Abstract
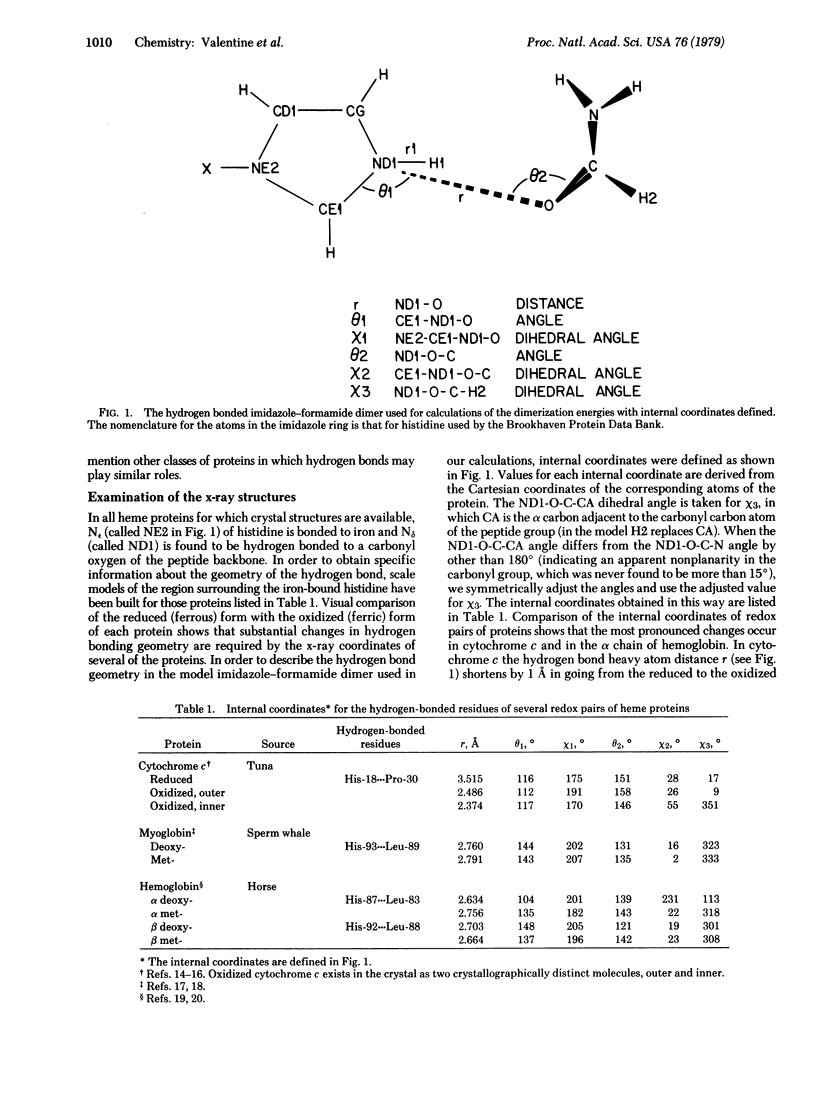
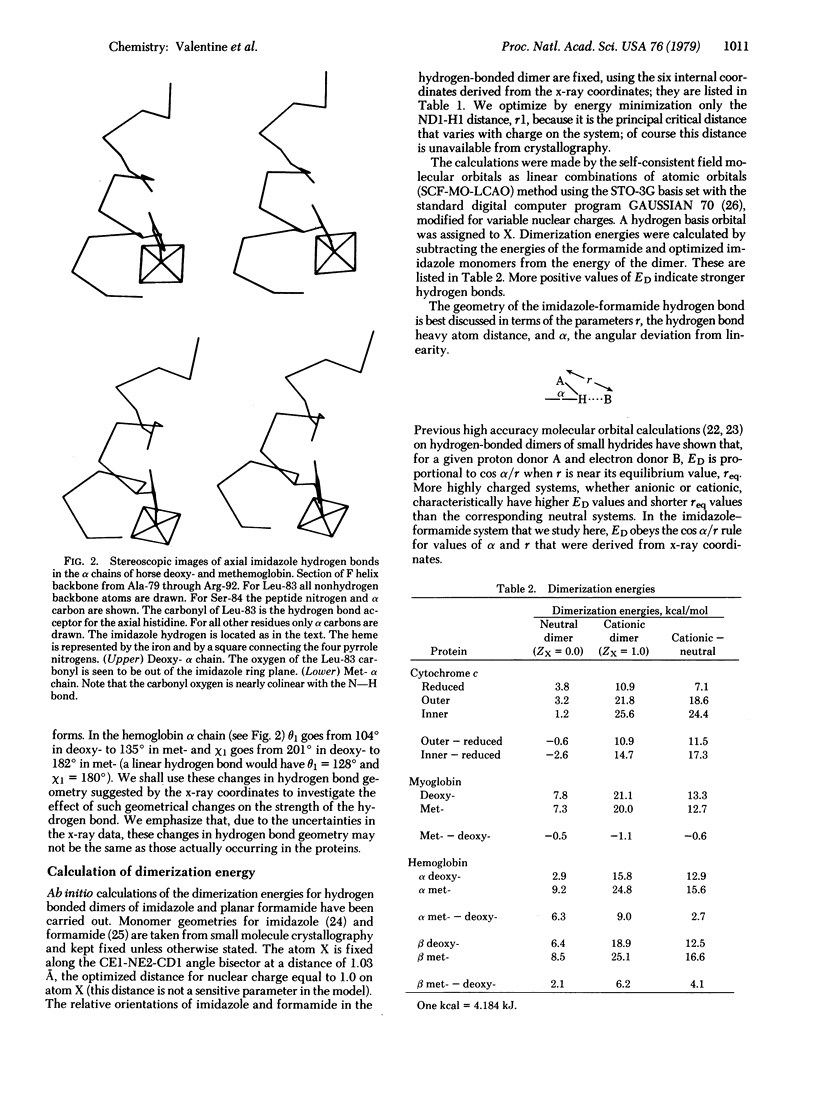
In all heme proteins for which crystal structures are available, the Nε of a histidyl residue is bonded to the heme iron and Nδ is hydrogen bonded to a carbonyl oxygen of the peptide backbone. We investigate here the possibility that a change in oxidation state of the iron or a change in the geometry of this hydrogen bond might change the hydrogen bond strength in a functionally significant way. Dimerization energies obtained from ab initio molecular orbital calculations on the hydrogen-bonded dimer of imidazole and planar formamide are used to represent the strength of this hydrogen bond in heme proteins. The effect of a change in iron oxidation state is modeled by varying the positive charge on imidazole. The effect of a change in hydrogen bond geometry is studied by employing x-ray coordinates for reduced and oxidized cytochrome c, deoxy- and metmyoglobin, and deoxy- and methemoglobin. Our conclusions are that the strength of this hydrogen bond in heme proteins is sensitive to both the oxidation state of the iron atom and to geometry changes on the order of those obtained from the x-ray coordinates. We speculate that the changes in oxidation state may be functionally coupled with changes in hydrogen bond geometry and that this hydrogen bond represents a feasible pathway to link protein conformation with redox potential or reactivity of the iron atom.
