCAAGMTGGCCGA |
| pfk-Rs | 50 | 19 | ACCATGCCKGCCARMAGCG |
| pgi-Fp | 60 | 25 | TGCAGGACTTCAGCATGCGCGAAGC |
| pgi-Rp | 60 | 25 | CGAGCCGCCCTGSGCCAGGTACCAG |
| pgi-Fs | 57 | 18 | TTCAGCATGCGCGAAGCG |
| pgi-Rs | 53 | 16 | TGCGCCAGGTACCAGG |
| rpoD-Fpc | 63 | 25 | AAGGCGARATCGAAATCGCCAAGCG |
| rpoD-Rpsc | 63 | 25 | GGAACWKGCGCAGGAAGTCGGCACG |
| rpoD-Fs | 53 | 19 | AAGCGTATCGAAGAAGGCATYCGTG |
F, forward primer; R, reverse primer; p, PCR primer; s, sequencing primer.
Tm, melting temperature.
Primers from reference 53.
PCR amplification was performed on 250 ng of template DNA by using Hybaid PCR Express thermal cyclers. MBI-Fermentas Taq polymerase and buffers were used with nucleotide concentrations of 200 μM each and primer concentrations of 1 μM. Thirty cycles of amplification were performed, with template denaturation at 94°C for 2 min, the appropriate annealing temperature (Table 2) for 1 min, and extension at 72°C for 1 min.
DNA sequencing was performed with the CEQ-DTCS Quick Start kit on a Beckman-Coulter CEQ 8000 DNA sequencer according to the manufacturer's instructions. Forward and reverse sequences were obtained by using either the PCR primers or internal primers for each locus (Table 2). These sequences were edited and aligned by using Sequencher (Gene Codes). A total of 399 to 650 bp of overlapping sequence was obtained from the seven housekeeping genes for each strain. Since the amount of data obtained was different for each strain, all sequences were trimmed to include only those regions for which we had data for all strains. Sequences from each locus were aligned by using ClustalW (4) with the “slow-accurate” default alignment parameters and were trimmed to the minimal shared length in GeneDoc (www.psc.edu/biomed/genedoc).
There were 40 unique sequence types (see the next section) among the 60 strains sequenced. Some analyses used the “nonredundant” data set, which did not include sequences that were identical to another sequence unless they had been isolated from different hosts. Other analyses used the “fully nonredundant” data set, which did not include any sequences that were identical to another, regardless of host of isolation.
MLST analyses.
Aligned sequences were analyzed with the Sequence Type Analysis and Recombination Test package (START) (32) or with applications available from the MLST home page (www.mlst.net). Allele assignments were made through the MLST nonredundant database program NRDB, which gave each strain an allele profile known as a sequence type (ST). These STs were then grouped by similarity by use of BURST (“based upon related sequence types”). Clonal complexes were defined as in the work of Feil et al. (16). A consensus group of a clonal complex is composed of those strains with the predominant allelic profile. Single-locus variants (SLVs) are those strains that differ from the consensus group at a single locus. Double-locus variants (DLVs) differ from the consensus group at two loci, while satellites (SATs) differ at three or more loci. A unique clonal group was defined as comprising strains that were identical at five or more loci (12, 40). SLVs were used to estimate the relative rates of recombination and mutation (16).
Phylogenetic analysis.
Analyses were performed on individual gene sequences as well as on the concatenated data set. Modeltest (46) was used to determine the optimal nucleotide substitution model for each gene. The evolutionary models chosen based on the likelihood ratio test implemented in Modeltest were found to be more strongly supported than the alternative Akaike information criteria parameters and were used for further analyses. Neighbor-joining (NJ) trees were generated in MEGA, version 2.1 (36), by using the Tamura-Nei evolutionary model with gamma correction and 1,000 bootstrap replicates for all sequences. Maximum-likelihood (ML) and maximum-parsimony (MP) trees were generated in PAUP*, version 4.0b10 for UNIX (59), by using the optimal Modeltest parameters and a starting NJ tree. Split decomposition (2, 11) analyses were performed with SplitsTree, version 3.2 (30), by using Hamming distances, equal edge lengths, and 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Split decomposition is a parsimony method that does not impose a branching or tree-like structure on the data set. It permits reticulations or network structure that may be indicative of past recombination events. Intragenic recombination was estimated by split decomposition of individual genes, while total recombination (intra- and intergenic) was estimated by using the concatenated data set.
Phylogenetic congruence between ML gene trees was tested by using the Shimodaira-Hasegawa (SH) (55) and likelihood congruence (LC) tests (14). The SH test determines the likelihood of a data set given alternative trees, while the LC test determines the likelihood of the tree topologies from the different genes relative to random tree topologies. To put it simplistically, the LC test asks if the evolutionary histories of the MLST loci are different, while the SH tests asks if the evolutionary histories of the MLST loci are the same. The LC test is significant whenever evolutionary histories are correlated and is rejected when there is free recombination. The SH test is significant only when evolutionary histories are essentially identical and is rejected when there is even a very small amount of recombination. The SH test was implemented via the Phylip program DNAML with no branch lengths (18). The LC test was implemented in PAUP*. The incongruence length difference (ILD) test (5, 45) was also performed to detect differences between the MP trees. The ILD test measures the increase in homoplasy seen when data sets are concatenated.
Population genetic analysis.
Pairwise nucleotide diversity (π) and the number of segregating sites (Watterson's θ) were calculated with DnaSP, version 3.53 (50). Three tests of selection were performed: Tajima's D, Fu's Fs statistic, and the Ka/Ks ratio test. The significance of the Fs statistic was determined by coalescent simulations. These calculations were performed with DnaSP or LDhat or through the START package. Genetic distances were calculated by using a Kimura 2-parameter model with a γ correction of 0.18 in MEGA, version 2.1 (36).
A number of recombination analyses were performed in addition to the MLST analysis. The index of association (IA) test (43) and the homoplasy ratio test (42) were conducted with the START package. Sliding-window analyses of phylogenetic congruence were performed using the difference of sums of squares (DSS) analysis of TOPALi, with a step size of 10 and a window size of 40 (www.bioss.ac.uk/∼iainm/topali/), and bootscanning (51) as implemented in SimPlot, version 2.5 (sray.med.som.jhmi.edu/RaySoft/SimPlot/Version2/SimPlot_Doc.html). Recombination rates were measured by using a coalescence-based method for detecting linkage disequilibrium as implemented in LDhat (44). Gene conversion model C and a mean tract length of 100 nucleotides were used for analysis of biallelic sites.
Demographic history.
We explored the demographic history of our sample by using classic skyline plots (49, 57). Skyline plots are graphical, nonparametric tests that use coalescent methods to estimate the effective size of a population through time. We used our fully nonredundant concatenated data set to make a fully resolved ML tree in PAUP*. This tree was analyzed with GENIE, version 3 (48), by using the differential evolution optimizer and models of constant, exponential, and expansion population growth.
Association tests.
We tested for associations between the genetic data and host of isolation or pathovar designation by using the analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) as implemented in Arlequin, version 2.0 (54). Pairwise distances were computed by using the Tamura and Nei distance measure with a gamma correction of 0.18. This correction was based on the PAUP* ML analysis. One thousand permutations of the data were used to create the null distribution.
