Abstract
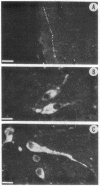
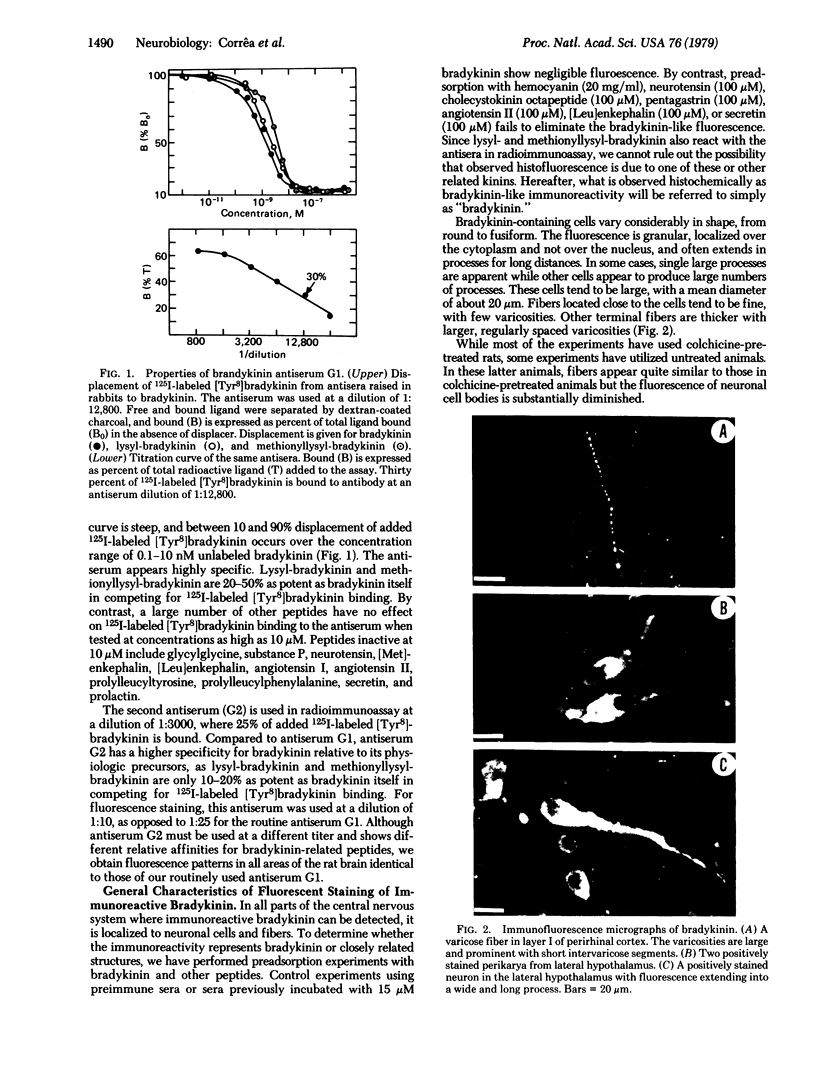
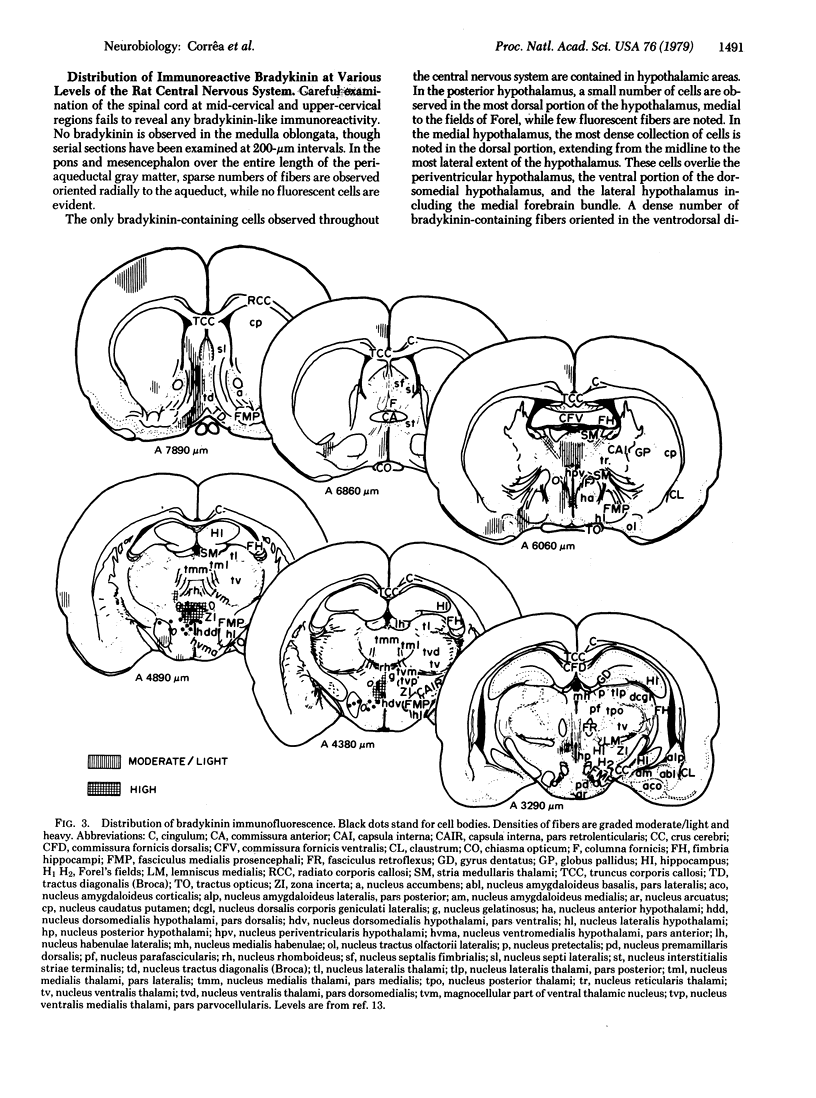
Bradykinin-like immunoreactive structures were localized in rat brain by the indirect immunofluorescence method. Specificity of staining was demonstrated by: (i) the absence of fluorescence when preimmune serum was used, (ii) the disappearance of fluorescence when sera were preadsorbed with bradykinin, and (iii) the presence of identical staining with two different antisera. Immunoreactive neuronal cells are observed only in the hypothalamus, with especially dense clusters overlying the periventricular and dorsomedial nuclei. Fibers and varicose processes are observed in the periaqueductal gray matter, hypothalamus, perirhinal and cingulate cortices, the ventral portion of caudate-putamen, and the lateral septal area.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa F. M., Graeff F. G. Central mechanisms of the hypertensive action of intraventricular bradykinin in the unanaesthetized rat. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jan;13(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Graeff F. G. Central site of the hypertensive action of bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):670–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Graeff F. G. On the mechanism of the hypertensive action of intraseptal bradykinin in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Nov;15(11):713–717. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Formation and function of kinins. Rheumatology. 1970;3(0):103–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Basbaum A. I. Brainstem control of spinal pain-transmission neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:217–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeff F. G., Arisawa E. A. Effect of intracerebroventricular bradykinin, angiotensin II, and substance P on multiple fixed-interval fixed-ratio responding in rabbits. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Apr 14;57(1):89–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00426963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S. The presence of bradykinin-like polypeptides, kinin-releasing and destroying activity in brain. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Dec 15;18(6):772–787. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S. Zetler's satellite polypeptides of substance P in subcellular particles of bovine peripheral nerves. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Dec 15;18(6):746–771. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S. Zetler's satellite polypeptides of substance P in subcellular particles of bovine peripheral nerves. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Dec 15;18(6):746–771. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INOUYE A., KATAOKA K., TSUJIOKA T. On a kinin-like substance in the nervous tissue extracts treated with trypsin. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Jun 15;11:319–334. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Jacobowitz D. M. Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. II. Hindbrain (mesencephalon, rhombencephalon). J Comp Neurol. 1974 Sep 1;157(1):29–42. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro S. A., Corrado A. P., Graeff F. G. Antinociceptive action of intraventricular bradykinin. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Nov;10(6):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. L., Mashford M. L. Possible physiological and pathological roles of the kallikrein-kinin system. Med J Aust. 1972 Oct 14;2(16):887–891. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb103604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Neurotensin: immunohistochemical localization in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4059–4063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]