Abstract
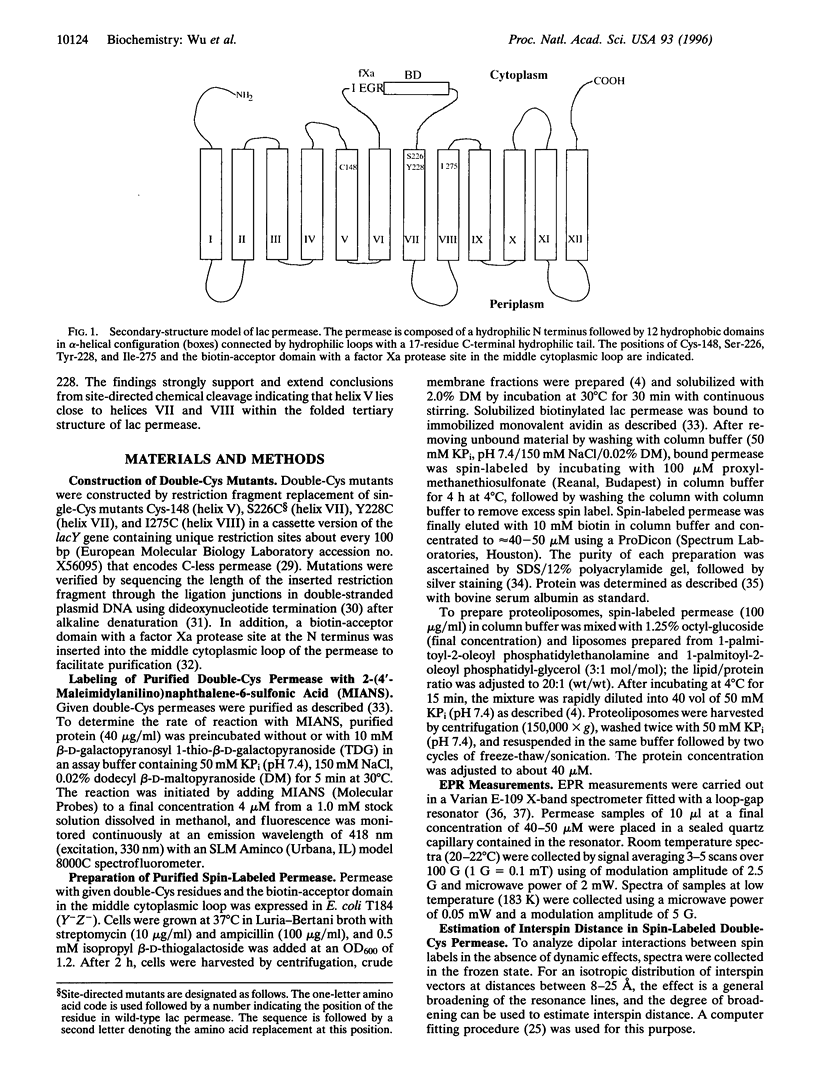
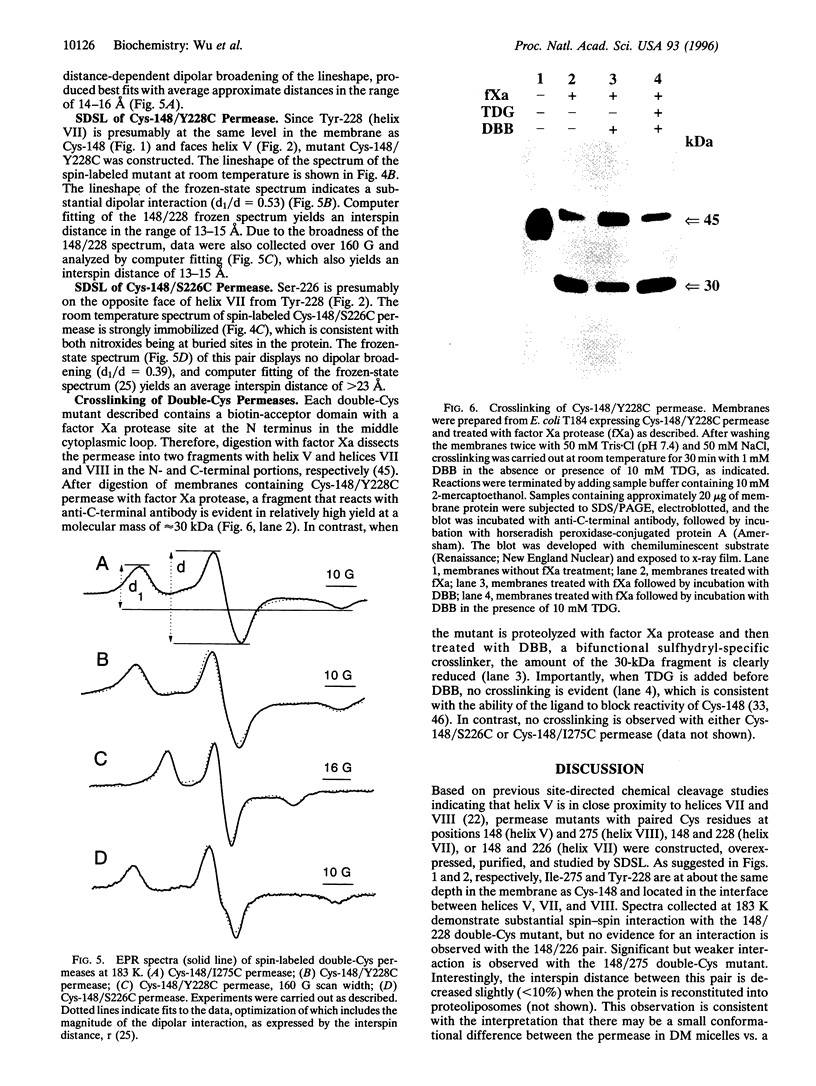
Site-directed chemical cleavage of lactose permease indicates that helix V is in close proximity to helices VII and VIII. To test this conclusion further, permease containing a biotin-acceptor domain and paired Cys residues at positions 148 (helix V) and 228 (helix VII), 148 and 226 (helix VII), or 148 and 275 (helix VIII) was affinity purified and labeled with a sulfhydryl-specific nitroxide spin label. Spin-spin interactions are observed with the 148/228 and 148/275 pairs, indicating close proximity between appropriate faces of helix V and helices VII and VIII. Little or no interaction is evident with the 148/226 pair, in all likelihood because position 226 is on the opposite face of helix VII from position 228. Broadening of the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra in the frozen state was used to estimate distance between the 148/228 and the 148/275 pairs. The nitroxides at positions 148 and 228 or 148 and 275 are within approximately 13-15 A. Finally, Cys residues at positions 148 and 228 are crosslinked by dibromobimane, a bifunctional crosslinker that is approximately 5 A. long, while no crosslinking is detected between Cys residues at positions 148 and 275 or 148 and 226. The results provide strong support for a structure in which helix V is in close proximity to both helices VII and VIII and is oriented in such a fashion that Cys-148 is closer to helix VII.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony-Cahill S. J., Benfield P. A., Fairman R., Wasserman Z. R., Brenner S. L., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L., DeGrado W. F. Molecular characterization of helix-loop-helix peptides. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):979–983. doi: 10.1126/science.1312255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. lac permease of Escherichia coli: topology and sequence elements promoting membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Viitanen P., Herzlinger D., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 1. Functional studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3681–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consler T. G., Persson B. L., Jung H., Zen K. H., Jung K., Privé G. G., Verner G. E., Kaback H. R. Properties and purification of an active biotinylated lactose permease from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunten R. L., Sahin-Tóth M., Kaback H. R. Role of the charge pair aspartic acid-237-lysine-358 in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):3139–3145. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farahbakhsh Z. T., Huang Q. L., Ding L. L., Altenbach C., Steinhoff H. J., Horwitz J., Hubbell W. L. Interaction of alpha-crystallin with spin-labeled peptides. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 17;34(2):509–516. doi: 10.1021/bi00002a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Kennedy E. P. Specific labeling and partial purification of the M protein, a component of the beta-galactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):891–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frillingos S., Kaback H. R. Probing the conformation of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli by in situ site-directed sulfhydryl modification. Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 2;35(13):3950–3956. doi: 10.1021/bi952601m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frillingos S., Sahin-Tóth M., Persson B., Kaback H. R. Cysteine-scanning mutagenesis of putative helix VII in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1994 Jul 5;33(26):8074–8081. doi: 10.1021/bi00192a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He M. M., Voss J., Hubbell W. L., Kaback H. R. Use of designed metal-binding sites to study helix proximity in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. 1. Proximity of helix VII (Asp237 and Asp240) with helices X (Lys319) and XI (Lys358). Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 5;34(48):15661–15666. doi: 10.1021/bi00048a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He M. M., Voss J., Hubbell W. L., Kaback H. R. Use of designed metal-binding sites to study helix proximity in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. 2. Proximity of helix IX (Arg302) with helix X (His322 and Glu325). Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 5;34(48):15667–15670. doi: 10.1021/bi00048a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung H., Jung K., Kaback H. R. Cysteine 148 in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli is a component of a substrate binding site. 1. Site-directed mutagenesis studies. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12160–12165. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung K., Jung H., Wu J., Privé G. G., Kaback H. R. Use of site-directed fluorescence labeling to study proximity relationships in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12273–12278. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung K., Voss J., He M., Hubbell W. L., Kaback H. R. Engineering a metal binding site within a polytopic membrane protein, the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1995 May 16;34(19):6272–6277. doi: 10.1021/bi00019a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Frillingos S., Jung H., Jung K., Privé G. G., Ujwal M. L., Weitzman C., Wu J., Zen K. The lactose permease meets Frankenstein. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:183–195. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. In and out and up and down with lac permease. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;137:97–125. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Jung K., Jung H., Wu J., Privé G. G., Zen K. What's new with lactose permease. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1993 Dec;25(6):627–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00770250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology and energetics of membrane transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):575–593. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The lac carrier protein in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02000610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. C., Hansen C. L., Wilson T. H. The interaction between aspartic acid 237 and lysine 358 in the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 25;1062(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90390-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. I., Hwang P. P., Hansen C., Wilson T. H. Possible salt bridges between transmembrane alpha-helices of the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20758–20764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. I., Varela M. F., Wilson T. H. Physiological evidence for an interaction between