Abstract
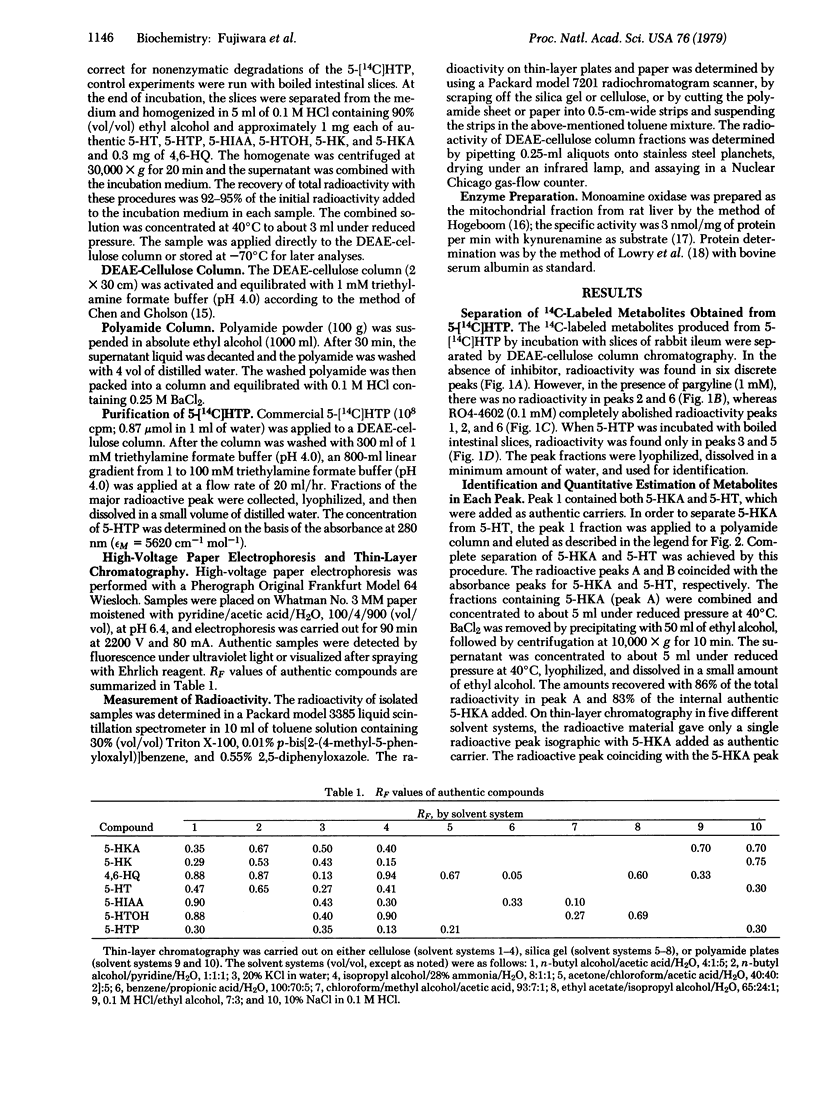
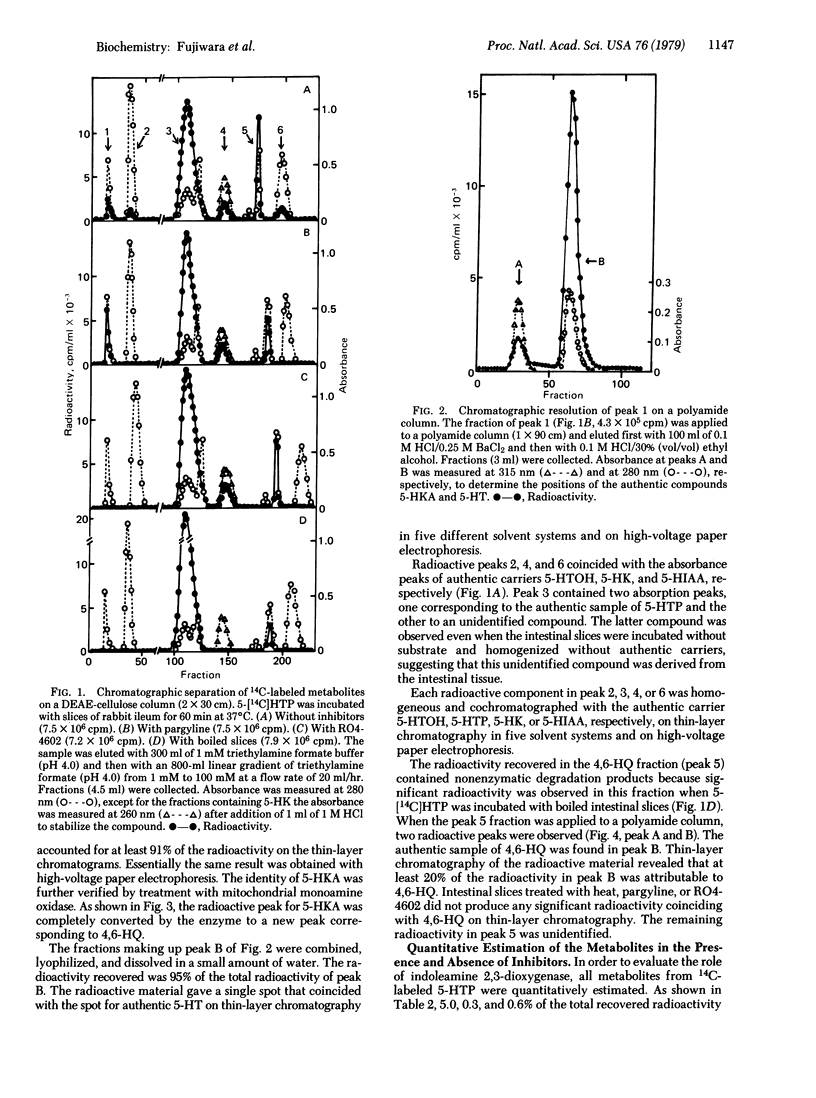
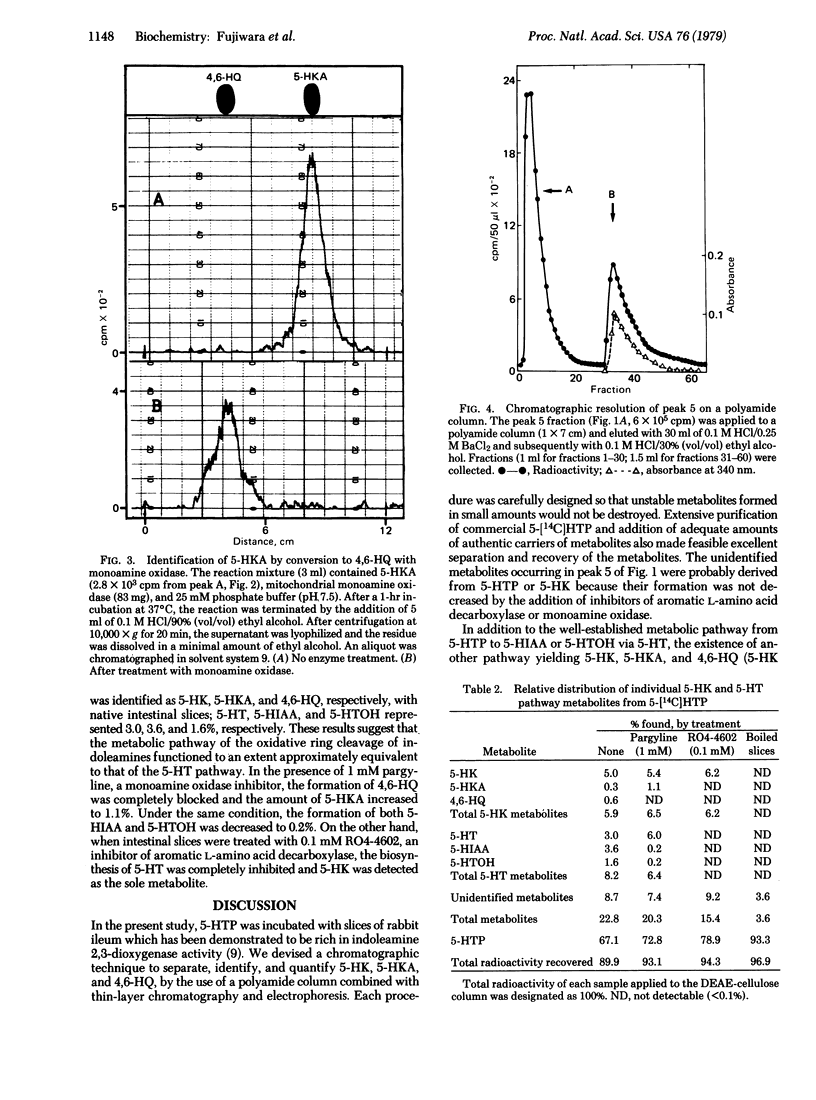
In order to clarify the role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase [indole:oxygen 2,3-oxidoreductase (decyclizing), EC 1.13.11.17] in the metabolism of serotonin, DL-5-hydroxy[methylene-14C]tryptophan, a precursor of serotonin, was incubated with slices of rabbit ileum. Resulting metabolites were separated by DEAE-cellulose column and polyamide column chromatography and identified by various chromatographic techniques and enzymatic analysis. Metabolites obtained in significant amounts were serotonin, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, 5-hydroxytryptophol, 5-hydroxykynurenine, 5-hydroxykynurenamine, and 4,6-dihydroxyquinoline, representing 13.2, 15.8, 7.0, 21.9, 1.3, and 2.6% of the total metabolites, respectively. The first three compounds were previously reported to be major metabolites produced from 5-hydroxytryptophan by the action of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase and monoamine oxidase, whereas the last three are formed by the cleavage of the indole ring by the action of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. In the presence of pargyline, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, the major metabolites obtained were serotonin, 5-hydroxykynurenine, and 5-hydroxykynurenamine, representing 29.6, 26.6, and 5.4% of the total metabolites, respectively. In the presence of RO4-4602, an aromatic amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor, 5-hydroxykynurenine was the sole major product. These results strongly suggest that the newly discovered metabolic pathway involving the cleavage of the indole ring of 5-hydroxytryptophan operates in vivo to a significant extent and that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase plays an important role in the regulation of serotonin levels in the small intestine of the rabbit.