RESULTS
Sequence analysis.
Sixty strains of P. syringae, representing 21 pathovars and 2 nonpathogens, and 1 strain of P. fluorescens were sequenced at the seven loci (Table 1). Forty unique sequence types were obtained for the P. syringae strains. Strains that were identical in sequence and had the same host were given common strain designations. All nine of the glycinea strains were identical. Eight of these strains are soybean pathogens and were given the common strain designation Pgy1. Strain PgyUnB647 was also identical in sequence to the Pgy1 strains, but it is a kidney bean pathogen. Four maculicola strains were found to be identical. All of these strains are Chinese cabbage pathogens and were given the common designation Pma1. Two other maculicola strains that are radish pathogens were also identical and were given the designation Pma2. Two of the lachrymans cucumber pathogens were identical in sequence and were given the common designation Pla1. Three phaseolicola strains were identical. Two of these strains are kidney bean pathogens and were given the common designation Pph1. The third, a kudzu pathogen, retained its designation PphY5_2. The five pea pathogens fell into two identity groups, which were labeled Ppi1 and Ppi2. Two lilac pathogens from the pathovar syringae were found to be identical and given the common designation Psy1. The paper mulberry pathogen PbrKOZ8101 and the tobacco pathogen Pta6606 were also identical in sequence. Both myricae pathogens of bayberry were identical and were given the designation Pmy1.
Phylogenetic analysis.
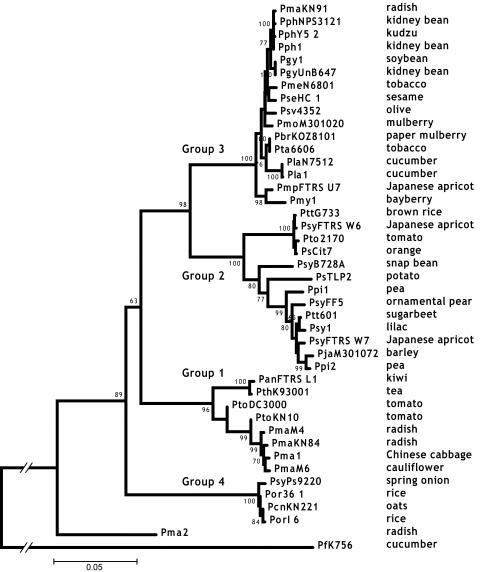
NJ, ML, and MP trees were constructed independently for each locus and for the concatenated data set. The trees were rooted with the orthologous sequences from P. fluorescens K56. All of the phylogenetic methods produced very similar trees, with identical major monophyletic groups for each data set. The monophyletic groups corresponded well to the three major groups identified by Sawada et al. (53) (Fig. 2). Group 1 contains primarily pathogens of brassicaceous crops such as radish and cabbage (pathovar maculicola) and tomato pathogens (Table 1). Group 1 also contains the tomato and Arabidopsis pathogen PtoDC3000, which has been sequenced by The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR). Group 2 has the greatest host diversity, containing strains that are pathogenic to hosts as diverse as tomatoes, brown rice, and lilacs (pathovars tomato, aptata, and syringae, respectively). Pea pathogens (pathovar pisi) appear to belong exclusively to this group. This group also contains the greatest number of syringae pathovars—a designation often applied rather indiscriminately. The nonpathogenic strains Cit7 and TLP2 belong to this group, as well as PsyB728a, which causes bacterial brown spot of bean and has been sequenced by DOE-JGI. Group 3 is dominated by bean pathogens (pathovars glycinea and phaseolicola). It also contains cucumber (pathovar lachrymans) and tobacco (pathovars tabaci and mellea) pathogens. Although not included in our original group of 60 strains, strain Pph1448A, which causes halo blight on beans and Arabidopsis thaliana, is also found in group 3. This strain is currently being sequenced by TIGR. Of special interest in this phylogenetic analysis is the identification of a new syringae group. Group 4 strains constitute the most basal clade of the major groups and are strictly pathogens of monocotyledon hosts (rice, onions, and oats). Of the six monocot pathogens in our study, four are in group 4. Only two strains do not cluster in one of the four syringae groups. PmaES4326 and PmaYm7930 are both radish pathogens (pathovar maculicola) that diverged prior to the diversification of the rest of the species. PmaES4326 has gained attention as an important model strain for the study of P. syringae pathogenesis (10, 23, 24, 26).
FIG. 2.
NJ tree of the concatenated data set. The four major groups discussed in the text are labeled. The host of isolation is given next to each strain designation. Bootstrap scores greater than 60 are given at each node. PfK756 is a P. fluorescens strain used as an outgroup.
gyrB is the only locus that showed a discrepancy from the four-group structure. Four strains that otherwise cluster with group 2 (PsCit7, PsyFTRS_W6, Pto2170, and PttG733) form a monophyletic cluster with three strains that are otherwise in group 3 (both Pmy1 strains and PmsFTRS_U7). These seven strains form a significant cluster (NJ bootstrap, 98; data not shown) equidistant from the rest of the group-2 and -3 strains. In the other six loci, the PsCit7, PsyFTRS_W6, Pto2170, and PttG733 clade and the Pmy1 and PmsFTRS_U7 clade are typically found to be among the most basal branches in groups 2 and 3, respectively. It is likely that a recombination event involving the gyrB locus occurred between the ancestors of these two clades early in the divergence of groups 2 and 3 and resulted in this discrepancy. A surprising conclusion of this analysis is that the gyrB locus, which is perhaps the most common intraspecific index gene, does not accurately represent the same evolutionary history as the majority of the core genome in P. syringae.
An LC test was performed on the nonredundant data set to determine the likelihood of the observed gene tree topologies relative to random topologies (which would be expected with truly independent evolutionary histories) (14). ML trees were constructed for each gene in PAUP* by using parameters for the model of best fit as chosen by Modeltest (46). The likelihood of these trees given the data for the other housekeeping genes was determined and compared to the likelihood of 1,000 random trees generated using the same parameters for the original data. The LC test showed that the differences in the likelihoods (ΔlnL) among MLST gene genealogies are significantly smaller than the differences observed between the MLST trees and random trees (Table 3). The range of likelihood differences among MLST trees was very small relative to the differences obtained by using the random trees, supporting strong congruence among the MLST genes.
TABLE 3.
LC test for phylogenetic congruence
| Tree | −lnL | Δ−lnL (99th percentile)a | Δ−lnL for each gene treeb
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acn | cts | gapA | gyrB | pfk | pgi | rpoD | |||
| acn | 1,461.39 | 1,221.90 | 119.37 | 508.64 | 392.03 | 346.13 | 152.89 | 329.43 | |
| cts | 1,637.94 | 1,228.97 | 196.22 | 440.81 | 509.47 | 420.48 | 184.67 | 404.46 | |
| gapA | 2,192.40 | 2,262.75 | 117.88 | 77.72 | 315.17 | 113.69 | 121.23 | 338.60 | |
| gyrB | 2,362.35 | 2,385.33 | 120.11 | 110.20 | 302.81 | 353.62 | 120.55 | 315.21 | |
| pfk | 2,172.93 | 2,628.07 | 135.84 | 129.34 | 315.06 | 397.38 | 181.20 | 319.90 | |
| pgi | 1,839.76 | 1,954.54 | 127.26 | 108.12 | 494.89 | 442.54 | 407.26 | 362.61 | |
| rpoD | 1,735.25 | 1,768.72 | 227.84 | 216.88 | 628.76 | 509.72 | 501.50 | 338.26 | |
The 99th percentile from the distribution of −lnL differences between the specified tree and the 1,000 random trees.
