Abstract
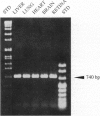
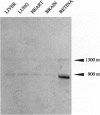
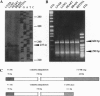
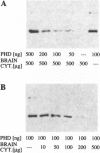
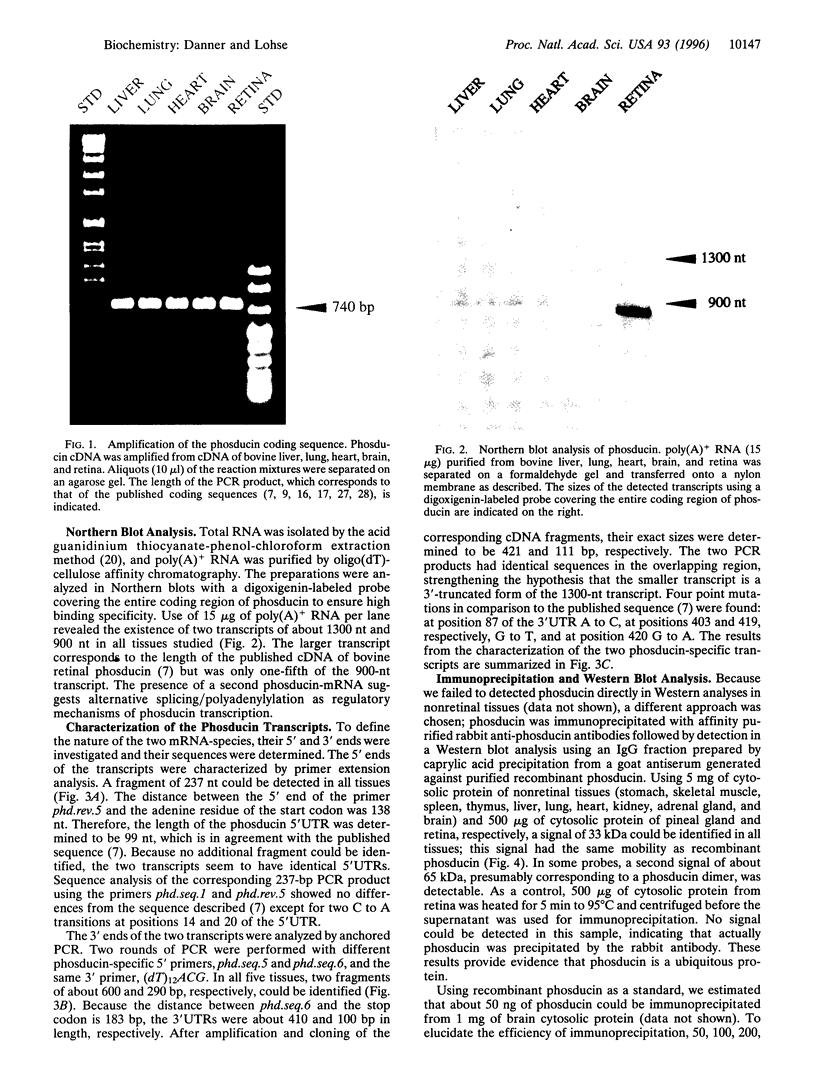
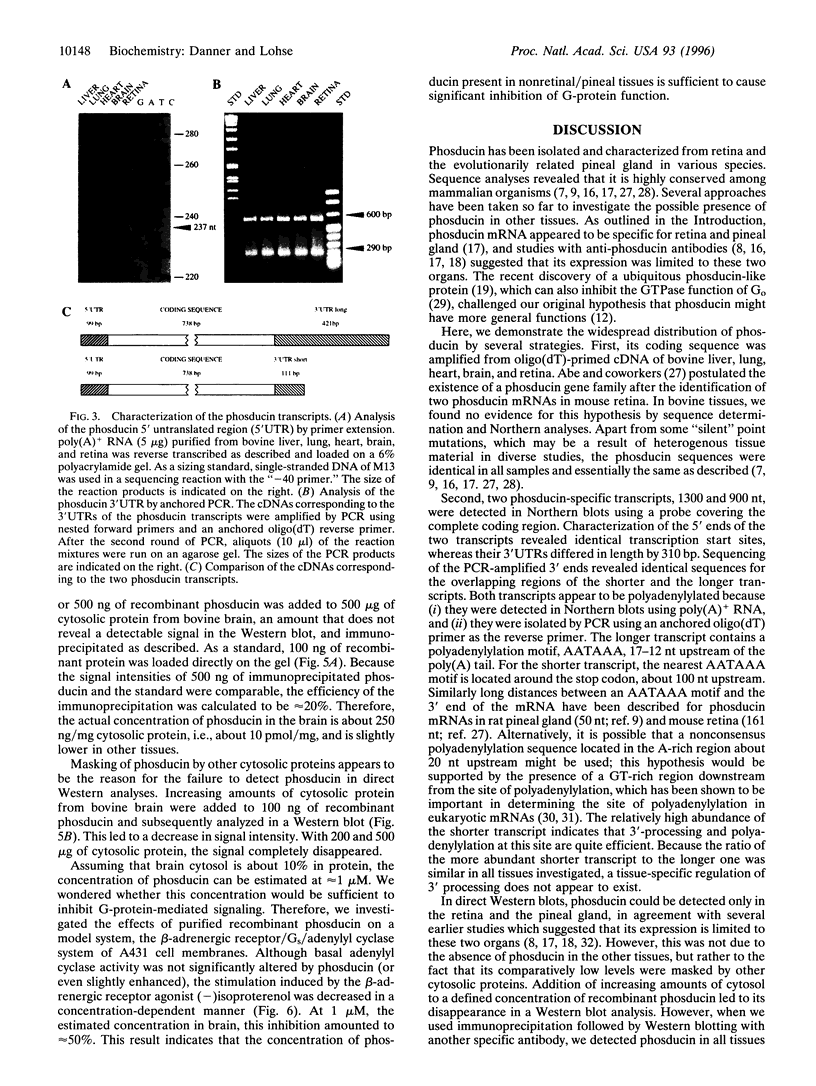
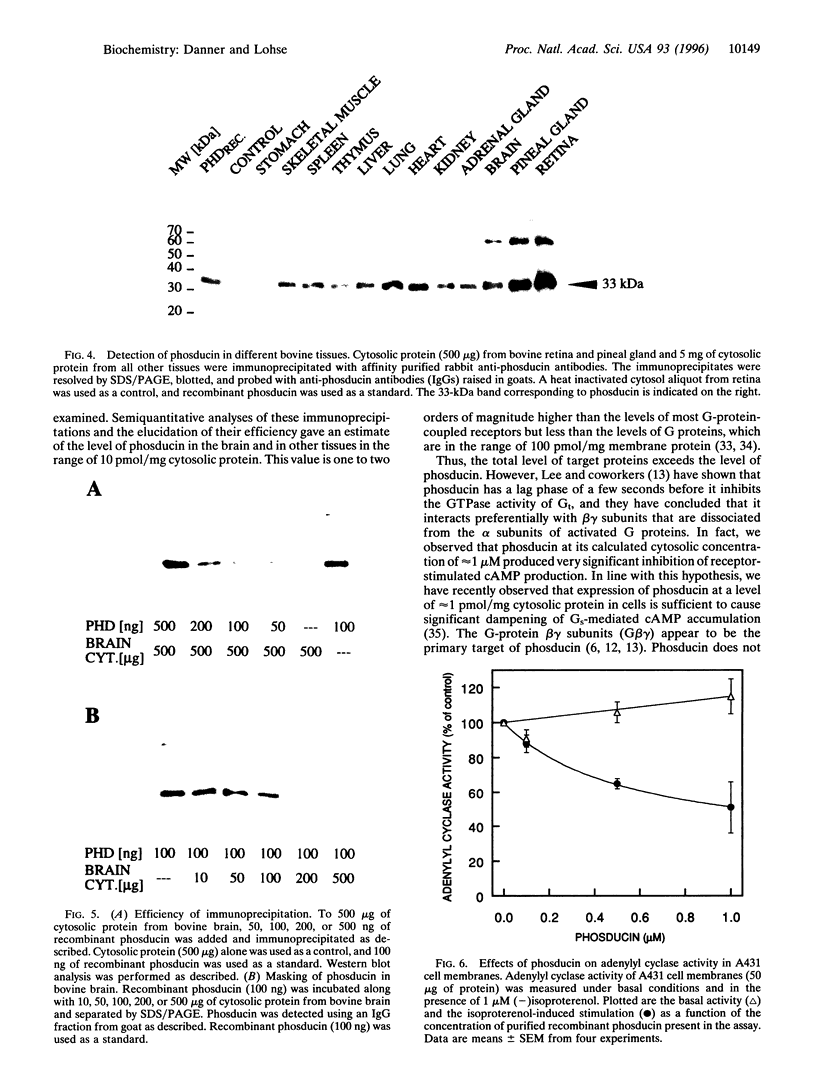
Phosducin is a 33-kDa cytosolic regulator of G-protein-mediated signaling that has previously been thought to be specific for retina and pineal gland. In this study, we show widespread tissue distribution of phosducin by the amplification of its cDNA and the detection of two different transcripts in Northern analyses in liver, lung, heart, brain, and retina. On the protein level, phosducin could be detected in 12 bovine tissues by immune precipitation and subsequent Western analysis using anti-phosducin antibodies generated in two different species. Masking of phosducin in direct Western blots appears to explain the failure to detect phosducin in earlier studies. The concentration of phosducin in bovine brain was calculated in the range of 10 pmol/mg total cytosolic protein (approximately 1 microM), whereas in the other tissues, it was slightly less. In these concentrations, phosducin inhibited receptor-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity in cell membranes by about 50%. Taken together, our results indicate that phosducin is a ubiquitous regulator of G-protein function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Kikuchi T., Chang T., Shinohara T. The sequence of the mouse phosducin-encoding gene and its 5'-flanking region. Gene. 1993 Nov 15;133(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90636-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe T., Kikuchi T., Shinohara T. The sequence of the human phosducin gene (PDC) and its 5'-flanking region. Genomics. 1994 Jan 15;19(2):369–372. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe T., Nakabayashi H., Tamada H., Takagi T., Sakuragi S., Yamaki K., Shinohara T. Analysis of the human, bovine and rat 33-kDa proteins and cDNA in retina and pineal gland. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90090-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. H., Müller S., Puzicha M., Pippig S., Obermaier B., Helmreich E. J., Lohse M. J. Phosducin is a protein kinase A-regulated G-protein regulator. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):73–76. doi: 10.1038/358073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm M., Larisch K., Erdmann E., Camps M., Jakobs K., Gierschik P. Failure of [32P]ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin to determine Gi alpha content in membranes from various human tissues. Improved radioimmunological quantification using the 125I-labelled C-terminal decapeptide of retinal transducin. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):223–229. doi: 10.1042/bj2770223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P. One-hour downward alkaline capillary transfer for blotting of DNA and RNA. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 14;201(1):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90185-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Niemela S. L., Miller R. H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft C. M., Lolley R. N., Seldin M. F., Lee R. H. Rat pineal gland phosducin: cDNA isolation, nucleotide sequence, and chromosomal assignment in the mouse. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):400–409. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., McDowell J. H. Rhodopsin and phototransduction: a model system for G protein-linked receptors. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2323–2331. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1544542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes B. E., Touhara K., Kurose H., Lefkowitz R. J., Inglese J. Determination of the G beta gamma-binding domain of phosducin. A regulatable modulator of G beta gamma signaling. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29825–29830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman M., Bauer P. H., Söhlemann P., Lohse M. J. Phosducin inhibits receptor phosphorylation by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase in a PKA-regulated manner. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 25;343(2):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. H., Akiyama M., Miki N. Isolation of a novel retina-specific clone (MEKA cDNA) encoding a photoreceptor soluble protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Fowler A., McGinnis J. F., Lolley R. N., Craft C. M. Amino acid and cDNA sequence of bovine phosducin, a soluble phosphoprotein from photoreceptor cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15867–15873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Lieberman B. S., Lolley R. N. A novel complex from bovine visual cells of a 33,000-dalton phosphoprotein with beta- and gamma-transducin: purification and subunit structure. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3983–3990. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Ting T. D., Lieberman B. S., Tobias D. E., Lolley R. N., Ho Y. K. Regulation of retinal cGMP cascade by phosducin in bovine rod photoreceptor cells. Interaction of phosducin and transducin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25104–25112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. H., Whelan J. P., Lolley R. N., McGinnis J. F. The photoreceptor-specific 33 kDa phosphoprotein of mammalian retina: generation of monospecific antibodies and localization by immunocytochemistry. Exp Eye Res. 1988 Jun;46(6):829–840. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(88)80035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles M. F., Barhite S., Sganga M., Elliott M. Phosducin-like protein: an ethanol-responsive potential modulator of guanine nucleotide-binding protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10831–10835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller S., Lohse M. J. The role of G-protein beta gamma subunits in signal transduction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Feb;23(1):141–148. doi: 10.1042/bst0230141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller S., Straub A., Schröder S., Bauer P. H., Lohse M. J. Interactions of phosducin with defined G protein beta gamma-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 17;271(20):11781–11786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.20.11781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reig J. A., Yu L., Klein D. C. Pineal transduction. Adrenergic----cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of cytoplasmic 33-kDa protein (MEKA) which binds beta gamma-complex of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5816–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo C., Callegaro L., Lanza E., Ferrone S. Re.: Purification of IgG monoclonal antibody by caprylic acid precipitation. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder S., Lohse M. J. Inhibition of G-protein betagamma-subunit functions by phosducin-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 5;93(5):2100–2104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.2100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Wu D., Slepak V. Z., Simon M. I. The N terminus of phosducin is involved in binding of beta gamma subunits of G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2086–2090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Willardson B. M., Wilkins J. F., Jensen G. J., Thornton B. D., Bitensky M. W. The phosphorylation state of phosducin determines its ability to block transducin subunit interactions and inhibit transducin binding to activated rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24050–24057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]