Glu-325 and His-322 in the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Jan 12;1278(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification and reconstitution of functional lactose carrier from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11804–11808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Konings W. N. Secondary solute transport in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 2;1183(1):5–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabenstein M. D., Shin Y. K. Determination of the distance between two spin labels attached to a macromolecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8239–8243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Dunten R. L., Gonzalez A., Kaback H. R. Functional interactions between putative intramembrane charged residues in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10547–10551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Kaback H. R. Properties of interacting aspartic acid and lysine residues in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10027–10035. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Lawrence M. C., Kaback H. R. Properties of permease dimer, a fusion protein containing two lactose permease molecules from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5421–5425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P., Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification, reconstitution, and characterization of the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:429–452. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman C., Consler T. G., Kaback H. R. Fluorescence of native single-Trp mutants in the lactose permease from Escherichia coli: structural properties and evidence for a substrate-induced conformational change. Protein Sci. 1995 Nov;4(11):2310–2318. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Frillingos S., Kaback H. R. Dynamics of lactose permease of Escherichia coli determined by site-directed chemical labeling and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8257–8263. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Frillingos S., Voss J., Kaback H. R. Ligand-induced conformational changes in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli: evidence for two binding sites. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2294–2301. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Kaback H. R. Cysteine 148 in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli is a component of a substrate binding site. 2. Site-directed fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12166–12171. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Perrin D. M., Sigman D. S., Kaback H. R. Helix packing of lactose permease in Escherichia coli studied by site-directed chemical cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9186–9190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen K. H., Consler T. G., Kaback H. R. Insertion of the polytopic membrane protein lactose permease occurs by multiple mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1995 Mar 14;34(10):3430–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00010a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden P. R., Pastore J. C., Konings W. N., Kaback H. R. Construction of a functional lactose permease devoid of cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9595–9600. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