The −lnL differences between the specified tree and the trees from the other housekeeping genes.
The SH test is conceptually similar to the LC test in that it compares the likelihoods of different data given specified tree topologies, but the SH test directly examines the likelihood of each MLST data set given the trees for all loci. The SH test was performed against ML trees from each of the seven loci, an ML tree for the concatenated data set, and an NJ tree for the concatenated data set (Table 4). The gapA, gyrB, and rpoD data were found to be significantly incongruent with the trees of all loci except their own. The pfk data were found to be incongruent with all but the pfk and gapA trees. Only the cts and pgi data were congruent with the majority of trees. All data sets were congruent with the tree generated from the concatenated data, regardless of the phylogenetic technique used.
TABLE 4.
SH Test for phylogenetic congruence
| Tree |
Pa
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acn | cts | gapA | gyrB | pfk | pgi | rpoD | Concatenated | |
| acn | 0.141 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.204 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| cts | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| gapA | 0.037 | 0.308 | 0.004 | 0.428 | 0.209 | 0.000 | 0.003 | |
| gyrB | 0.137 | 0.139 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.309 | 0.001 | 0.000 | |
| pfk | 0.041 | 0.135 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.112 | 0.001 | 0.000 | |
| pgi | 0.030 | 0.142 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| rpoD | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Concatenated ML | 0.699 | 0.717 | 0.79 | 0.565 | 0.731 | 0.828 | 0.082 | |
| Concatenated NJ | 0.719 | 0.757 | 0.69 | 0.588 | 0.709 | 0.738 | 0.064 | 0.835 |
Significant differences are boldfaced.
We also used the ILD test (5, 45), which tests for significant differences in branch lengths of MP trees between different data sets. Identical sequences were removed from the analysis, and a P value of 0.05 was used. The ILD test found all trees to be incongruent (data not shown), although it should be noted that there has been significant controversy over the use of the ILD test due to its conservative assumptions and its failure when there are many MP trees for each gene (3, 7).
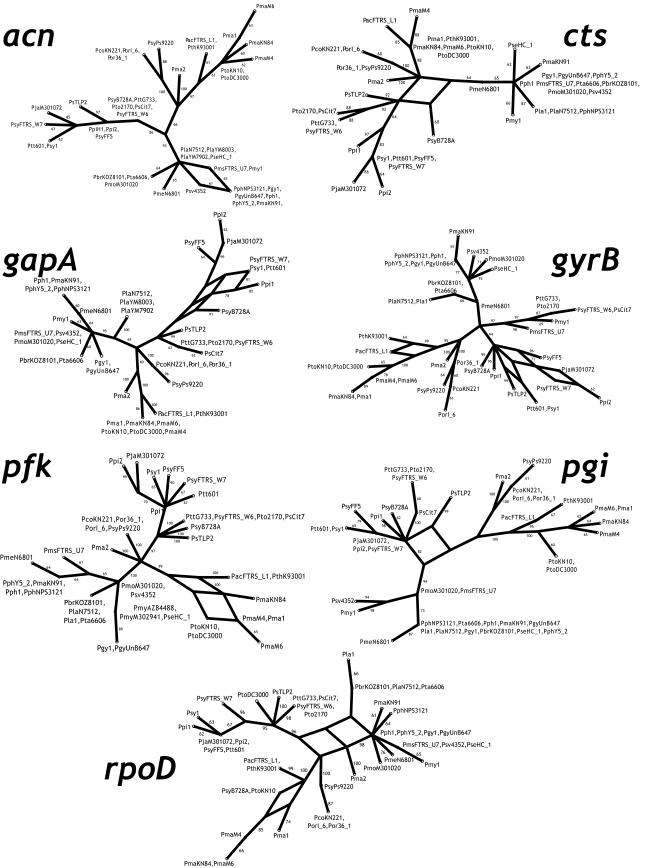
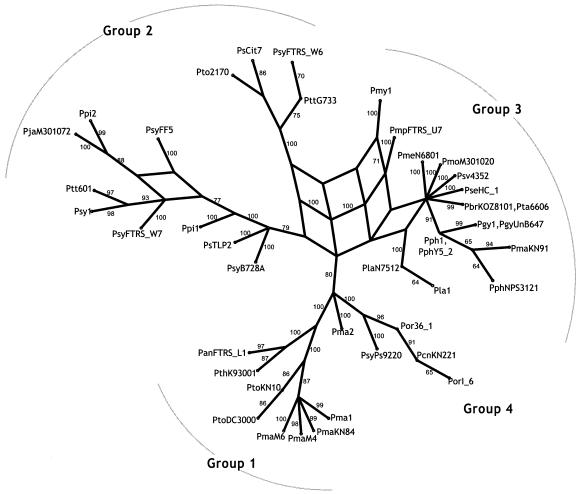
Split decomposition analysis was used to investigate the influence of recombination on the evolution of each locus (2, 11). Split decomposition constructs a network connection between taxa whenever there is a phylogenetic inconsistency due to homoplasy or recombination. Recombination is generally inferred when competing splits have equal support. Split decomposition analysis of the individual MLST loci recovered the same phylogenetic clusters as the other, more traditional phylogenetic approaches (Fig. 3). This included very strong support (bootstrap, 97%) for the unusual grouping of some group-2 and -3 strains at the gyrB locus as previously mentioned. In general there was very little network structure for the individual genealogies, and that which was seen was primarily localized near the tips, indicating some recombination within groups but not between groups. acn, cts, gyrB, pfk, pgi, and rpoD had no significant reticulations, while gapA had a single significant reticulation in the group-2 strains. Significant reticulations are indicated when there are alternate statistically supported paths in the graph. These are regions of the graph where alternate paths have roughly the same high level of statistical support, as determined by bootstrap analysis. Split decomposition analysis of the concatenated data set showed much more significant network structure (Fig. 4). The majority of the reticulations occurred near the base of the graph, with one supported by bootstrap analysis (100% along one path and 71% along the alternate path). This reticulation corresponds to the recombination event seen in the gyrB locus.
FIG. 3.
Split decomposition analysis of each housekeeping gene. Bootstrap scores greater than 60 are given at each node. Significant reticulations are those in which there is a roughly equal high level of support for alternative paths in the graph.
FIG. 4.
Split decomposition analysis of the concatenated data set. The four major groups discussed in the text are indicated. Bootstrap scores greater than 60 are given at each node.
MLST analyses.
A traditional MLST clonal group is defined as comprising strains that are identical at five or more loci (16). The strains in the clonal group included the predominant (consensus) ST along with its SLVs, DLVs, and SATs. Among the 60 strains in our study, only two traditional MLST clonal groups, containing only 5 strains, could be assigned. Of the other 55 isolates, 15 fell into six monomorphic groups (were completely identical), 21 fell in four groups that had only DLVs and/or SATs, and 19 were singletons (had no similarity to any other isolates).
