Abstract
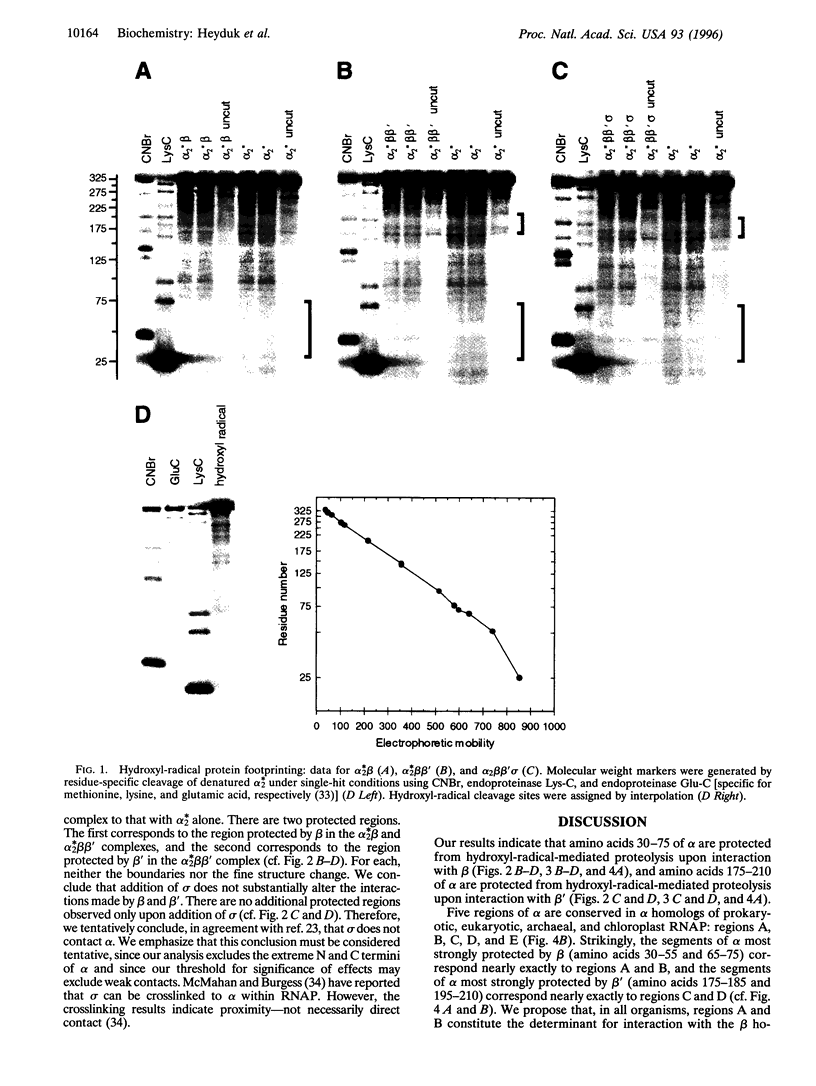
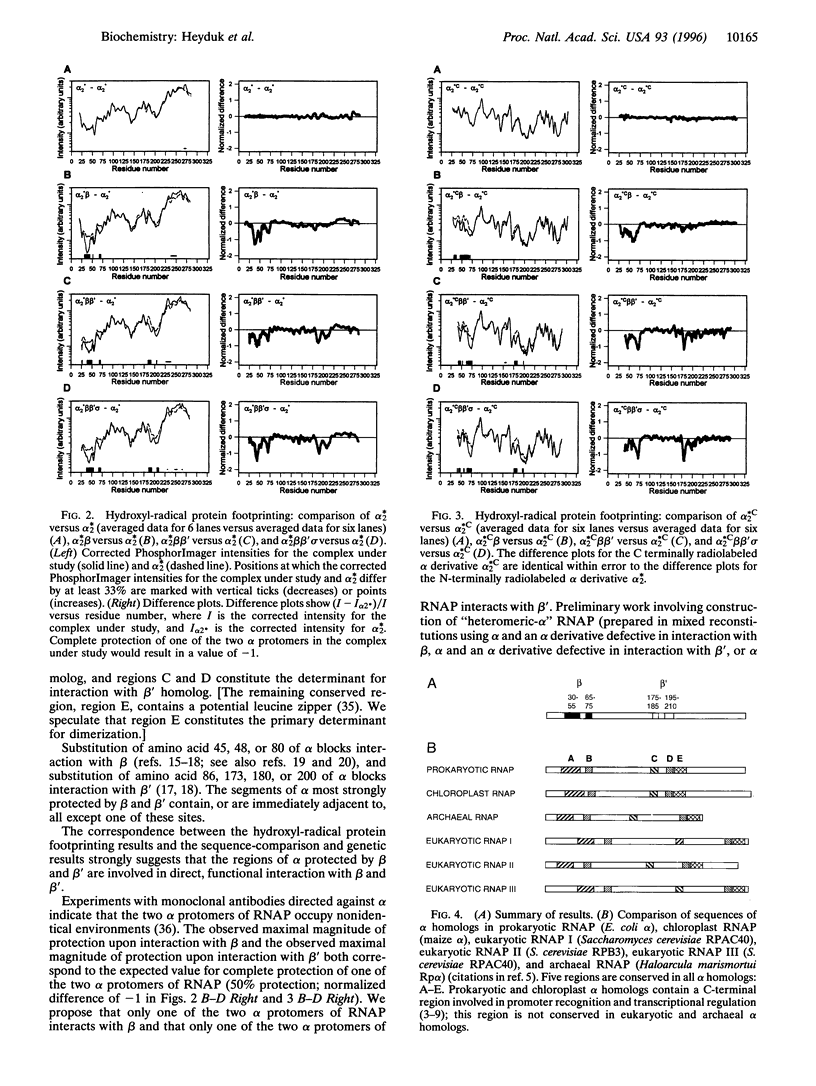
Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP) alpha subunit serves as the initiator for RNAP assembly, which proceeds according to the pathway 2 alpha-->alpha 2-->alpha 2 beta-->alpha 2 beta beta'-->alpha 2 beta beta' sigma. In this work, we have used hydroxyl-radical protein footprinting to define determinants of alpha for interaction with beta, beta', and sigma. Our results indicate that amino acids 30-75 of alpha are protected from hydroxyl-radical-mediated proteolysis upon interaction with beta (i.e., in alpha 2 beta, alpha 2 beta beta', and alpha 2 beta beta' sigma), and amino acids 175-210 of alpha are protected from hydroxyl-radical-mediated proteolysis upon interaction with beta' (i.e., in alpha 2 beta beta' and alpha 2 beta beta' sigma). The protected regions are conserved in the alpha homologs of prokaryotic, eukaryotic, archaeal, and chloroplast RNAPs and contain sites of substitutions that affect RNAP assembly. We conclude that the protected regions define determinants of alpha for direct functional interaction with beta and beta'. The observed maximal magnitude of protection upon interaction with beta and the observed maximal magnitude of protection upon interaction with beta' both correspond to the expected value for complete protection of one of the two alpha protomers of RNAP (i.e., 50% protection). We propose that only one of the two alpha protomers of RNAP interacts with beta and that only one of the two alpha protomers of RNAP interacts with beta'.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma Y., Yamagishi M., Ishihama A. Subunits of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA polymerase II: enzyme purification and structure of the subunit 3 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3749–3754. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ross W., Tang H., Gourse R. L., Ebright R. H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase alpha subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Goldfarb A. Recombinant Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: purification of individually overexpressed subunits and in vitro assembly. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Dec;4(6):503–511. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Ebright R. H. Promoter structure, promoter recognition, and transcription activation in prokaryotes. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):743–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Identification of the target of a transcription activator protein by protein-protein photocrosslinking. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):90–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8016656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy H. E., Park S. W., Aki T., Parrack P., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Adhya S. Repression and activation of transcription by Gal and Lac repressors: involvement of alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4523–4529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Busby S. The Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: structure and function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Apr;5(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermácora M. R., Ledman D. W., Hellinga H. W., Hsu G. W., Fox R. O. Mapping staphylococcal nuclease conformation using an EDTA-Fe derivative attached to genetically engineered cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13625–13641. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. P., Hughes K. A., Gunasekera A. H., Meares C. F. Binding of the sigma 70 protein to the core subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, studied by iron-EDTA protein footprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. S., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyduk E., Heyduk T. Mapping protein domains involved in macromolecular interactions: a novel protein footprinting approach. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 16;33(32):9643–9650. doi: 10.1021/bi00198a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Identification of a subunit assembly domain in the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Sequence analysis of two temperature-sensitive mutations in the alpha subunit gene (rpoA) of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):5945–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Ishihama A. Defective assembly of ribonucleic acid polymerase subunits in a temperature-sensitive alpha-subunit mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3491–3495. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Deletion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 16;242(2):107–115. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: amino acid substitution within the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 1;254(3):342–349. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: insertion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 12;248(4):756–767. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Mutations in the three largest subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II that affect enzyme assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4669–4678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalo D., Carles C., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Interactions between three common subunits of yeast RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B. L., Langer J. A., Schwartz B., Pestka S. Creation of phosphorylation sites in proteins: construction of a phosphorylatable human interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):558–562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K., Zhang Y., Severinov K., Das A., Hanna M. M. Role of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit in modulation of pausing, termination and anti-termination by the transcription elongation factor NusA. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):150–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan S. A., Burgess R. R. Use of aryl azide cross-linkers to investigate protein-protein interactions: an optimization of important conditions as applied to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and localization of a sigma 70-alpha cross-link to the C-terminal region of alpha. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12092–12099. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi T., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Structural map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: structural domains identified by proteolytic cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 12;248(4):723–728. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platis I. E., Ermácora M. R., Fox R. O. Oxidative polypeptide cleavage mediated by EDTA-Fe covalently linked to cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12761–12767. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana T. M., Meares C. F. Transfer of oxygen from an artificial protease to peptide carbon during proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10578–10582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riftina F., DeFalco E., Krakow J. S. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of the topological arrangement of the alpha subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3299–3305. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Mustaev A., Severinova E., Bass I., Kashlev M., Landick R., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A., Darst S. A. Assembly of functional Escherichia coli RNA polymerase containing beta subunit fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Ebright R. H. Rapid RNA polymerase genetics: one-day, no-column preparation of reconstituted recombinant Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]