Keywords: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; indole ring cleavage; serotonin
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOGDANSKI D. F., PLETSCHER A., BRODIE B. B., UNDENFRIEND S. Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazelon M., Paine R. S., Coeiw V. A., Hunt P., Houck J. C., Mahanand D. Reversal of hypotonia in infants with Down's syndrome by administration of 5-hydroxytryptophan. Lancet. 1967 May 27;1(7500):1130–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. C., Gholson R. K. An improved column chromatographic method for isolation of tryptophan metabolites. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi K., Hayaishi O. Enzymic formation of D-kynurenine from D-tryptophan. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 May;120(2):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Hayaishi O. New degradative routes of 5-hydroxytryptophan and serotonin by intestinal tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1112–1119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90949-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido R., Noguchi T., Matsumura Y. The isolation and identification of 5-hydroxy-L-kynurenine from the urine of hens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 25;141(2):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido R., Noguchi T., Tsuji T., Matsumura Y. The identification of 4, 6-quinolinediol and 4,8-quinolinediol in the urine of hens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 7;136(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi N., Noguchì T., Kido R. The pyrrole ring cleavaging enzyme of 5-hydroxytryptophan. Life Sci II. 1971 Apr 22;10(8):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKINO K., JOH Y., HASEGAWA F. The detection of mausamine in the brain of mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jan 24;6:432–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuma M., Tokuyama T., Senoh S., Hirata F., Hayaishi O. Antagonism of 5-hydroxykynurenamine against serotonin action on platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):643–645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano I. L-5-Hydroxytryptophan(L-5-HTP)-Therapie bei endogener Depression. 1. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1972 Oct 6;114(40):1713–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano I., Taniguchi K. L-5-Hydroxytryptophan(L-5-HTP)-Therapie des Morbus Parkinson. 2. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1972 Oct 6;114(40):1717–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Tokuyama T., Seno S., Hirata F., Hayaishi O. Effects of 5-hydroxykynurenamine, a new serotonin metabolite, on isolated dog basilar arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):122–124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H., Noguchi T., Kido R. 5-hydroxytryptophan pyrrolase in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):887–890. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH H., SMITH T. E., DALY J. W., WITKOP B., UDENFRIEND S. A rapid spectrophotometric assay of mono-amine oxidase based on the rate of disappearance of kynuramine. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1160–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Hayaishi O. Tryptophan pyrrolase of rabbit intestine. D- and L-tryptophan-cleaving enzyme or enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5260–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