Each of the two clonal groups had one SLV. One of these, PlaN7512, differed from the concensus (as represented by Pla1) at a single nucleotide site of the rpoD locus. This was a synonymous change that resulted in the creation of a unique allele. The other SLV, PtoKN10, differed at 34 nucleotide sites from the consensus (as represented by PtoDC3000), also at the rpoD locus. Interestingly, the PtoKN10 rpoD allele was the same as the allele found in the highly divergent bean pathogen PsyB728A. Of the 34 pairwise differences between the PtoKN10 and PtoDC3000 alleles, 2 are nonsynonymous (Ks = 0.3612; Ka = 0.0061). Given the large number of differences between these alleles and the fact that an identical allele is present in the population, it is very likely that the PtoKN10 rpoD allele was introduced into the strain by recombination. Based on these very limited groups we can calculate a recombination-to-mutation ratio (16, 22). Of the two SLVs, one change is presumably due to mutation and the other is presumably due to recombination; therefore, the per-gene ratio would be 1:1. The putative recombination event resulted in 34 changes, while the mutation resulted in a single change, giving a per-site recombination-to-mutation ratio of 34:1. Given the extremely small sample size from which these numbers are derived, they must be interpreted with caution. A better estimate of the recombination-to-mutation ratio, which is based on a coalescent analysis, is presented below.
Polymorphism.
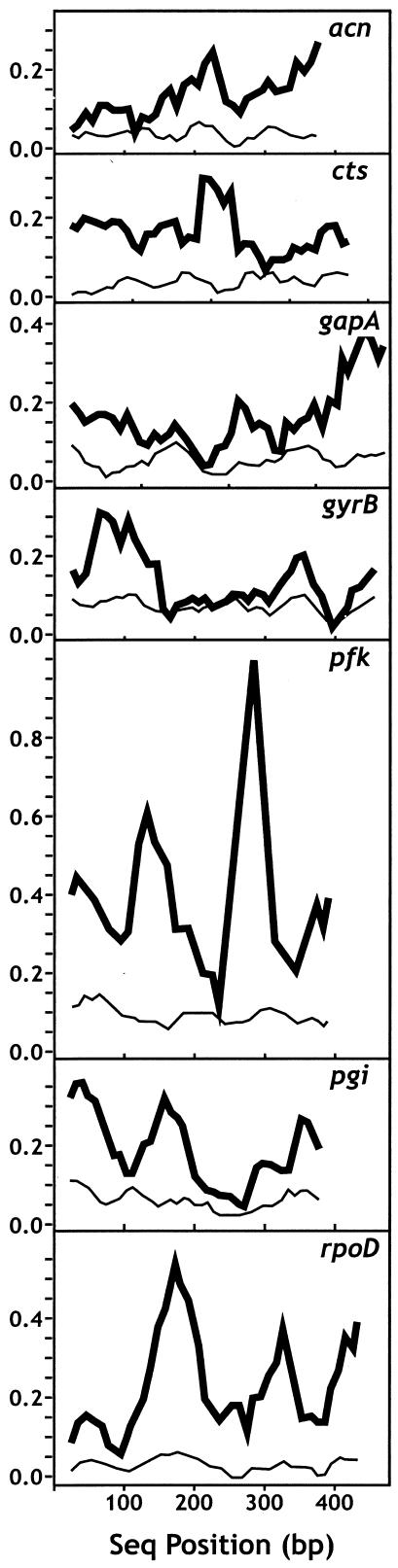
The rates of evolution are roughly the same among loci. All loci have 23 to 31 alleles, and the average number of alleles per locus is 27 (Table 5), resulting in more than 1010 (277)potential STs. Watterson's θ and the pairwise nucleotide diversity (π) are also highly consistent across loci (Table 5), ranging from 0.03977 to 0.08547 for θ and from 0.04211 to 0.10035 for π. The average synonymous nucleotide diversity was 0.2411, while the average nonsynonymous nucleotide diversity was 0.0108. The average divergence from P. fluorescens was 0.1792. A sliding-window analysis of the total pairwise nucleotide diversity and divergence from P. fluorescens is presented in Fig. 5. Nucleotide diversity remains fairly constant over the seven loci, while substantial variation is seen in the degree of divergence, particularly in the pfk and rpoD loci. These peaks in divergence are presumably not due to positive selection (see below) but may be due to the relaxation of selective constraints for part of the gene. The genetic distances within and between phylogenetic groups (Fig. 2) are presented in Table 6. The mean within-group distance is 0.017, while the mean between-group distance is 0.150.
TABLE 5.
Population genetic analyses
| Gene | Length (bp) | No. of haplotypes | θ (total) | πa
|
Divergence from P. fluorescens | Tajima's D | Fu's Fs | Ka/Ks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Synon. | Nonsynon. | ||||||||
| acn | 399 | 26 | 0.0398 | 0.0437 | 0.1728 | 0.0056 | 0.1310 | 0.3384 | 0.39 | 0.0303 |
| cts | 445 | 23 | 0.0429 | 0.0421 | 0.1765 | 0.0029 | 0.1487 | −0.0628 | 2.353 | 0.0135 |
| gapA | 497 | 26 | 0.0536 | 0.0627 | 0.2282 | 0.0075 | 0.1547 | 0.5958 | 4.558 | 0.0208 |
| gyrB | 480 | 31 | 0.0693 | 0.0797 | 0.3310 | 0.0072 | 0.1295 | 0.5316 | 2.967 | 0.0149 |
| pfk | 414 | 27 | 0.0855 | 0.1004 | 0.3265 | 0.0304 | 0.3157 | 0.6131 | 6.835 | 0.0520 |
| pgi | 448 | 26 | 0.0646 | 0.0682 | 0.2448 | 0.0112 | 0.1683 | 0.1948 | 4.385 | 0.0325 |
| rpoD | 452 | 28 | 0.0563 | 0.0531 | 0.2077 | 0.0105 | 0.2062 | −0.1984 | 1.256 | 0.0312 |
| Mean | 447.9 | 26.7 | 0.0589 | 0.0643 | 0.2411 | 0.0108 | 0.1792 | 0.2875 | 3.249 | 0.0279 |
Synon., synonymous; Nonsynon., nonsynonymous.
FIG. 5.
Sliding-window analysis of polymorphism (thin lines) and divergence from P. fluorescens (heavy lines) for each of the seven housekeeping genes.
TABLE 6.
Genetic distances within and between groups
| Group | Genetic distancea ± SE for group:
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1 | 0.017 ± 0.002 | |||
| 2 | 0.164 ± 0.014 | 0.035 ± 0.003 | ||
| 3 | 0.137 ± 0.011 | 0.111 ± 0.009 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | |
| 4 | 0.160 ± 0.013 | 0.160 ± 0.014 | 0.168 ± 0.015 | 0.004 ± 0.001 |
Calculated using the Kimura two-parameter model with a gamma correction of 0.18. The mean within-group distance was 0.017; the mean between-group distance was 0.0150.
Selection.
