Abstract
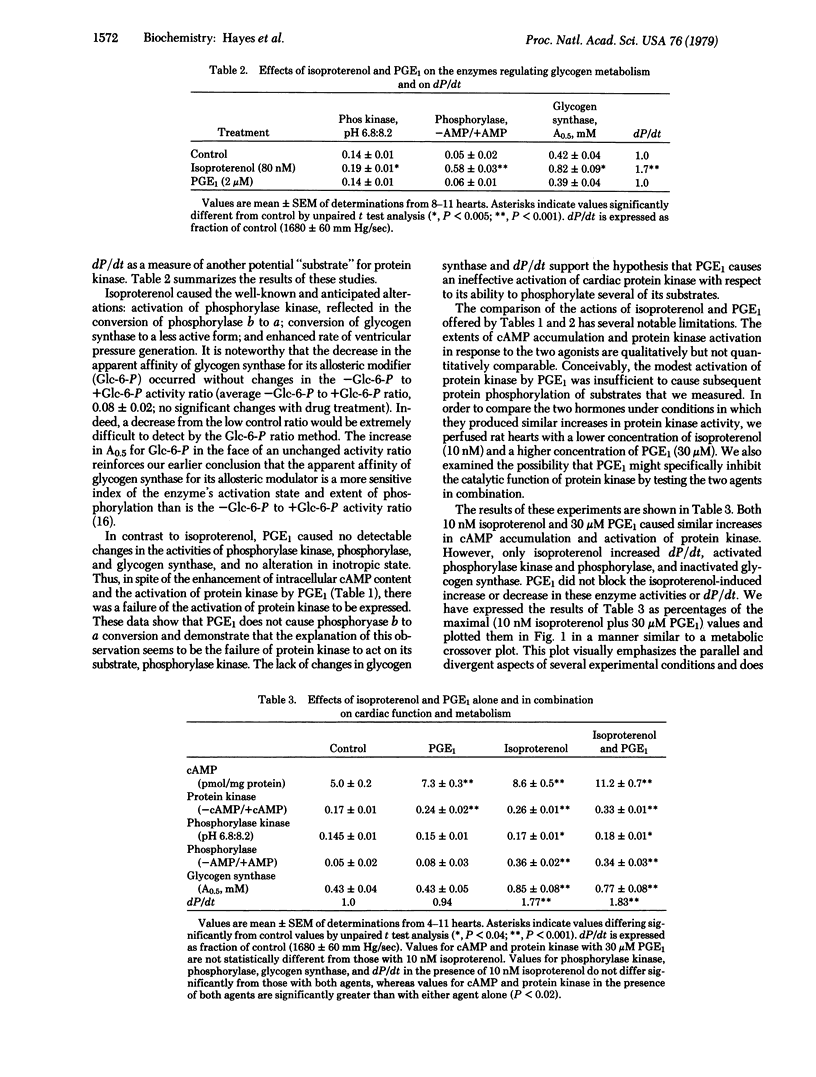
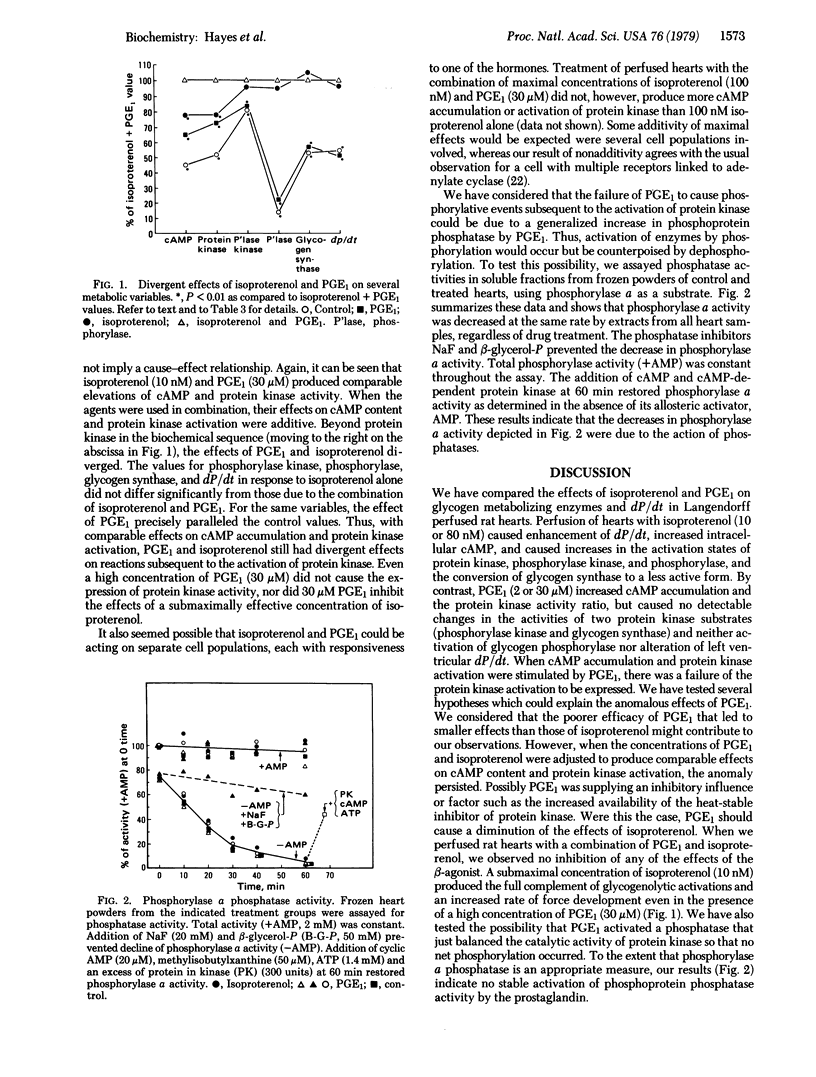
The relationship between the effects of isoproterenol and prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) on contractile state, cyclic AMP accumulation, and the activation states of protein kinase (ATP: protein phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37), phosphorylase kinase, glycogen synthase, and glycogen phosphorylase have been studied in the isolated perfused rat heart. Perfusion of hearts with isoproterenol (10 or 80 nM) caused enhancement of left ventricular dP/dt (P, pressure), increased intracellular cyclic AMP, increased the activation states of protein kinase, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, and conversion of glycogen synthase to a less active form. PGE1 (2 or 30 μM) increased cyclic AMP accumulation and activated protein kinase, but caused no detectable changes in dP/dt or the activation states of the protein kinase substrates involved in glycogen metabolism. Perfusion of hearts with either 10 nM isoproterenol or 30 μM PGE1 produced comparable increases in cyclic AMP accumulation and protein kinase activity. Exposure of hearts to a combination of these agents caused additive effects on cyclic AMP content and protein kinase activity. However, values for phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, glycogen synthase, and dP/dt did not differ from those observed in the presence of 10 nM isoproterenol alone. The failure of PGE1 to stimulate phosphorylation of protein kinase substrates was not due to an increase in phosphorylase phosphatase activity. We conclude that an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP and the subsequent activation of protein kinase are insufficient to change either the activities of phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, and glycogen synthase or the inotropic state of heart muscle.
Keywords: cardiac cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, hormonal specificity, glycogenolytic cascade, prostaglandin E1, β-adrenergic stimulation
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Michiel H., Krans M. J., Rodbell M. The actions of hormones on the adenyl cyclase system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1970;3:185–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Thompson B., Mayer S. E. Conversion of skeletal muscle glycogen synthase to multiple glucose 6-phosphate dependent forms by cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent and independent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5501–5508. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton L. L., Maguire M. E., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of genes for metabolism of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in somatic cells. beta-Adrenergic and PGE1 receptors in parental and hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1293–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. I., Duncan L., Hertzman E. Effect of epinephrine on phosphorylase b kinase in perfused rat hearts. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5899–5903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Correlation between contraction and phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin in perfused rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMERMEISTER K. E., YUNIS A. A., KREBS E. G. STUDIES ON PHOSPHORYLASE ACTIVATION IN THE HEART. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:986–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman J. G., Mayer S. E., Clark B. Cocaine potentiation of the cardiac inotropic and phosphorylase responses to catecholamines as related to the uptake of H3-catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Dec;150(3):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Comparison of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rabbit skeletal and bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7795–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L. Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase without a corresponding increase in phosphorylase activity. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;18(2):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Corbin J. D., Park C. R. Regulation of adenosine 3:5-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4832–4840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Steinberg D., Huang J. J., Vagelos P. R. Triglyceride, diglyceride, monoglyceride, and cholesterol ester hydrolases in chicken adipose tissue activated by adenosine 3':5'-Monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Chromatographic resolution and immunochemical differentiation from lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2882–2890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. I. Isolation and characterization of the protein-glycogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6642–6648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura A. M., Simpkins H. The effects of hormones and prostaglandins on the calcium pools in cultured myocardial cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1976 Oct;5(5):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(76)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Oye I., Morgan H. E., Sutherland E. W. The effect of epinephrine on adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate levels in the isolated perfused rat heart. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):168–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J. Reversible autophosphorylation of a cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7788–7794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Hickenbottom J. P., Reimann E. M., Hunkeler F. L., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthetase and activation of phosphorylase kinase by muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6317–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Mayer S. E. Regulation of phosphorylase activation in skeletal muscle in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5716–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Cyclic AMP and contractile activity in heart. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:363–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