Keywords: cytochrome c, hemoglobin, myoglobin, cooperativity, histidine
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E., Watenpaugh K. D., Jensen L. H. NH---S hydrogen bonds in Peptococcus aerogenes ferredoxin, Clostridium pasteurianum rubredoxin, and Chromatium high potential iron protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4854–4858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen L. C. A model for the hydrogen bond. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4701–4705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. M. Structure and function of haemoglobin. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(3):225–320. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W., Perutz M. F. Three dimensional fourier synthesis of horse deoxyhaemoglobin at 2.8 Angstrom units resolution. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):551–552. doi: 10.1038/228551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Kraut J., Freer S. T., Alden R. A. Comparison of oxidation-reduction site geometries in oxidized and reduced Chromatium high potential iron protein and oxidized Peptococcus aerogenes ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr New stereochemical analogies between iron-sulfur electron transport proteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7802–7811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey W. S., Barlow C. H., Maxwell J. C., Volpe J. A., Wallace W. J. Reactions of oxygen with hemoglobin, cytochrome c oxidase and other hemeproteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Wodak S., Janin J. Role of subunit interfaces in the allosteric mechanism of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3793–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman J. P., Brauman J. I., Halbert T. R., Suslick K. S. Nature of O2 and CO binding to metalloporphyrins and heme proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3333–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman J. P., Brauman J. I., Rose E., Suslick K. S. Cooperativity in O2 binding to iron porphyrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1052–1055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demma L. S., Salhany J. M. Direct generation of superoxide anions by flash photolysis of human oxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1226–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J. Cooperative interactions of hemoglobin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:209–232. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelin B. R., Karplus M. Mechanism of tertiary structural change in hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):801–805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Relation between structure, co-operativity and spectra in a model of hemoglobin action. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):207–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladner R. C., Heidner E. J., Perutz M. F. The structure of horse methaemoglobin at 2-0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):385–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel N., Mandel G., Trus B. L., Rosenberg J., Carlson G., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. III. Coordinate optimization and comparison of structures. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4619–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews F. S., Argos P., Levine M. The structure of cytochrome b 5 at 2.0 Angstrom resolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:387–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr P., Scheler W., Schumann H., Müller K. Ligand-protein interactions in imidazole and 1,2,4-triazole complexes of methaemoglobin from Chironomus plumosus. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):158–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nappa N., Valentine J. S., Snyder P. A. Imidazolate complexes of ferric porphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Aug 17;99(17):5799–5800. doi: 10.1021/ja00459a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J. An interim report on electronic control of oxygenation of heme proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:187–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Blumberg W. E., Adler A. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of iron porphin and chlorin systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;206:310–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb43219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Mims W. B. Linear electric field effect in electron paramagnetic resonance for two bisimidazole--heme complexes, model compounds for B and H hemichromes of hemoglobin and for cytochrome b5. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2795–2799. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Nature of haem-haem interaction. Nature. 1972 Jun 30;237(5357):495–499. doi: 10.1038/237495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):726–739. doi: 10.1038/228726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Lipscomb W. N. Carboxypeptidase A: a protein and an enzyme. Adv Protein Chem. 1971;25:1–78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J., Thomas K. A., Rubin B. H., Richardson D. C. Crystal structure of bovine Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase at 3 A resolution: chain tracing and metal ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salemme F. R. Structure and function of cytochromes c. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:299–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterlee J. D., La Mar G. N., Frye J. S. Dynamics and thermodynamics of axial ligation in metalloporphyrins. 5. Affinity of ferric porphyrins for nitrogenous bases and the stoichiometry and spin states of the product complexes. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Nov 10;98(23):7275–7282. doi: 10.1021/ja00439a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Hopfield J. J., Ogawa S. Allosteric interpretation of haemoglobin properties. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 Jul;8(3):325–420. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. W., Burnett R. M., Darling G. D., Ludwig M. L. Structure of the semiquinone form of flavodoxin from Clostridum MP. Extension of 1.8 A resolution and some comparisons with the oxidized state. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):195–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. I. Ferricytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):759–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T. Structure of myoglobin refined at 2-0 A resolution. I. Crystallographic refinement of metmyoglobin from sperm whale. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):537–568. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T. Structure of myoglobin refined at 2-0 A resolution. II. Structure of deoxymyoglobin from sperm whale. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):569–584. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Swanson R., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. II. Ferrocytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):776–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. A., Lo M. W., Ree M. T. Electronic effects in transition metal porphyrins. The reactions of imidazoles and pyridines with a series of para-substituted tetraphenylporphyrin complexes of chloroiron(III). J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Sep 1;98(18):5552–5560. doi: 10.1021/ja00434a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A. Energy-structure correlation in metalloporphyrins and the control of oxygen binding by hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1789–1793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yammoto T., Palmer G. The valence and spin state of iron in oxyhemoglobin as inferred from resonance Raman spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5211–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