MLST analysis assumes that the loci under study are representative of the core genome of the species. Core genes are those that are required by all members of the species and therefore are less likely to be horizontally transferred among strains. If these loci are essential, then it is a reasonable assumption that the predominant form of selection acting on them will be purifying. We tested this assumption with three population genetic tests of selection. Tajima's D statistic (60) looks at differences between the two estimators of nucleotide polymorphism (θ and π), while Fu's Fs statistic (19) is a one-sided test that looks for an excess of rare alleles. This test is particularly powerful for detecting genetic hitchhiking and population expansion (34). Neither of the tests produced any significant results (Table 5). The final test of selection performed was the Ka/Ks test, which measures the ratio of the nonsynonymous to the synonymous substitution rate. This ratio should be equal to 1 under strict neutrality, greater than 1 under positive selection, and less than 1 under purifying selection. All Ka/Ks ratios were substantially less than 1, ranging from 0.0135 for cts to 0.052 for pfk, indicating that all the loci are under fairly strong purifying selection.
Recombination.
Maynard Smith's IA (43) was used to assess the linkage disequilibrium between alleles among loci. An IA significantly greater than 1 indicates linkage disequilibrium in the sample. IA for the complete MLST data set was highly significant at 3.689, with an observed variance of 2.143 and an expected variance of 0.457. IA calculated for the four major monophyletic groups had roughly the same values, ranging from 3.290 for group 1 to 3.713 for group 2, and therefore showed significant linkage within groups. This indicates a population structure where recombination is limited both within and between groups.
The homoplasy ratio test determines if there is a significant excess of homoplasies in a phylogenetic tree relative to an estimate of the number of homoplasies expected by repeated mutation in a strictly clonal species (42). Recombination should result in an excess of homoplasies. When this test was applied to the P. syringae data, it actually resulted in homoplasy ratios below zero, which is expected to be the lower bound for a strictly clonal organism (data not shown). Tests on all loci gave nonsignificant results, indicating that there were significantly fewer homoplasies than would be expected under free recombination.
McVean et al. (44) have developed a coalescence-based method for detecting recombination that is implemented in LDhat. This program permits the estimation of the per-locus population recombination rate, 2Ner (Ne, effective population size; r, recombination rate), by using a coalescence-based approximate-likelihood method. Intragenic recombination was estimated by using individual genes, while intergenic recombination was estimated by using the concatenated data set. By use of an average tract length of 100 nucleotides, limited recombination was detected in the seven housekeeping genes, with 2Ner estimated at 3.03 to 10.10 for the individual genes and 11.11 for the concatenated data set (Table 7). The highest recombination rate detected was 10.101, in gyrB. We also tested for recombination within the major monophyletic groups. Very little intragenic or intergenic recombination was detected in groups 1 and 4 (2Ner of the concatenated data = 0), but significant recombination was seen in groups 2 and 3 (2Ner of the concatenated data, 4.04 and 16.16, respectively).
TABLE 7.
LDhat recombination analysis
| Gene | Complete
|
Group 1
|
Group 2
|
Group 3
|
Group 4a
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | ρ | ɛ | θ | ρ | ɛ | θ | ρ | ɛ | θ | ρ | ɛ | θ | ρ | ɛ | |
| acn | 0.029 | 0.005 | 0.172 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 0.332 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 1.508 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| cts | 0.034 | 0.009 | 0.264 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.178 | 0.026 | 0.004 | 0.158 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| gapA | 0.034 | 0.009 | 0.271 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.027 | 0.004 | 0.151 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.044 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| gyrB | 0.054 | 0.010 | 0.189 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.031 | 0.006 | 0.196 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 2.880 |
| pfk | 0.050 | 0.006 | 0.121 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.039 | 0.006 | 0.157 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| pgi | 0.049 | 0.030 | 0.622 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.465 | |||
| rpoD | 0.040 | 0.005 | 0.126 | 0.037 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.653 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Concat.b | 0.054 | 0.011 | 0.207 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.028 | 0.004 | 0.144 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 1.275 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Mean | 0.041 | 0.011 | 0.252 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.003 | 0.114 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.403 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.576 |
Values for pfk and pgi could not be calculated because of the lack of informative sites for the four members. Values for ρ were obtained by dividing the per-locus recombination rate estimate from LDhat by 1,000 (the approximate average length of a P. syringae gene).
Concat., concatenated data set.
A very informative recombination analysis is performed by calculating the recombination rate (r) relative to the rate of neutral mutation (μ) (15, 22, 42, 47). In this manner we can determine the relative probability that any single nucleotide will be changed due to mutation versus recombination. We can obtain this information by calculating ɛ, the ratio of the population recombination rate ρ (2Ner) to the population mutation parameter θ (2Neμ), where Ne is the effective population size. By dividing these two population parameters, we cancel out the Ne and are left with r/μ, the relative strength of recombination versus mutation in generating genetic variability. Using the values of θ and ρ obtained from LDhat, we see that ɛ ranges from 0.121 for pfk to 0.622 for pgi, with an average ɛ of 0.252 (Table 7). These numbers are in general agreement with those derived from DnaSp, which uses the Hudson recombination rate estimator (29). The simple interpretation of these results is that any single nucleotide in the P. syringae genome is 4 times more likely to change due to mutation than it is to change due to recombination. When the data set is broken down into the four major clades, a striking pattern emerges. Although the mutation rate stays roughly the same across the groups, the recombination rates are dramatically different. Essentially all of the recombination in the species appears to be happening in groups 2 and 3, while groups 1 and 4 appear to be almost strictly clonal (Table 7). Split decomposition analyses of the individual groups also support this conclusion (data not shown). These results may once again reflect the early recombination event that occurred between the subset of group-2 (PsCit7, PsyFTRS_W6, Pto2170, and PapG733) and group-3 (Pmy1 and PmsFTRS_U7) strains at or near the gyrB locus.
We attempted to localize putative recombination breakpoints via sliding-window phylogenetic analysis. Both TOPALi, which performs a DSS test on trees generated from the two halves of a window moved across the target sequence, and bootscanning (as implemented in SIMPLOT), which scans for changes in the phylogenetic relatedness of individual sequences among clades, failed to find any significant recombination breakpoints (data not shown).
Demographic history.
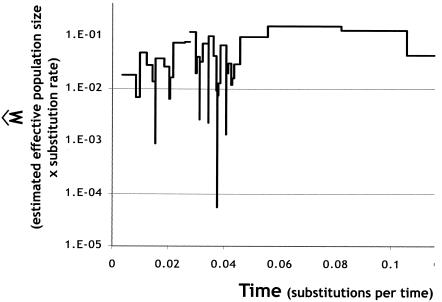
An exciting recent development in coalescent analyses of sequence data is the ability to make estimates of the sample's effective population size through time. Skyline plots are coalescence-based analyses of demographic history. These analyses provide a visual and intuitive method to determine if population sizes have been constant or changed during recent evolutionary history. Skyline plots that are roughly parallel to the x axis indicate a constant population size. Those that drop off as time increases indicate population expansion. The exact shape of the curve can be used to infer more details about the nature of the population size changes (57). Rapid population expansion is indicative of epidemic pathogens, while constant population sizes are indicative of endemic pathogens. A classic skyline plot was constructed for our fully nonredundant sample by using the concatenated data. The skyline plot (Fig. 6) shows no indications of dropping off as time increases, thereby indicating that the sample maintains a fairly constant effective population size through time. These results are consistent with P. syringae being an endemic pathogen.
FIG. 6.
Skyline plot of the concatenated data set.
Population structure and host association.
We used AMOVA to test for population structure resulting from associations between the genetic data and host association (Table 8). When the total sample was used, 38% of the variation was within the host, while 62% was among hosts. To remove some of the biases in the sample, we reanalyzed the data by using only the nonredundant sample set (removing those sequences that both were identical and shared a common host). Under these conditions, the within-host variation jumped to 80%, with the among-host variation at 20%. The fixation index (FST) was 0.62 in the former analysis and 0.20 in the latter analysis. As expected, very similar results were obtained when the pathovar designation was used instead of the host of isolation.
TABLE 8.
AMOVA
| Source of variation | df | Sum of squares | Variance competent | % Variation | FST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full data set | |||||
| Among hosts | 27 | 6,174.2 | 84.4 | 61.9 | |
| Within hosts | 32 | 1,661.3 | 51.9 | 38.1 | |
| Total | 59 | 7,835.4 | 136.5 | 0.62 | |
| Nonredundant data set | |||||
| Among hosts | 27 | 4,230.4 | 28.5 | 20.0 | |
| Within hosts | 14 | 1,603.0 | 114.5 | 80.0 | |
| Total | 41 | 5,833.4 | 143.0 | 0.20 |
DISCUSSION
The dynamic evolution of bacterial pathogens allows for their evasion of host surveillance systems, resistance to antimicrobial agents, and rapid adaptation to new hosts. Intraspecific recombination and interspecific horizontal gene transfer are known to facilitate this dynamic evolutionary process by introducing the genetic diversity that underlies many, if not most, adaptive virulence phenotypes, but virulence-associated genes do not act in isolation. They must function within a genomic context and ultimately contribute to the overall fitness of a clone if they are to be successfully propagated. Therefore, understanding bacterial clonal population structure is an essential component to understanding bacterial pathogenesis. Knowing how clonal lineages arise in bacterial populations is not only an indispensable epidemiological tool but also provides a means for identifying and characterizing virulence-associated factors.
Phylogenetics of P. syringae.
Our phylogenetic analysis of P. syringae reveals four major groups of strains, three of which largely correspond to those identified by Sawada et al. (53). Group 4 is intriguing because it is the most divergent major clade and contains only pathogens of monocots (rice, oats, and onions). Only two other monocot pathogens are present in our study; both of these strains are found in group 2, but they are highly divergent from each other. Of the nine strains that overlapped between our analysis and that made by Sawada et al. (53), all were in agreement with respect to their phylogenetic grouping.
Host association was found to be relatively weak in the nonredundant sample set. Almost 80% of the total variation was found within populations defined by host of isolation. Alternatively stated, less than 20% of the variation was host specific. These numbers shift fairly dramatically to 61% within-host variation and 39% among-host variation when the full sample set is used, revealing a significant sampling bias. The bias is most apparent with the high level of identity found in the glycinea and maculicola pathovars. It is possible that this bias has a biological basis, but a simpler explanation is that most of the strains came from the same stock center, and many were collected from the same geographic area. This critical weakness must be corrected before a full picture of P. syringae population structure is obtained.
Although sampling biases are almost universally considered negative aspects of studies, in this case these “problems” actually provide tantalizing glimpses into the dynamics of natural bacterial populations. Eight soybean (glycinea) pathogens collected over a 13-year period are genetically identical, while four Chinese cabbage pathogens (maculicola) remained genetically uniform over 12 years. Three strains are genetically identical, yet all were isolated from different hosts; most interesting is the identity between the paper mulberry pathogen PbrKOZ8101 and the tobacco pathogen Pta6606 despite their different hosts and 13 years separating their collection. Finally, the two radish pathogens PmaES4326 and PmaYM7930 are genetically identical despite the fact that the former was collected in the United States in 1965 while the latter was collected 14 years later in Japan. If we take the conservative assumption of 2 generations per day, then 14 years encompass more than 10,000 generations, during which no mutations occurred in the 3,135 bp of sequence we analyzed. This may indicate a stabilized host-pathogen relationship.
Conversely, there are also quite a few cases where strains isolated from the same host turn out to be extremely divergent. The radish pathogen PmaKN91 clusters with the bean pathogens in group 3, while all other maculicola pathovars are in group 1 or are species outliers. There are tomato pathogens both in group 1 (PtoDC3000 and PtoKN10) and in group 2 (Pto2170). The well-characterized snap bean pathogen PsyB728a is found in group 2, while all other bean pathogens are tightly clustered in group 3. There are two widely divergent Japanese apricot pathogens in group 2 (PsyFTRS_W7835 and PsyFTRS_W6601) and a third in group 3 (PmpFTRS_U7805). Finally, although two rice pathogens are in group 4 (PorI_6 and Por36_1), there is a third (PttG733) that clusters tightly with apricot and tomato pathogens and with Cit7, a nonpathogenic isolate from oranges. These instances of host convergence may be due to common features of the flexible genome.
P. syringae species definition.
Gardan et al. (20) have proposed that group-3 strains be given separate species status as P. savastanoi. A numerical taxonomy analysis of DNA-DNA hybridization data showed that savastanoi pathovars clustered with glycinea and phaseolicola pathovars and that this cluster was distinct from the syringae pathovars. These hybridization results are largely consistent with our MLST analysis; nevertheless, a cladistic analysis of our data strongly refutes the ascension of pathovar savastanoi to species status. Our analyses reveal that P. syringae group 3 is not monophyletic at the gyrB locus and that it is consistently a sister clade to group 2. Raising group 3 to species status would leave the rest of the species paraphyletic, thereby violating cladistic rules of systematics. If group 3 is to be given species status, then each of the other groups would likewise necessarily have to be given the same status, thus splitting P. syringae into four separate species.
Should P. syringae be split into four distinct species based on this study? We do not believe the data support this proposal. The ecology of all P. syringae strains is very similar: all are commensal and/or pathogens of aerial plant surfaces. Additionally, there are no reliable biochemical or physiological distinctions that differentiate the four groups (35). There are also a small number of core genome alleles shared among strains that belong to different P. syringae groups. Finally, the evolutionary histories of a very large number of noncore genes (e.g., virulence-associated genes such as type III effectors) are highly incongruent with that derived from the core genome and are supportive of extensive horizontal gene transfer among strains (24; D. S. Guttman, unpublished data). In conclusion, given the relatively small size of the present data set and the lack of distinctiveness of the four groups, we believe that splitting the species into four is unjustified at this time.
Recombination and clonality.
Recombination plays an extremely important role in bacterial evolution by homogenizing genetic variation within clones and introducing genetic variation between clones. The relative importance of recombination in generating genetic variation and breaking down clonal complexes has been a source of substantial controversy and intensive investigation (14, 15, 21, 22, 41, 43, 56, 61). The extent of recombination in P. syringae has been addressed only once before. Maynard Smith et al. (41) analyzed the multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MLEE) data collected by Denny et al. (9) from two pathovars of P. syringae. They found extremely high levels of linkage disequilibrium in the total sample and slightly lower, but still significant, levels within each pathovar. There is difficulty in interpreting these data simply due to the imperfect correspondence between linkage disequilibrium and clonality; nevertheless, the extraordinarily high level of linkage seen (nearly three times higher than that of any other species in the study) is prima facie evidence that P. syringae is a highly clonal species.
Our analyses support the conclusion that P. syringae is a highly clonal organism. The high level of congruence between gene trees and the inability of the sliding-window phylogenetic tests to identify recombination breakpoints within loci support a common evolutionary history for loci widely separated around the genome. The relative lack of reticulation in the split decomposition graphs, particularly when individual loci are examined, further supports a relatively limited role for recombination. The coalescence-based estimates of ɛ, the recombination-to-mutation rate ratio, indicate that mutation is perhaps four times more likely to change any particular nucleotide than recombination. The MLST-based recombination analyses are also interesting, but much less reliable. The per-locus rate of recombination was estimated to be equal to the mutation rate, while the per-site recombination rate was 34 times that of the per-site mutation rate. These numbers must be accepted with extreme caution, because this analytical technique was developed for much larger data sets and is probably inappropriate for a data set of the present size. Calculation of Maynard Smith's IA (41) again is in agreement with the findings of the MLEE study, with highly significant levels of linkage observed in the total sample and within each group. The homoplasy ratio test reached its lower limit, indicating that there was far less homoplasy than would be expected under free recombination. In summary, all of the analyses are in general agreement that recombination is relatively rare in this species. The conclusions from the coalescence-based approach are perhaps most meaningful in this analysis given the size and structure of the data set.
How does P. syringae compare to other species studied? Taking all of the analyses together, it appears that the variation-generating potential of recombination is roughly equal to or slightly less than that of mutation in this species. This recombination rate is dramatically lower than that seen in most other species. Neisseria meningitidis has the highest per-nucleotide ratio of the recombination rate to the mutation rate on record, at 100:1 (14), while Escherichia coli has a ratio of approximately 50:1 (22) and Streptococcus pneumoniae has a ratio of 24:1 (14). The lowest ratio on record is that of Staphylococcus aureus, where any nucleotide site is 15 times more likely to be changed by mutation than by recombination (ratio, 1:15) (13).
Population structure of P. syringae.
In synthesizing these analyses, we are left with a picture of a species that is highly clonal. There is essentially no genetic exchange of the core genome among strains on different hosts. The split decomposition analysis reveals a significant network structure only in the concatenated data set, which may correspond to a past intergenic recombination (occurring at loci other than those sequenced) or to the one event seen at the gyrB locus. All of the significant reticulations in this analysis are near the center of the graph. The most likely explanation for this pattern is that early in the origin of the species there was limited genetic exchange between strains, but as the strains diverged and specialized on their respective hosts, they became more reproductively isolated. The result is clonal lineages that are evolving essentially independently of the rest of the species with respect to their core genome. The finding of remarkable genetic homogeneity among soybean, cabbage, or radish pathogens isolated over a dozen years further supports this conclusion.
The remarkable genetic stability of these strains is supported by the analysis of demographic history. The skyline plot clearly indicates that the P. syringae population has maintained a roughly constant size through time. This is an excellent indication that the species is endemic in plant populations and that large-scale (affecting a significant fraction of the total species) outbreaks of new and more virulent pathogens are rare. What cannot be ruled out at this time is smaller-scale, host-specific outbreaks. The emergence and spread of a new strain that is more virulent on a single host would result in a selective sweep, or purge, of the genetic variation within that host-specific population. Importantly, this epidemic would not affect strains on other hosts. We would expect these dynamics to result in genetic homogeneity within host-specific populations and in extensive divergence and perhaps isolation between populations. This is not inconsistent with the present data, but much more extensive natural population sampling would be required to confirm this hypothesis and identify these epidemics.
If the core genome of P. syringae were responsible for determining host specificity, it would be reasonable to assume that the genetic variation in the housekeeping genes would be very tightly associated with the host of isolation. Additionally, since the core genome is effectively clonal, we would expect phenotypic differences between clonal lineages to accumulate as they wandered down their independent evolutionary paths. However, host of isolation explains only 20% of the variation in the core genome. Short of host specificity, one pathovar of P. syringae is largely phenotypically indistinguishable from another. Clearly, factors outside of the core genome must be maintaining the cohesion of the species and must play very significant roles in determining host suitability. Likely flexible-genome candidates for this role include a wide range of virulence factors, such as type III secreted effector proteins, toxins, and resistance genes. Hopefully, the intensive study of P. syringae virulence factors currently under way will shed light on the complex mechanisms used by this important organism to adapt to its diverse set of hosts.
Acknowledgments
We thank the individuals who provided strains for this study. Pauline Wang, Susan Gropp, John Stavrinides, and two anonymous reviewers provided valuable input and critiques.
D.S.G. is supported by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation. S.F.S. is partially supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship and a Vedanta Society of Toronto Vivekananda Scholarship.
REFERENCES
- 1.Awadalla, P. 2003. The evolutionary genomics of pathogen recombination. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4:50-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bandelt, H. J., and A. W. Dress. 1992. Split decomposition: a new and useful approach to phylogenetic analysis of distance data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1:242-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barker, F. K., and F. M. Lutzoni. 2002. The utility of the incongruence length difference test. Syst. Biol. 51:625-637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chenna, R., H. Sugawara, T. Koike, R. Lopez, T. J. Gibson, D. G. Higgins, and J. D. Thompson. 2003. Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:3497-3500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cunningham, C. W. 1997. Can three incongruence tests predict when data should be combined? Mol. Biol. Evol. 14:733-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cuppels, D. A. 1986. Generation and characterization of Tn5 insertion mutations in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51:323-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Darlu, P., and G. Lecointre. 2002. When does the incongruence length difference test fail? Mol. Biol. Evol. 19:432-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Debener, T., H. Lehnackers, M. Arnold, and J. L. Dangl. 1991. Identification and molecular mapping of a single Arabidopsis thaliana locus determining resistance to a phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae isolate. Plant J. 1:289-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Denny, T. P., M. N. Gilmour, and R. K. Selander. 1988. Genetic diversity and relationships of two pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:1949-1960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dong, X., M. Mindrinos, K. R. Davis, and F. M. Ausubel. 1991. Induction of Arabidopsis defense genes by virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas syringae strains and by a cloned avirulence gene. Plant Cell 3:61-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dopazo, J., A. Dress, and A. Haeseler. 1993. Split decomposition: a technique to analyze viral evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:10320-10324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Enright, M. C., and B. G. Spratt. 1999. Multilocus sequence typing. Trends Microbiol. 7:482-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Feil, E. J., J. E. Cooper, H. Grundmann, D. A. Robinson, M. C. Enright, T. Berendt, S. J. Peacock, J. M. Smith, M. Murphy, B. G. Spratt, C. E. Moore, and N. P. Day. 2003. How clonal is Staphylococcus aureus? J. Bacteriol. 185:3307-3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Feil, E. J., E. C. Holmes, D. E. Bessen, M. S. Chan, N. P. Day, M. C. Enright, R. Goldstein, D. W. Hood, A. Kalia, C. E. Moore, J. Zhou, and B. G. Spratt. 2001. Recombination within natural populations of pathogenic bacteria: short-term empirical estimates and long-term phylogenetic consequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:182-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Feil, E. J., M. C. Maiden, M. Achtman, and B. G. Spratt. 1999. The relative contributions of recombination and mutation to the divergence of clones of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16:1496-1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Feil, E. J., J. M. Smith, M. C. Enright, and B. G. Spratt. 2000. Estimating recombinational parameters in Streptococcus pneumoniae from multilocus sequence typing data. Genetics 154:1439-1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Feil, E. J., and B. G. Spratt. 2001. Recombination and the population structures of bacterial pathogens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55:561-590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Felsenstein, J. 1993. PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package), 3.5c ed. Distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle.
- 19.Fu, Y. X. 1997. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147:915-925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gardan, L., C. Bollet, M. Abughorrah, F. Grimont, and P. A. D. Grimont. 1992. DNA relatedness among the pathovar strains of Pseudomonas syringae subsp. savastanoi Janse (1982) and proposal of Pseudomonas savastanoi sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42:606-612. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guttman, D. S. 1997. Recombination and clonality in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Trends Ecol. Evol. 12:16-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guttman, D. S., and D. E. Dykhuizen. 1994. Clonal divergence in Escherichia coli as a result of recombination, not mutation. Science 266:1380-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guttman, D. S., and J. T. Greenberg. 2001. Functional analysis of the type III effectors AvrRpt2 and AvrRpm1 of Pseudomonas syringae with the use of a single-copy genomic integration system. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 14:145-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guttman, D. S., B. A. Vinatzer, S. F. Sarkar, M. Ranall, and J. T. Greenberg. 2002. A functional screen for the type III (Hrp) secretome of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Science 295:1722-1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hacker, J., and E. Carniel. 2001. Ecological fitness, genomic islands and bacterial pathogenicity: a Darwinian view of the evolution of microbes. EMBO Rep. 2:376-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hendrickson, E. L., P. Guevera, and F. M. Ausubel. 2000. The alternative sigma factor RpoN is required for hrp activity in Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola and acts at the level of hrpL transcription. J. Bacteriol. 182:3508-3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hirano, S. S., and C. D. Upper. 2000. Bacteria in the leaf ecosystem with emphasis on Pseudomonas syringae—a pathogen, ice nucleus, and epiphyte. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64:624-653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Horst, R. K. 1990. Westcott's plant disease handbook, 5th ed. Chapman & Hall, New York, N.Y.
- 29.Hudson, R. R. 1987. Estimating the recombination parameter of a finite population model without selection. Genet. Res. 50:245-250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huson, D. H. 1998. SplitsTree: analyzing and visualizing evolutionary data. Bioinformatics 14:68-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Janisiewicz, W. 2002. Pseudomonas syringae (saprophytic strain) and “fruit yeasts.” In C. Weeden, T. Shelton, Y. Li, and M. Hoffmann (ed.), Biological control: a guide to natural enemies in North America. [Online.] Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y. http://www.nysaes.cornell.edu/ent/biocontrol.
- 32.Jolley, K. A., E. J. Feil, M.-S. Chan, and M. C. J. Maiden. 2001. Sequence type analysis and recombinational tests (START). Bioinformatics 17:1230-1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.King, E. O., M. K. Ward, and D. E. Raney. 1954. Two simple media for the demonstration of phycocyanin and fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 44:301-307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kreitman, M. 2000. Methods to detect selection in populations with applications to the human. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 1:539-559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Krieg, N. R., and J. G. Holt (ed.). 1984. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 1. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
- 36.Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei. 1994. MEGA—molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 10:189-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lindgren, P. B., R. C. Peet, and N. J. Panopoulos. 1986. Gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola controls pathogenicity of bean plants and hypersensitivity of nonhost plants. J. Bacteriol. 168:512-522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lindow, S. E. 1987. Competitive exclusion of epiphytic bacteria by Ice− Pseudomonas syringae mutants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53:2520-2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Loper, J. E., and S. E. Lindow. 1987. Lack of evidence for in situ fluorescent pigment production by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae on bean leaf surfaces. Phytopathology 77:1449-1454. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Maiden, M. C. J., J. A. Bygraves, E. Feil, G. Morelli, J. E. Russell, R. Urwin, Q. Zhang, J. J. Zhou, K. Zurth, D. A. Caugant, I. M. Feavers, M. Achtman, and B. G. Spratt. 1998. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:3140-3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maynard Smith, J., E. J. Feil, and N. H. Smith. 2000. Population structure and evolutionary dynamics of pathogenic bacteria. Bioessays 22:1115-1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Maynard Smith, J., and N. H. Smith. 1998. Detecting recombination from gene trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15:590-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Maynard Smith, J., N. H. Smith, M. O'Rourke, and B. G. Spratt. 1993. How clonal are bacteria? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:4384-4388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.McVean, G., P. Awadalla, and P. Fearnhead. 2002. A coalescent-based method for detecting and estimating recombination from gene sequences. Genetics 160:1231-1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mickevich, M. E., and J. S. Farris. 1981. The implications of congruence in Menidia. Syst. Zool. 30:351-370. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Posada, D., and K. A. Crandall. 1998. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817-818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Posada, D., K. A. Crandall, and E. C. Holmes. 2002. Recombination in evolutionary genomics. Annu. Rev. Genet. 36:75-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pybus, O. G., and A. Rambaut. 2002. GENIE: estimating demographic history from molecular phylogenies. Bioinformatics 18:1404-1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pybus, O. G., A. Rambaut, and P. H. Harvey. 2000. An integrated framework for the inference of viral population history from reconstructed genealogies. Genetics 155:1429-1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rozas, J., and R. Rozas. 1999. DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Salminen, M. O., J. K. Carr, D. S. Burke, and F. E. McCutchan. 1995. Identification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV type 1 by bootscanning. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 11:1423-1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sawada, H., S. Kanaya, M. Tsuda, F. Suzuki, K. Azegami, and N. Saitou. 2002. A phylogenomic study of the OCTase genes in Pseudomonas syringae pathovars: the horizontal transfer of the argK-tox cluster and the evolutionary history of OCTase genes on their genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 54:437-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sawada, H., F. Suzuki, I. Matsuda, and N. Saitou. 1999. Phylogenetic analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pathovars suggests the horizontal gene transfer of argK and the evolutionary stability of hrp gene cluster. J. Mol. Evol. 49:627-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schneider, S., D. Roessli, and L. Excoffier. 2000. Arlequin: a software for population genetics data analysis, 2.0 ed. Genetics and Biometry Lab, Department of Anthropology, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland.
- 55.Shimodaira, H., and M. Hasegawa. 1999. Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16:1114-1116. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Spratt, B. G., W. P. Hanage, and E. J. Feil. 2001. The relative contributions of recombination and point mutation to the diversification of bacterial clones. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 4:602-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Strimmer, K., and O. G. Pybus. 2001. Exploring the demographic history of DNA sequences using the generalized skyline plot. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18:2298-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sundin, G. W., and C. L. Bender. 1993. Ecological and genetic analysis of copper and streptomycin resistance in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59:1018-1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Swofford, D. L. 1993. PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, 3.1 ed. Illinois Natural History Survey, University of Illinois, Champaign.
- 60.Tajima, F. 1989. Statistical methods for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Whittam, T. S., H. Ochman, and R. K. Selander. 1983. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:1751-1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]